First Principles Calculation and Analysis of Adsorption of Choline Deep with Zinc Oxide
-
摘要:
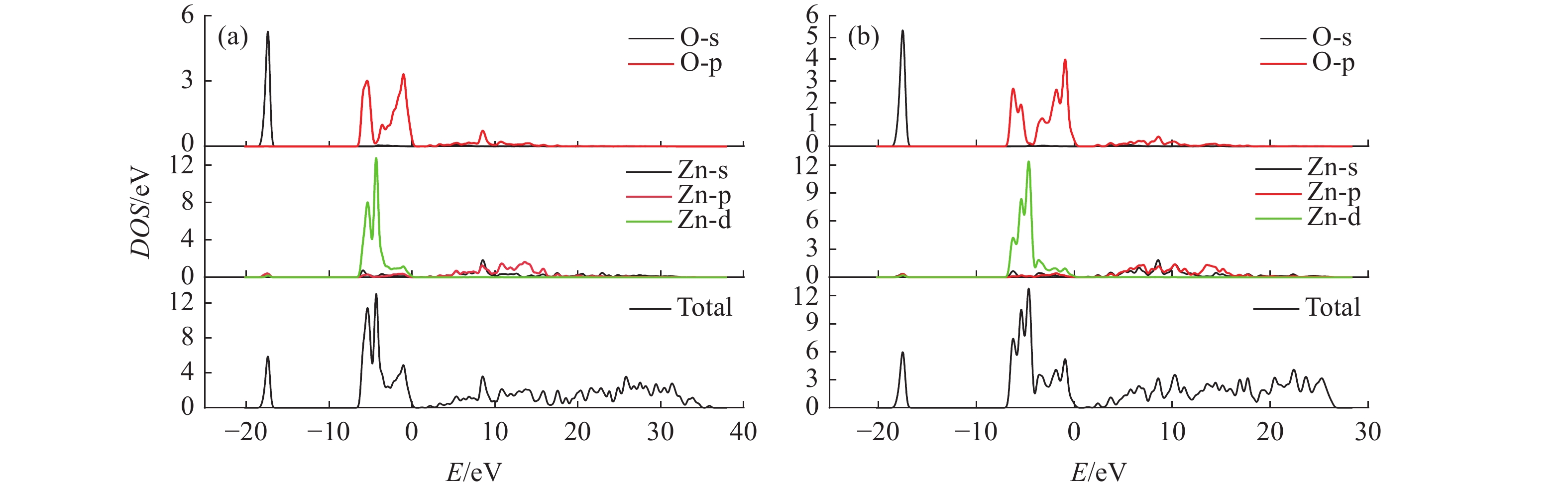
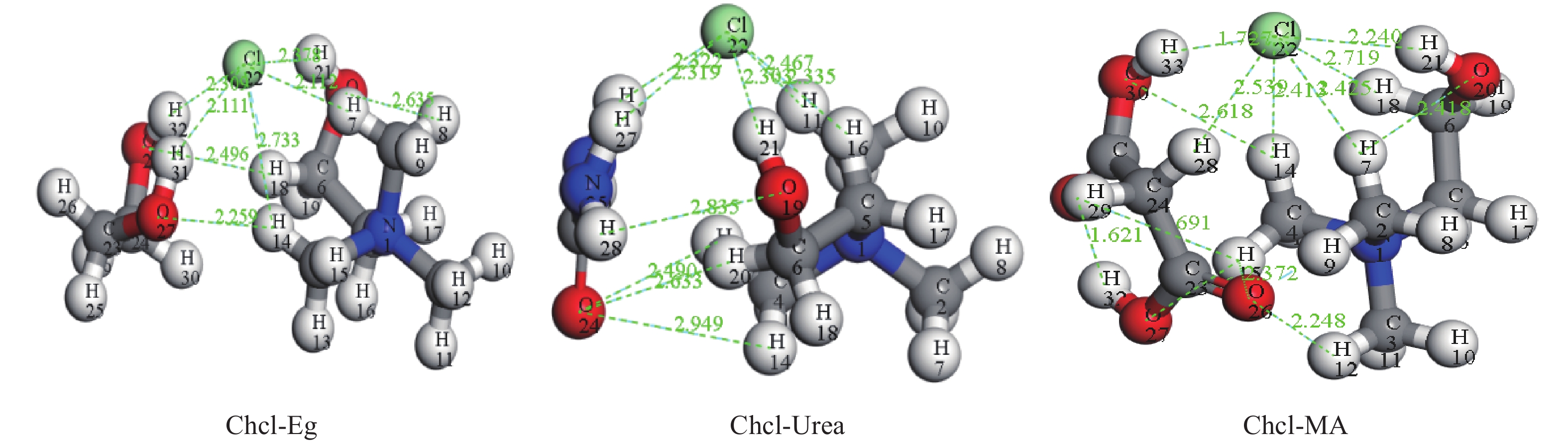
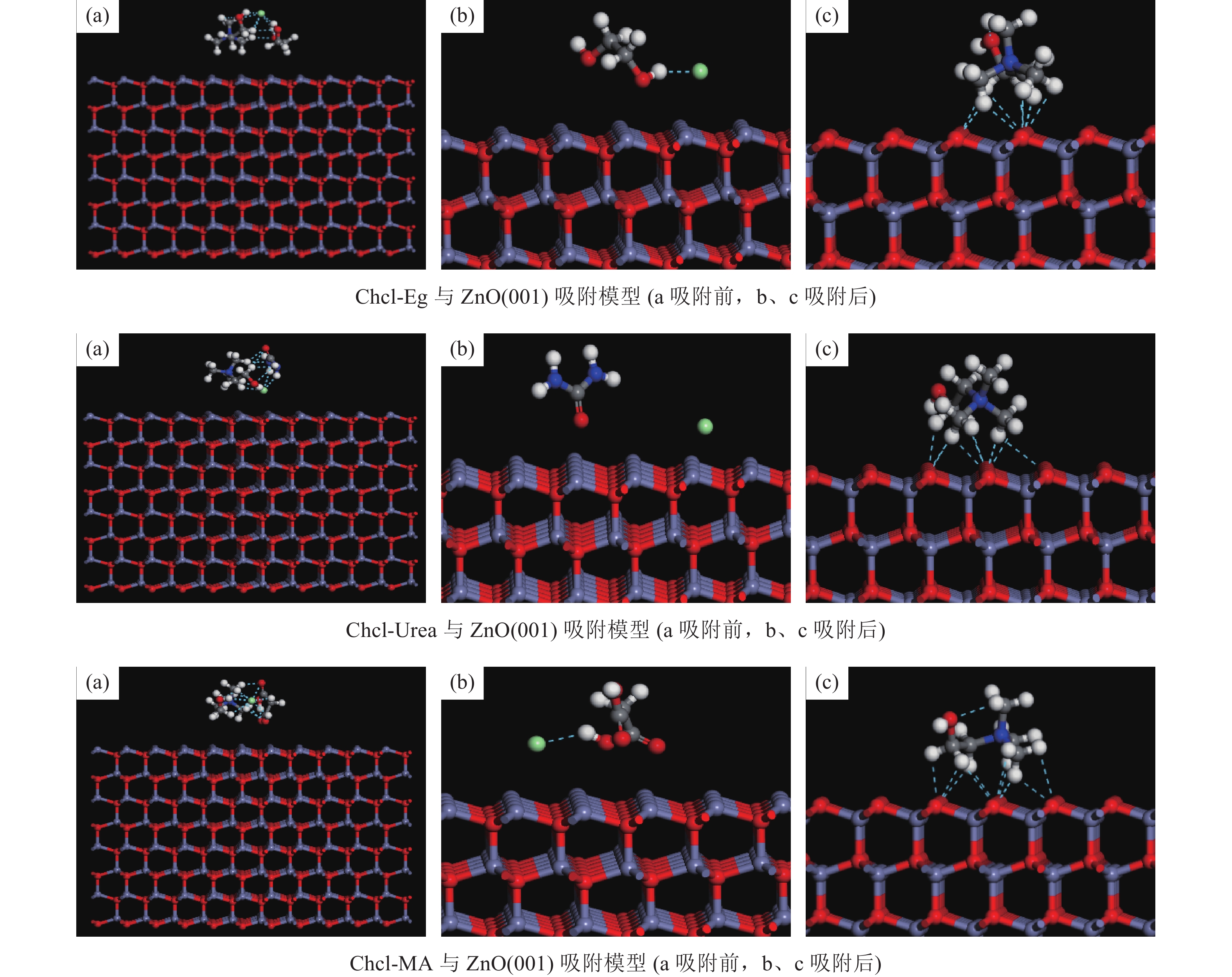
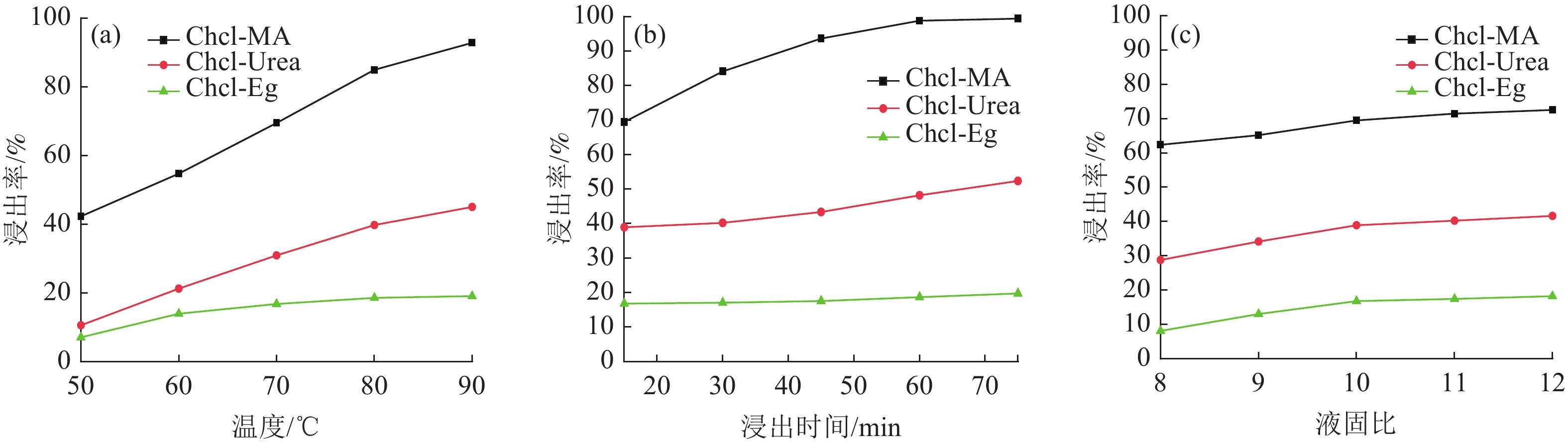
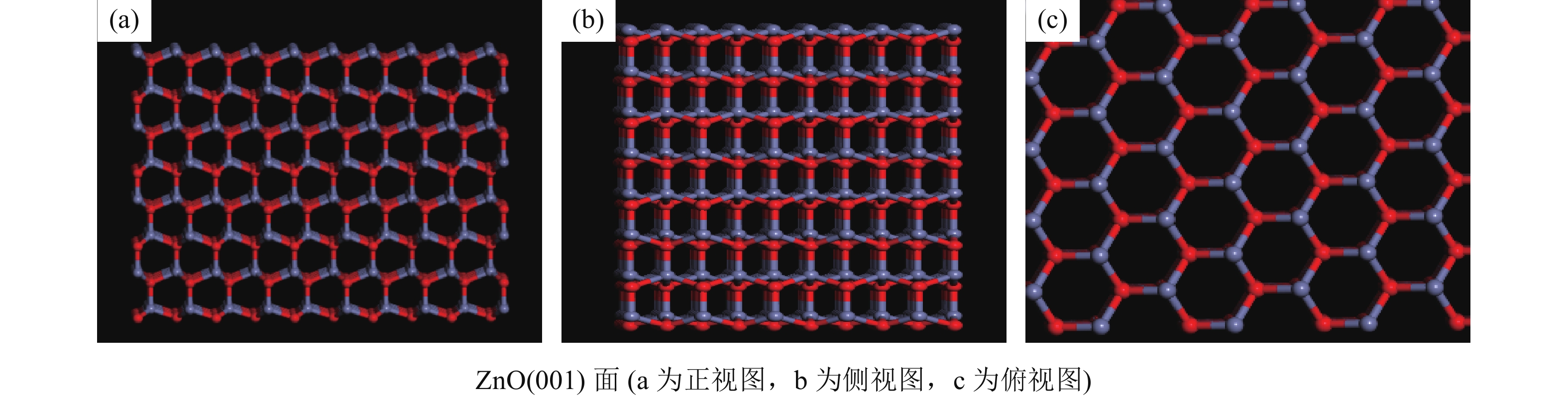
这是一篇冶金工程领域的论文。为了更好实现含锌尘泥中氧化锌的浸出,采用基于密度泛函理论的Materials Studio 软件模拟优化氧化锌晶体结构以及三种胆碱类低共熔溶剂结构,并对两者相互吸附模型进行计算。计算结果表明:ZnO(001)面为完全解理面,在费米能级附近最高占据态向左发生偏移,且最高占据态的波峰增加,峰值升高,在最高占据态中O的p轨道以及Zn的d轨道活性较大,为ZnO(001)面反应活性位点。对三种胆碱类低共熔溶剂优化发现氯化胆碱与三种不同氢键供体形成以氯原子为中心的多重分子间氢键。运用Forcite模块对低共熔溶剂与氧化锌吸附模型计算结果表明,氧化锌与三种胆碱类低共熔溶剂相互作用强弱为Chcl-MA>Chcl-Urea>Chcl-Eg。径向分布函数得出丙二酸使得氯化胆碱中的Cl更容易与Zn发生化学吸附,三种氢键供体中与Zn形成化学键的氧原子官能团活泼性为C=O、N-O、C-O,由此说明丙二酸中的C=O使得Chcl-MA与ZnO结合更稳定。通过实验验证发现Chcl-MA在浸出温度为70 ℃、液固比为10∶1、浸出时间1 h条件下可将氧化锌单矿物几乎完全浸出,浸出效果远远大于Chcl-Urea、Chcl-Eg两种药剂,从而证明了分子模拟的准确性,为胆碱类低共熔溶剂浸出含锌尘泥提供了理论指导。
Abstract:This is an article in the field of metallurgical engineering. In order to better realize the leaching of zinc oxide from zinc-containing dust, Materials Studio software based on density functional theory was used to simulate and optimize the crystal structure of zinc oxide and the structure of three kinds of choline deep eutectic solvents, and the mutual adsorption model of the two was calculated. The calculated results show that the ZnO(001) plane is a complete cleavage plane, and the highest occupied state near the Fermi level shifts to the left, and the peak of the highest occupies state increases, and the p orbital of O and the d orbital of Zn are more active, which are the active sites of the ZnO(001) plane. Optimization of three choline hyper eutectic solvent shows that choline chloride forms multiple intermolecular hydrogen bonds with three different hydrogen bond donors centered on chlorine atom. The adsorption model of deep eutectic solvents and zinc oxide was calculated using Forcite module. The results shows that the interaction strength of zinc oxide with three choline deep eutectic solvent is Chcl-MA >Chcl-Urea>Chcl-Eg. The radial distribution function shows that malonic acid makes it easier for Cl in choline chloride to chemisorb with Zn. In the three kinds of hydrogen bond donors, the activity of oxygen atomic functional groups forming chemical bonds with Zn is C=O, N-O and C-O, indicating that C=O in malonic acid makes the combination of Chcl-MA and ZnO more stable. Results show that the leaching temperature of Chcl-MA is 70 ℃ and the liquid-solid ratio is 10∶1. Under the condition of leaching time of 1 h for 60 min, single mineral zinc oxide can be almost completely leached, and the leaching effect is far greater than that of Chcl-Urea and Chcl-Eg, thus proving the accuracy of molecular simulation and providing theoretical guidance for the leaching of zinc-containing dust in choline deep eutectic solvent.
-

-
表 1 ZnO交换相关能、截断能参数计算
Table 1. Calculation of exchange correlation energy and truncation energy parameters of ZnO
晶胞参数/ ×10-10m 晶胞参数误差/% 带隙/eV 总能/eV a c a c 交换相关能 LDA(CA-PZ) 3.191 5.158 1.78 0.922 0.794 -4300.24 GGA(PBE) 3.289 5.309 1.23 1.98 0.733 -4294.54 GGA(RPBE) 3.319 5.358 2.15 2.92 0.836 -4296.55 GGA(PW91) 3.288 5.291 1.20 1.63 0.719 -4299.28 截断能 350 3.191 5.158 1.78 0.922 0.794 -4300.24 400 3.289 5.309 1.23 1.98 0.733 -4294.54 450 3.319 5.358 2.15 2.92 0.836 -4296.55 500 3.287 5.298 1.14 1.75 0.735 -4299.95 550 3.332 5.343 2.52 2.61 0.762 -4298.32 表 2 氧化锌常见表面能/(J/m2)
Table 2. Common surface energy of zinc oxide
晶面 001 011 111 101 110 表面能 0.8177 3.9275 3.9271 2.0852 2.4053 表 3 原子层数对表面能的影响
Table 3. Effect of atomic layer number on surface energy
完全解理面 原子层数 原子数 表面能/(J/m2) ZnO(001) 2 8 1.5438 3 12 1.5908 4 16 1.6079 5 20 1.6088 6 24 1.6093 表 4 前线分子轨道能量值/eV
Table 4. Frontline molecular orbital energy
HOMO LUMO △E1 △E2 ZnO(001) -0.1625 -0.0221 Chcl-Eg -0.1828 0.0342 0.1607 0.1283 Chcl-Urea -0.1851 -0.7605 0.1630 0.09230 Chcl-MA -0.2077 -0.1064 0.1856 0.0564 其中ΔE1=|HOMODES-LUMOZnO(001) | 、△E2=|HOMOZnO(001)-LUMODES| 表 5 低共熔溶剂与ZnO(001)面相互作用能(Ha)
Table 5. Interaction energy between deep eutectic solvents and ZnO(001) adsorption configuration
DES ZnO(001) Energy △E Chcl-Eg 92.2259 -253287.6632 -253366.6631 -171.2258 Chcl-Urea -84.1064 -253287.6632 -253722.4735 -350.7039 Chcl-MA -35.4970 -253287.6632 -254162.7930 -839.6328 -
[1] Mehmet Kul, KürşadOskay, Mehmet ŞİMŞİR, et al. Optimization of selective leaching of Zn from electric arc furnace steelmaking dust using response surface methodology[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China, 2015, 25(8):2753-2762. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(15)63900-0
[2] 谢泽强, 郭宇峰, 陈凤, 等. 钢铁厂含锌粉尘综合利用现状及展望[J]. 烧结球团, 2016, 41(5): 53-55, 61.XIE Z Q, GUO Y F, CHEN F, et al. Research status and prospect of comprehensive utilization of zinc-bearing dust in iron and steel plants[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing. 2016, 41(5): 53-55, 61.
XIE Z Q, GUO Y F, CHEN F, et al. Research status and prospect of comprehensive utilization of zinc-bearing dust in iron and steel plants[J]. Sintering and Pelletizing. 2016, 41(5): 53-55, 61.
[3] 张晋霞, 牛福生, 徐之帅. 钢铁工业冶金含铁尘泥铁、碳、锌分选技术研究[J]. 矿山机械, 2014, 42(6):97-102.ZHANG J X, NIU F S, XU Z S. Research on separation of iron, carbon and zinc in metallurgical dust slime from iron and steel industry[J]. Mining machinery, 2014, 42(6):97-102.
ZHANG J X, NIU F S, XU Z S. Research on separation of iron, carbon and zinc in metallurgical dust slime from iron and steel industry[J]. Mining machinery, 2014, 42(6):97-102.
[4] 何环宇, 陈振红, 崔一芳, 等. 含锌冶金尘泥还原烟气沉积特性[J]. 钢铁, 2015, 50,(12):80-84.HE H Y, CHEN Z H, CUI Y F, et al. Sediment of flus gas in direct reduction treated by zinc-bearing metallurgical dust[J]. Iron and steel, 2015, 50,(12):80-84.
HE H Y, CHEN Z H, CUI Y F, et al. Sediment of flus gas in direct reduction treated by zinc-bearing metallurgical dust[J]. Iron and steel, 2015, 50,(12):80-84.
[5] 王飞, 张建良, 毛瑞, 等. 含铁尘泥自还原团块固结机理及强度劣化[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(2):367-372.WANG F, ZHANG J L, MAO R, et al. Bonding mechanism and strength deterioration of self-reducing briquettes made from iron-bearing dust and sludge[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2016, 47(2):367-372.
WANG F, ZHANG J L, MAO R, et al. Bonding mechanism and strength deterioration of self-reducing briquettes made from iron-bearing dust and sludge[J]. Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2016, 47(2):367-372.
[6] 蒋武锋, 马腾飞, 郝素菊, 等. 利用钢渣余热还原含锌粉尘可行性的探讨[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2019(6):140-144.JIANG W F, MA T F, HAO S J, et al. Discussion on feasibility of reducing zinc-containing dust by residual heat of steel slag[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(6):140-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.06.030
JIANG W F, MA T F, HAO S J, et al. Discussion on feasibility of reducing zinc-containing dust by residual heat of steel slag[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2019(6):140-144. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2019.06.030
[7] 马爱元, 郑雪梅, 李松, 等. 含锌钢铁冶金渣尘处理技术现状[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(4):1-7.MA A Y, ZHENG X M, LI S, et al. Present situation of zinc metallurgical slags and dusts treatment technology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.001
MA A Y, ZHENG X M, LI S, et al. Present situation of zinc metallurgical slags and dusts treatment technology[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(4):1-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.04.001
[8] Wu Zhaojin, Huang Wei, Cui Keke, et al. Sustainable synthesis of metals-doped ZnO nanoparticles from zinc-bearing dust for photodegradation of phenol[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2014, 278(8):91-99.
[9] 张晋霞, 冯洪均, 王龙, 等. 含锌冶金尘泥氨浸溶蚀实验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(1):124-129.ZHANG J X FENG H J, WANG L, et al. Study on treating zinc-bearing dust by Ammonia leaching process[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):124-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.021
ZHANG J X FENG H J, WANG L, et al. Study on treating zinc-bearing dust by Ammonia leaching process[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):124-129. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.021
[10] 马爱元, 郑雪梅, 李松, 等. 响应曲面优化NH3-(NH4)3AC-H2O 体系浸出冶金废渣提锌工艺研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(1):186-192.MA A Y, ZHENG X M, LI S, et al. Study on zinc extraction process of NH3-(NH4)3AC-H2O system by response surface optimization[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):186-192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.031
MA A Y, ZHENG X M, LI S, et al. Study on zinc extraction process of NH3-(NH4)3AC-H2O system by response surface optimization[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):186-192. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.01.031
[11] 谭鑫, 何发钰, 谢宇. 钨锰矿(010)表面电子结构及性质第一性原理计算[J]. 金属矿山, 2015(6):52-58.TAN X, HE F Y, XIE Y. Structural and electronic properties of MnWO4( 010) surface studied by first-principles calculation[J]. Metal Mine, 2015(6):52-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2015.06.012
TAN X, HE F Y, XIE Y. Structural and electronic properties of MnWO4( 010) surface studied by first-principles calculation[J]. Metal Mine, 2015(6):52-58. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1250.2015.06.012
[12] Yang Z Q, Bai X H, Zheng W W, et al. Electronic properties of bare doped (Tio2)3clustera density functionaltheory investigation[J]. Molecular Physics, 2015, 32(6):962-970.
[13] 张慧婷. 十二胺和油酸组合捕收剂在锂云母表面吸附的分子动力学模拟[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2017.ZHANG H T. Molecular dynamics simulation of adsorption of combined collectors of dodecylamine and oleic acid on surface of lepidolite[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2017.
ZHANG H T. Molecular dynamics simulation of adsorption of combined collectors of dodecylamine and oleic acid on surface of lepidolite[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2017.
-



 下载:
下载: