Remediation of Cadmium-contaminated Soil by Cadmium-resistant Sulfate-reducing Bacteria
-
摘要:
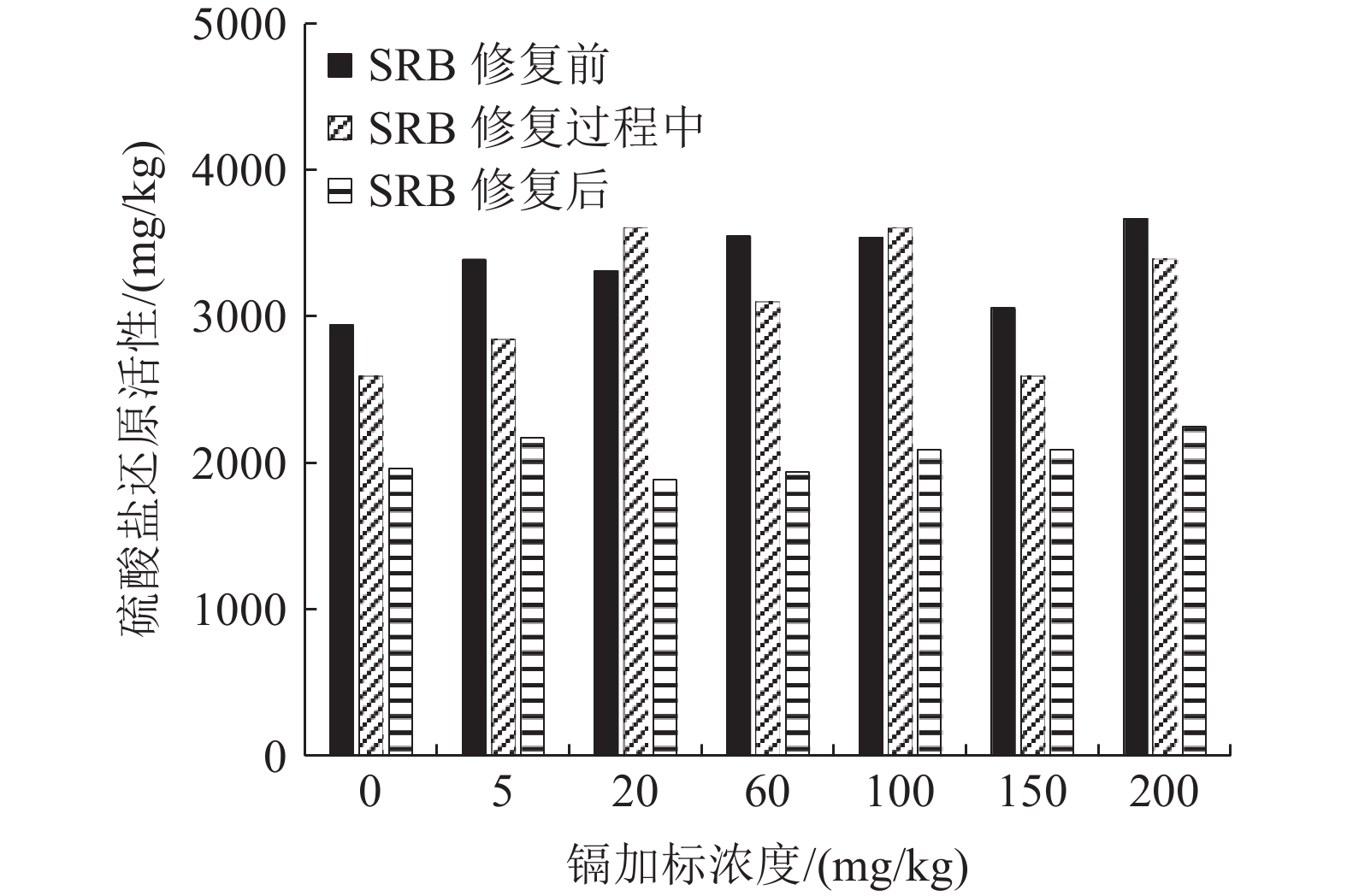
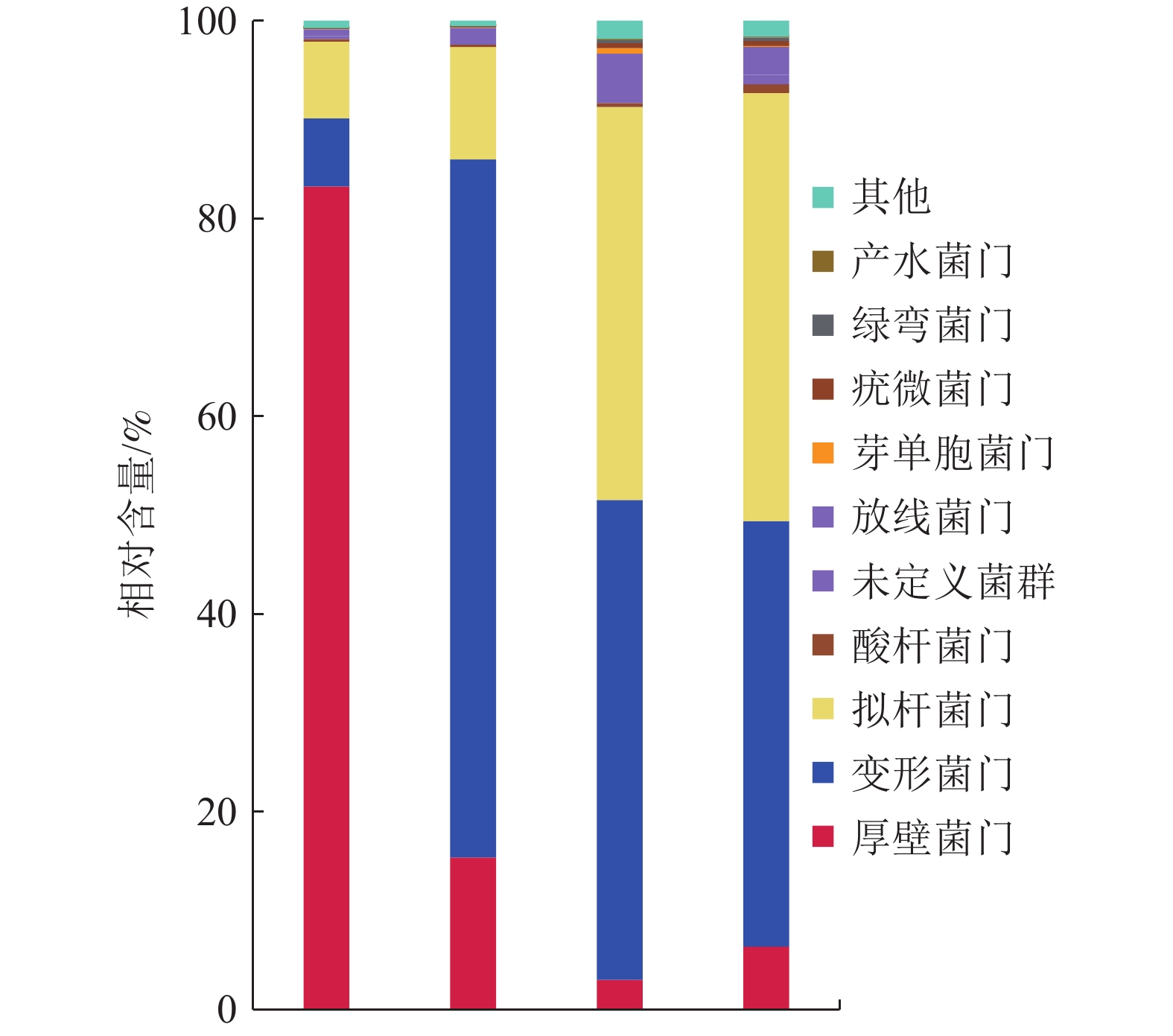
为探究耐镉硫酸盐还原菌(SRB)对镉污染土壤的修复效果,以耐镉硫酸盐还原污泥为种泥筛选分离出耐镉SRB,并将其投加于不同镉污染程度(轻度、中度、重度)的土壤中,考查SRB作用下土壤镉的赋存形态、硫酸盐还原活性及微生物群落结构的变化特征。结果表明,经耐镉SRB修复53 d后,不同镉污染程度土壤的总镉含量未发生明显变化,不稳定态镉(可交换态、碳酸盐结合态)的占比由修复前的45%~68%降至26%~40%,稳定态镉(铁锰氧化态、有机结合态、残渣态)占比由最初的30%~50%大幅增加至60%~75%,实现了不同重金属镉污染程度土壤中镉的有效钝化;修复过程中,不同镉污染程度土壤的硫酸盐含量均呈现先逐步降低后增加的趋势,硫酸盐还原活性则逐步降低,体系存在硫酸盐的再生;耐镉SRB修复过程中各污染土壤细菌门类的变化趋势大致相同,Proteobacteria和Bacteroidetes为主要门类,Desulfosporosinus和Desulfobacca为主要的SRB菌属,修复过程中其丰度逐步降低,硫氧化菌则有增高的趋势。由此可见耐镉SRB可降低镉污染土壤中不稳定态镉含量,降低了镉的迁移性,但修复过程中优化修复参数强化硫酸盐还原及抑制硫氧化是有必要的。
Abstract:In order to investigate the cadmium reduction effect of cadmium-tolerant sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB) on cadmium-contaminated soil, cadmium-tolerant SRB was screened and isolated using cadmium-tolerant sulfate-reducing sludge as seed sludge, and was injected into soils with different degrees of cadmium contamination (mild, moderate, and severe) to investigate the fugitive morphology of soil cadmium, the changes in sulfate reduction activity and microbial community structure. The results showed that after 53 d of Cd-tolerant SRB remediation, the total Cd content of soils with different Cd contamination levels did not change significantly, the proportion of unstable Cd (exchangeable state, carbonate-bound state) decreased from the initial 45%~68% to 26%~40%, and the proportion of stable Cd (Fe-Mn oxidation state, organic-bound state, residue state) increased significantly from the initial 30%~50% to 60%~75%. The effective passivation of cadmium in soils with different degrees of heavy metal cadmium pollution was achieved. The sulfate content of soils with different degrees of cadmium pollution showed a trend of gradually decreasing and then increasing during the remediation process, while the sulfate reduction activity gradually decreased, and there was regeneration of sulfate in the system. The change trend of each contaminated soil bacterial phylum during the remediation of cadmium-tolerant SRB was more or less the same, with Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes as the main phylum, Desulfosporosinus and Desulfobacca as the main SRB genera, and their abundance gradually decreased during the remediation process, while sulfur-oxidizing bacteria had a tendency to increase. This shows that cadmium-tolerant SRB can reduce the content of unstable cadmium in cadmium-contaminated soil, and reduce the mobility of cadmium, but it is necessary to optimize the remediation parameters to enhance sulfate reduction and inhibit sulfur oxidation in the remediation process.
-

-
表 1 加标后各组土壤中总镉含量(n=2)
Table 1. Total Cd concentration in the soil samples (n=2)
土壤样品编号 总镉的含量/(mg/kg) C0 3.38 ± 1.61 C5 6.63 ± 0.02 C20 23.68 ± 1.23 C60 62.04 ± 3.35 C100 113.31 ± 20.49 C150 153.98 ± 7.45 C200 197.49 ± 18.36 表 2 土壤中主要功能菌群组成
Table 2. Composition of the main functional flora in soils
菌属 修复前,C5 修复前,C100 修复53d,C5 修复53d,C100 Alcaligenes 0.214 35.393 0.250 0.389 Flavobacterium 0.056 0.063 31.708 34.718 Proteiniclasticum 0.266 13.034 1.420 3.338 Brevundimonas 0.288 6.635 11.855 9.214 Massilia 0.068 0.466 9.660 0.117 Pseudochrobactrum 0.293 8.517 0.297 0.452 Desulfosporosinus 0.180 0.182 0.124 0.081 Desulfobacca 0 0.045 0.005 0.016 Pseudomonas 0.122 0.088 1.328 1.123 Citrobacter 0.065 0.371 0.063 0.018 Thiobacillus 0.009 0.005 0.722 0.018 -
[1] 朱晓丽, 寇志健, 王军强, 等. 生物炭固定化硫酸盐还原菌对Cd2+吸附及作用机制分析[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(7):2682-2690.ZHU X L, KOU Z J, WANG J Q, et al. Adsorption of Cd2+ by sulfate reducing bacteria immobilized biochar[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(7):2682-2690.
ZHU X L, KOU Z J, WANG J Q, et al. Adsorption of Cd2+ by sulfate reducing bacteria immobilized biochar[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(7):2682-2690.
[2] 杨飞, 房晓红, 曾凡桂, 等. 高岭石表面吸附铅和镉的模拟计算[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(5):196-202.YANG F, FANG X H, ZENG F G, et al. Simulation calculation of adsorption of lead and cadmium on kaolinite surface[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(5):196-202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.05.031
YANG F, FANG X H, ZENG F G, et al. Simulation calculation of adsorption of lead and cadmium on kaolinite surface[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(5):196-202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.05.031
[3] 邓敏, 程蓉, 舒荣波, 等. 攀西矿区典型重金属污染土壤化学-微生物联合修复技术探索[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(4):1-9.DENG M, CHENG R, SHU R B, et al. Exploration of chemical-microbial remediation technology for soil contaminated by typical heavy metals in Panxi mining area[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(4):1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.04.001
DENG M, CHENG R, SHU R B, et al. Exploration of chemical-microbial remediation technology for soil contaminated by typical heavy metals in Panxi mining area[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(4):1-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.04.001
[4] 石浩, 胡静敏, 陈忻, 等. 矿山土壤镉污染微生物修复技术研究进展[J]. 矿产保护与利用, 2020, 40(4):17-22.SHI H, HU J M, CHEN X, et al. Research progress on microbial remediation technology of cadmium contaminated mine soil[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 40(4):17-22.
SHI H, HU J M, CHEN X, et al. Research progress on microbial remediation technology of cadmium contaminated mine soil[J]. Conservation and Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020, 40(4):17-22.
[5] 环境保护部, 国土资源部. 全国土壤污染状况调查公报[J]. 中国环保产业, 2014, 36(5):1689-1692.Ministry of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Land and Resources, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. Bulletin of national soil pollution survey[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2014, 36(5):1689-1692.
Ministry of Environmental Protection, Ministry of Land and Resources, Ministry of Natural Resources of the People's Republic of China. Bulletin of national soil pollution survey[J]. China Environmental Protection Industry, 2014, 36(5):1689-1692.
[6] 马娇阳, 保欣晨, 王坤, 等. 土壤镉污染的人体健康风险评价研究: 生物有效性与毒性效应[J/OL]. 生态毒理学报, 2022. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.5470.X.20220106.1717.004.html.MA J Y, BAO X C, WANG K, et al. Human health risk assessment of cadmium in soils: role of bioavailability and toxic effects [J/OL]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology. https://kns. cnki. net/kcms/detail/11. 5470.X.20220106. 1717. 004. html, 2022.
MA J Y, BAO X C, WANG K, et al. Human health risk assessment of cadmium in soils: role of bioavailability and toxic effects [J/OL]. Asian Journal of Ecotoxicology. https://kns. cnki. net/kcms/detail/11. 5470.X.20220106. 1717. 004. html, 2022.
[7] 蒋永荣, 梁英, 张学洪, 等. 铅锌矿区不同程度尾矿砂重金属污染土壤的纵向微生物群落结构分析[J]. 生态环境学报, 2019, 28(10):2079-2088.JIANG Y R, LIANG Y, ZHANG X H, et al. Vertical microbial community structure of heavy metal contaminated soils from mine tailings of different degrees in lead-zinc mining areas[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(10):2079-2088.
JIANG Y R, LIANG Y, ZHANG X H, et al. Vertical microbial community structure of heavy metal contaminated soils from mine tailings of different degrees in lead-zinc mining areas[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2019, 28(10):2079-2088.
[8] 陈灿明, 卫泽斌, 彭建兵, 等. 土壤有效态镉与稻米镉污染风险广东案例研究[J/OL]. 农业环境科学学报. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/12.1347.S.20220104.1534.002.html, 2022.CHEN C M, WEI Z B, PENG J B, et al. Risk assessment of cadmium contamination of rice using soil available cadmium in paddy fields: Case studies of Guangdong Province[J/OL]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science. https://kns. cnki. net/kcms/detail/12. 1347. S. 20220104. 1534. 002. html, 2022.
CHEN C M, WEI Z B, PENG J B, et al. Risk assessment of cadmium contamination of rice using soil available cadmium in paddy fields: Case studies of Guangdong Province[J/OL]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science. https://kns. cnki. net/kcms/detail/12. 1347. S. 20220104. 1534. 002. html, 2022.
[9] LI J R, XU Y M. Immobilization of Cd in paddy soil using moisture management and amendment[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2015, 22(7):5580-5586. doi: 10.1007/s11356-014-3788-5
[10] 邵佳, 赵远来, 冯琰玉, 等. 生物质炭对长期铅镉复合污染土壤微生物群落丰度及活性的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2022, 41(1):66-74.SHAO J, ZHAO Y L, FENG Y Y, et al. Effects of biochar on microbial community abundance and activity in long-term Pb and Cd contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Agro-environment Science, 2022, 41(1):66-74. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2021-0478
SHAO J, ZHAO Y L, FENG Y Y, et al. Effects of biochar on microbial community abundance and activity in long-term Pb and Cd contaminated soils[J]. Journal of Agro-environment Science, 2022, 41(1):66-74. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2021-0478
[11] 刘马养, 张玉盛, 肖欢, 等. 新型改良剂"良田宝"对土壤有效镉及稻米镉含量的影响[J]. 作物研究, 2020, 34(3):258-261,278.LIU M Y, ZHANG Y S, XIAO H, et al. The effect of a new modifier “Liangtianbao”on cadmium content in the soil and rice[J]. Crop Research, 2020, 34(3):258-261,278.
LIU M Y, ZHANG Y S, XIAO H, et al. The effect of a new modifier “Liangtianbao”on cadmium content in the soil and rice[J]. Crop Research, 2020, 34(3):258-261,278.
[12] 童辉, 乔江涛, 周继梅, 等. 硫酸盐还原菌介导针铁矿表面硫的转化及镉固定脱毒效应[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(5):1069-10.TONG H, QIAO J T, ZHOU J M, et al. Coupled transformation of sulfur and cadmium on goethite induced by sulfate-reducing bacterium[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(5):1069-10.
TONG H, QIAO J T, ZHOU J M, et al. Coupled transformation of sulfur and cadmium on goethite induced by sulfate-reducing bacterium[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(5):1069-10.
[13] 董净, 代群威, 赵玉连, 等. 硫酸盐还原菌的分纯及对Cd2+钝化研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2019, 42(5):34-40.DONG J, DAI Q W, ZHAO Y L, et al. Isolation of sulfate-reducing bacteria and study on its passivation of Cd2+[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(5):34-40.
DONG J, DAI Q W, ZHAO Y L, et al. Isolation of sulfate-reducing bacteria and study on its passivation of Cd2+[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2019, 42(5):34-40.
[14] ZHANG M L, WANG H X. Preparation of immobilized sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) granules for effective bioremediation of acid mine drainage and bacterial community analysis[J]. Minerals Engineering, 2016, 92:63-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mineng.2016.02.008
[15] YAN J, ZHONG K Q, WANG S J, et al. Carbon metabolism and sulfate respiration by a non-conventional Citrobacter freundii strain SR10 with potential application in removal of metals and metalloids[J]. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 2018, 133:238-246.
[16] 朱煜. 硫酸盐还原菌对重金属污染土壤的处理研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2021, 43(8):952-955.ZHU Y. Treatment of heavy metal contaminated soil using sulfate reducing bacteria[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2021, 43(8):952-955.
ZHU Y. Treatment of heavy metal contaminated soil using sulfate reducing bacteria[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2021, 43(8):952-955.
[17] 范文宏, 姜维, 王宁. 硫酸盐还原菌修复污染土壤过程中镉的地球化学形态分布变化[J]. 环境科学学报, 2008, 28(11):2291-2298.FAN W H, JIANG W, WANG N. Changes of cadmiumgeo chemical speciation in the process of soil bioremediation by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantia, 2008, 28(11):2291-2298. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.11.019
FAN W H, JIANG W, WANG N. Changes of cadmiumgeo chemical speciation in the process of soil bioremediation by Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantia, 2008, 28(11):2291-2298. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-2468.2008.11.019
[18] 郑婉盈, 张色, 吴明林, 等. 耐镉硫酸盐还原活性污泥的驯化及其微生物群落结构分析[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2021, 43(1):47-51,56.ZHENG W Y, ZHANG S, WU M L, et al. The domestication of cadmium-resistant sulfate reducing activated sludge and analysis of its microbial community[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2021, 43(1):47-51,56.
ZHENG W Y, ZHANG S, WU M L, et al. The domestication of cadmium-resistant sulfate reducing activated sludge and analysis of its microbial community[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2021, 43(1):47-51,56.
[19] 蒋永荣, 周亶, 容翠娟, 等. 高效硫酸盐还原菌的分离及特性研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2009, 32(11):13-17.JIANG Y R, ZHOU D, RONG C J, et al. Isolation of high efficient sulfate-reducing bacteria and its biological desulfurization capability[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 32(11):13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2009.11.004
JIANG Y R, ZHOU D, RONG C J, et al. Isolation of high efficient sulfate-reducing bacteria and its biological desulfurization capability[J]. Environmental Science & Technology, 2009, 32(11):13-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6504.2009.11.004
[20] 杜刚, 孙静贤, 张广求, 等. 硫酸盐还原菌的分离筛选及鉴定[J]. 基因组学与应用生物学, 2017, 36(1):246-251.DU G, SUN J X, ZHANG G Q, et al. Isolation screening and identification of sulfate-reducing bacteria[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2017, 36(1):246-251.
DU G, SUN J X, ZHANG G Q, et al. Isolation screening and identification of sulfate-reducing bacteria[J]. Genomics and Applied Biology, 2017, 36(1):246-251.
[21] ALBORES A F, CID B P, GOMEZ E F, et al. Comparison between sequential extraction procedures and single extractions for metal partitioning in sewage sludge samples[J]. Analyst, 2000, 125(7):1353-1357. doi: 10.1039/b001983f
[22] 朱晓丽, 张建霞, 徐雅雅, 等. 常温等离子体诱变选育高效耐镉硫酸盐还原菌[J]. 西北大学学报, 2015, 45(2):304-306.ZHU X L, ZHANG J X, XU Y Y, et al. Screening of sulfur efficient and Cd-tolerant sulfate reducing bacteria by DBD Plasma mutation[J]. Journal of Northwest University, 2015, 45(2):304-306.
ZHU X L, ZHANG J X, XU Y Y, et al. Screening of sulfur efficient and Cd-tolerant sulfate reducing bacteria by DBD Plasma mutation[J]. Journal of Northwest University, 2015, 45(2):304-306.
[23] 国家环境保护总局. 水和废水监测分析方法[M]. (第四版). 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2002.State Environmental Protection Administration. Monitoring and analysis methods of water and wastewater [M]. (Fourth Edition). Beijing: China Environmental Press, 2002.
State Environmental Protection Administration. Monitoring and analysis methods of water and wastewater [M]. (Fourth Edition). Beijing: China Environmental Press, 2002.
[24] 陈立航, 李顺群, 程学磊, 等. 基于EDTA淋洗离心—硫酸盐还原菌固化法去除污泥中重金属镉的研究[J]. 水资源与水工程学报, 2021, 31(6):109-115.CHEN L H, LI S Q, CHENG X L, et al. Removal of heavy metal-cadmium in sludge based on EDTA eluting centrifugation-sulfate-reducing bacteria solidification method[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 2021, 31(6):109-115. doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2021.06.15
CHEN L H, LI S Q, CHENG X L, et al. Removal of heavy metal-cadmium in sludge based on EDTA eluting centrifugation-sulfate-reducing bacteria solidification method[J]. Journal of Water Resources & Water Engineering, 2021, 31(6):109-115. doi: 10.11705/j.issn.1672-643X.2021.06.15
[25] 韩林宝. 典型菌株的硫价态双向调控行为对镉赋存状态影响研究[D]. 绵阳: 西南科技大学, 2018.HAN L B. Study on the effect of S-valence-state bidirectional regulation behavior on the occurrence of Cd in typical bacteria[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2018.
HAN L B. Study on the effect of S-valence-state bidirectional regulation behavior on the occurrence of Cd in typical bacteria[D]. Mianyang: Southwest University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[26] 徐伯钧. 土壤重金属植物有效性的控制因素研究[J]. 种子科技, 2018, 36(4):117-118.XU B J. Study on controlling factors of plant availability of heavy metals in soil[J]. Seed Science & Technology, 2018, 36(4):117-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2690.2018.04.094
XU B J. Study on controlling factors of plant availability of heavy metals in soil[J]. Seed Science & Technology, 2018, 36(4):117-118. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2690.2018.04.094
[27] 闫潇, 刘兴宇, 张明江, 等. 分离自活性污泥的硫酸盐还原菌用于铅锌冶炼渣重金属污染修复[J]. 微生物学通报, 2019, 46(8):1907-1916.YAN X, LIU X Y, ZHANG M J, et al. Remediation of heavy metal pollution by sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) isolated from activated sludge in lead-zinc smelter slag[J]. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(8):1907-1916.
YAN X, LIU X Y, ZHANG M J, et al. Remediation of heavy metal pollution by sulfate reducing bacteria (SRB) isolated from activated sludge in lead-zinc smelter slag[J]. Microbiology China, 2019, 46(8):1907-1916.
[28] 吕琴, 陈中云, 闵航. 重金属污染对水稻田土壤硫酸盐还原菌种群数量及其活性的影响[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报, 2005, 11(3):399-405.LYU Q, CHEN Z Y, MIN H. Effect of heavy metal contamination on the population of sulfate-reducing bacteria and the sulfate-reducing activity in paddy rice soils[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2005, 11(3):399-405. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2005.03.020
LYU Q, CHEN Z Y, MIN H. Effect of heavy metal contamination on the population of sulfate-reducing bacteria and the sulfate-reducing activity in paddy rice soils[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers, 2005, 11(3):399-405. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1008-505X.2005.03.020
[29] LIU M, XUE Y Y, Yang J. Rare plankton subcommunities are far more affected by DNA extraction kits than abundant plankton [J]. Frontiers in Microbiology, 2019, 10.
[30] 冯云飞. 硫氧化细菌的分离鉴定及其氧化除硫的研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学, 2021.FENG Y F. Isolation and identification of sulfur oxidizing bacteria and their study on sulfur removal by oxidation [D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2021.
FENG Y F. Isolation and identification of sulfur oxidizing bacteria and their study on sulfur removal by oxidation [D]. Daqing: Northeast Petroleum University, 2021.
[31] 徐帆. Pseudomonas C27代谢碳氮硫过程中单质硫的生成与胞内外分布规律研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2021.XU F. Study on the formation and distribution of biosulfur during the metabolismof carbon nitrogen and sulfide in pseudomonas c27 [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021.
XU F. Study on the formation and distribution of biosulfur during the metabolismof carbon nitrogen and sulfide in pseudomonas c27 [D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2021.
[32] 黄瑞林, 张娜, 孙波, 等. 典型农田根际土壤伯克霍尔德氏菌群落结构及其多样性[J]. 土壤学报, 2020, 57(4):975-985.HUANG R L, ZHANG N, SUN B, et al. Community structure of burkholderiales and its diversity in typical maize rhizosphere soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(4):975-985. doi: 10.11766/trxb201901040008
HUANG R L, ZHANG N, SUN B, et al. Community structure of burkholderiales and its diversity in typical maize rhizosphere soil[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 2020, 57(4):975-985. doi: 10.11766/trxb201901040008
[33] 龙冬艳. 解糖假苍白杆菌Pseudochrobactrum saccharolyticum LY10还原Cr(Ⅵ)的机制研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2013.LONG D Y. The mechanism of Cr(Ⅵ) reduction by Pseudochrobactrum saccharolyticum LY10 [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013.
LONG D Y. The mechanism of Cr(Ⅵ) reduction by Pseudochrobactrum saccharolyticum LY10 [D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2013.
-




 下载:
下载: