Improvement of Acidic Yellow Soil by Wollastonite- sodium Silicate- biochar Composites
-
摘要:
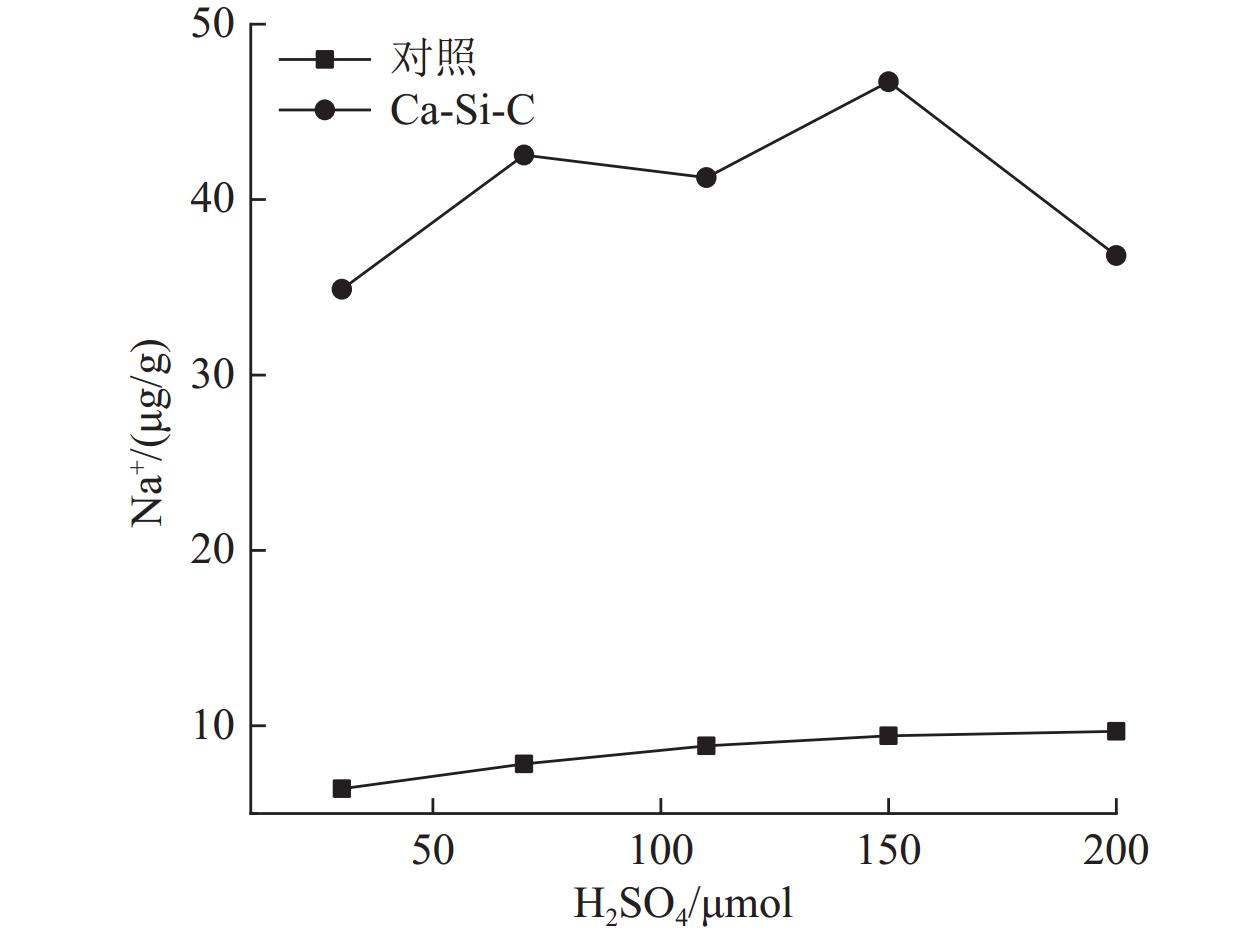
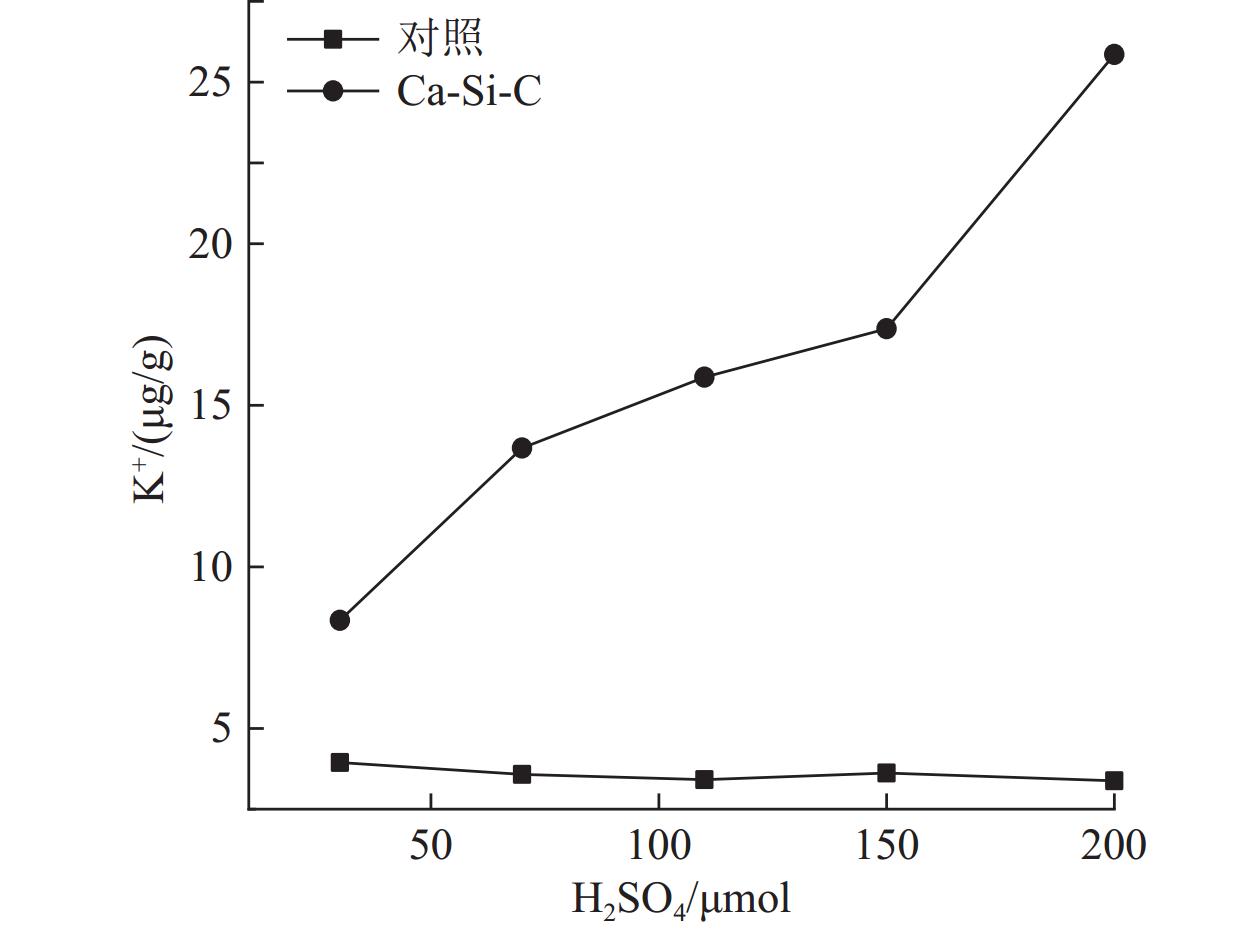
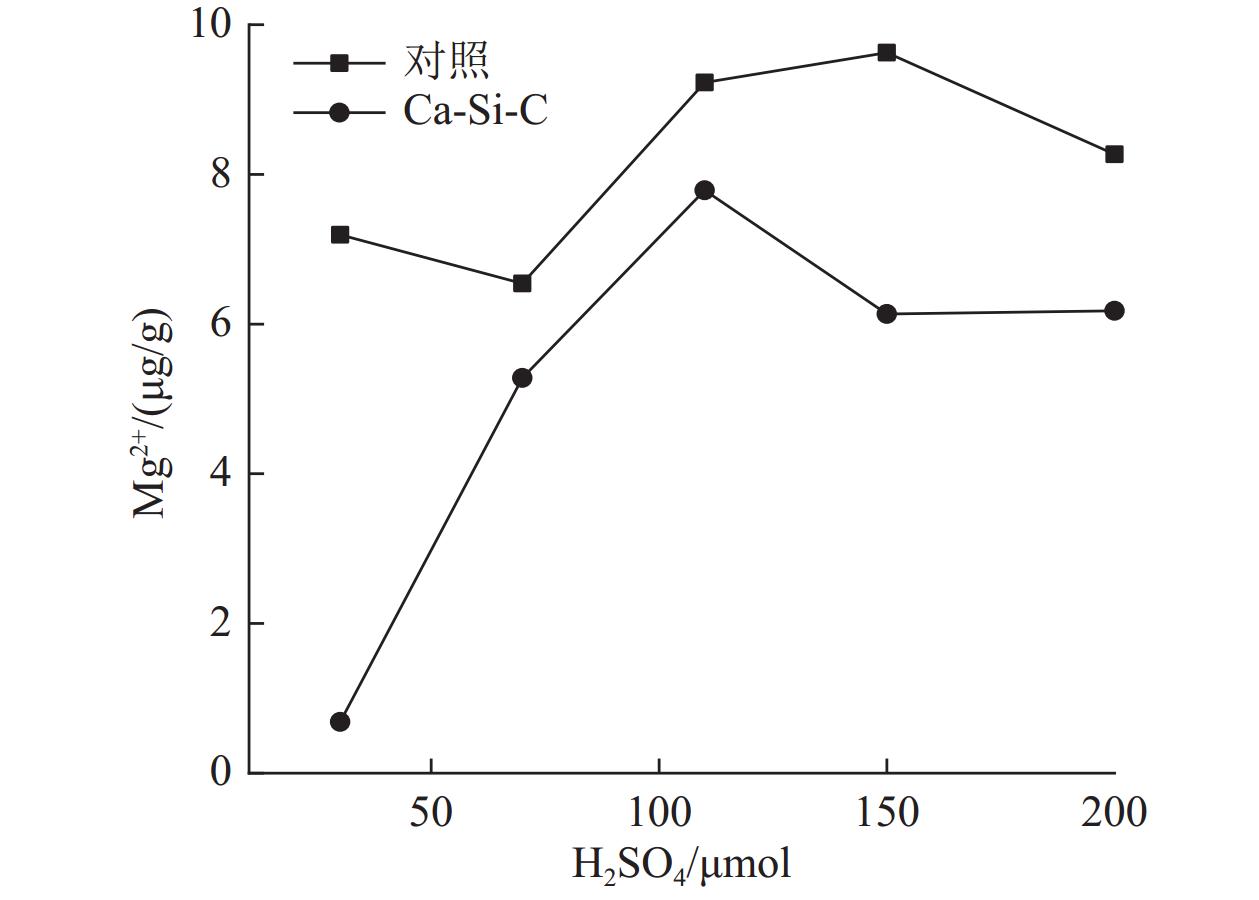
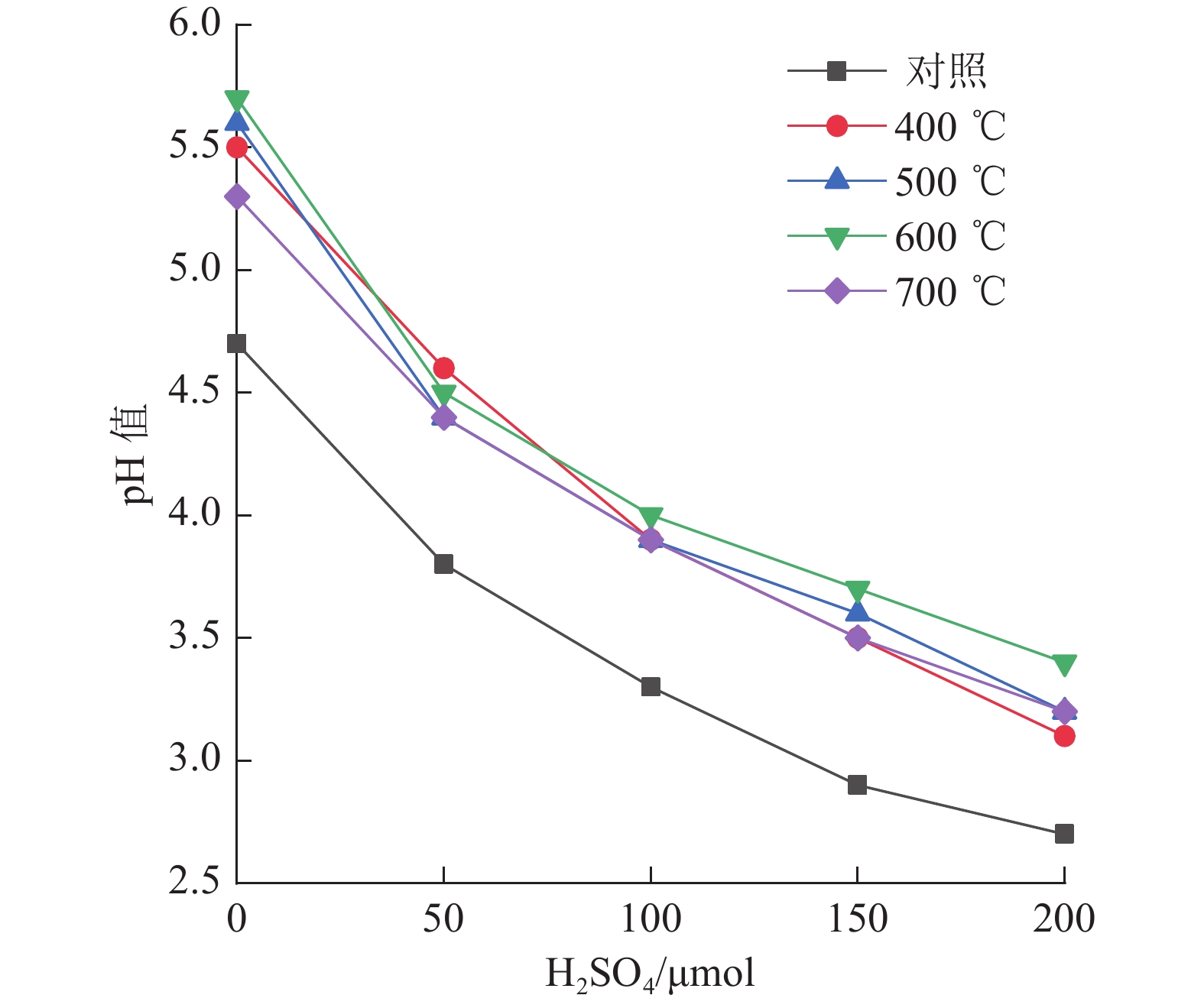
以硅灰石为基体材料,添加一定量的油菜秸秆与硅酸钠,高温煅烧制备硅灰石-硅酸钠-生物炭的复合材料(Ca-Si-C),并应用于酸性黄壤的改良。复合材料的较佳制备条件为硅灰石∶油菜杆∶硅酸钠的质量比为7∶1∶2、在600 ℃马弗炉煅烧1.5 h。XRD、IR、SEM表征结果表明,Ca-Si-C复合材料表面负载有生物炭,孔隙多,且含较多的-OH、C≡C、-COOH、C-O等官能团。施加2%的Ca-Si-C到pH值为4.7的黄壤,相比于对照,土壤的初始pH值增加1.4个单位;酸害容量增加了11.5 mmol/kg;土壤中钠、钾的溶出量增大;钙、镁、铝的溶出量降低;土壤酸缓冲曲线与铝离子溶出曲线交点由pH值 3.5增大至4.1。Ca-Si-C应用于酸性土壤改良,具有良好的应用前景。
Abstract:Wollastonite-sodium silicate-biochar composite material (Ca-Si-C) was prepared by calcination with wollastonite as the matrix material and adding a certain amount of rape straw and sodium silicate. And then the Ca-Si-C was applied to the improvement of acidic yellow soil. The optimum preparation conditions of the composite materials is as follows∶ the mass ratio of wollastonite, rape rod, sodium silicate is 7∶1∶2, the mixture calcines in 600 ℃and muffle furnace for 1.5 h. The results of XRD, IR and SEM show that Ca-Si-C composite loaded with biochar has more surface pores and contains functional groups such as -OH, C≡C, -COOH and C-O. When 2% Ca-Si-C is applied to yellow soil with pH value 4.7, the initial pH value of the soil increases by 1.4 units compared with the control, and the acid damage capacity increases by 11.5 mmol/kg, the dissolution of sodium and potassium in soil increases, the dissolution of calcium, magnesium and aluminum decreases, the intersection point of soil acid buffer curve and aluminum ion dissolution curve increases from pH value 3.5 to 4.1. The Ca-Si-C has a good application prospect in acid soil improvement.
-
Key words:
- Wollastonite /
- Acid soil /
- Acid damage capacity /
- Base cations /
- Soil improvement
-

-
表 1 供试土壤机械组成
Table 1. Mechanical composition of the tested soil
项目 粘粒 粉粒 砂粒 粒度/mm -0.005 -0.01+0.005 -0.05+0.01 -0.075+0.01 -0.25+0.075 -0.5+0.25 -1.0+0.5 含量/% 43.10 11.10 28.80 5.60 9.40 0.90 1.10 表 2 供试土壤主要化学组成/%
Table 2. Main chemical composition of the tested soil
Fe2O3 SiO2 Al2O3 K2O MnO Na2O CaO MgO 2.71 50.37 14.23 16.15 0.017 0.19 0.14 0.47 -
[1] 徐仁扣. 土壤酸化及其调控研究进展[J]. 土壤, 2015, 47(2):238-244.XU R K. Research progress of soil acidification and its control[J]. Soils, 2015, 47(2):238-244.
XU R K. Research progress of soil acidification and its control[J]. Soils, 2015, 47(2):238-244.
[2] 吴道铭, 傅友强, 于智卫, 等. 我国南方红壤酸化和铝毒现状及防治[J]. 土壤, 2013, 45(4):577-584.WU D M, FU Y Q, YU Z W, et al. Status of red soil acidification and aluminum toxicity in south china and prevention[J]. Soils, 2013, 45(4):577-584.
WU D M, FU Y Q, YU Z W, et al. Status of red soil acidification and aluminum toxicity in south china and prevention[J]. Soils, 2013, 45(4):577-584.
[3] 倪中应, 谢国雄, 章明奎. 酸化对耕地土壤镉铅有效性及农产品中镉铅积累的影响[J]. 江西农业学报, 2017, 29(8):52-56.NI Z Y, XIE G X, ZHANG M K. Effects of acidification on bioavailability of cadmium and lead in cultivated land soil and their accumulation in agricultural products[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2017, 29(8):52-56.
NI Z Y, XIE G X, ZHANG M K. Effects of acidification on bioavailability of cadmium and lead in cultivated land soil and their accumulation in agricultural products[J]. Acta Agriculturae Jiangxi, 2017, 29(8):52-56.
[4] Hu Y, Cheng H, Tao S. The challenges and solutions for cadmium-contaminated rice in China: a critical review[J]. Environment international, 2016, 92:515-532.
[5] Fageria N K, Nascente A S. Management of soil acidity of South American soils for sustainable crop production[J]. Advances in Agronomy, 2014, 128:221-275.
[6] Zhang X, Guo J, Vogt R D, et al. Soil acidification as an additional driver to organic carbon accumulation in major Chinese croplands[J]. Geoderma, 2020, 366:114234. doi: 10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114234
[7] Pan X Y, Li J Y, Deng K Y, et al. Four-year effects of soil acidity amelioration on the yields of canola seeds and sweet potato and N fertilizer efficiency in an ultisol[J]. Field Crops Research, 2019, 237:1-11. doi: 10.1016/j.fcr.2019.03.019
[8] 张玲玉, 赵学强, 沈仁芳. 土壤酸化及其生态效应[J]. 生态学杂志, 2019, 38(6):1900-1908.ZHANG L Y, ZHAO X Q, SHEN R F. Soil acidification and its ecological effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(6):1900-1908.
ZHANG L Y, ZHAO X Q, SHEN R F. Soil acidification and its ecological effects[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2019, 38(6):1900-1908.
[9] 靳辉勇, 齐绍武, 朱益, 等. 硅酸盐土壤调理剂对蔬菜Cd污染的治理效果[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2017(1):149-152.JIN H Y, QI S W, ZHU Y, et al. The governance effect of siliate soil conditioner on cadmium-contaminated in vegetables[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2017(1):149-152. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20170125
JIN H Y, QI S W, ZHU Y, et al. The governance effect of siliate soil conditioner on cadmium-contaminated in vegetables[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2017(1):149-152. doi: 10.11838/sfsc.20170125
[10] 庄钟娟, 杜迎辉, 朱瑞艳, 等. 硅酸盐菌剂对水稻生物学性状及养分累积的影响[J]. 中国稻米, 2015, 21(6):88-90+93.ZHUANG Z J, DU Y H, ZHU R Y, et al. Effects of sillicate bacterium on biological character and nutrients accumulation of rice vegetables[J]. China Rice, 2015, 21(6):88-90+93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8082.2015.06.020
ZHUANG Z J, DU Y H, ZHU R Y, et al. Effects of sillicate bacterium on biological character and nutrients accumulation of rice vegetables[J]. China Rice, 2015, 21(6):88-90+93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8082.2015.06.020
[11] Shepherd J G, Joseph S, Sohi S P, et al. Biochar and enhanced phosphate capture: mapping mechanisms to functional properties[J]. Chemosphere, 2017, 179:57-74. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.02.123
[12] Zhang M, Shu L, Shen X, et al. Characterization of nitrogen-rich biomaterial-derived biochars and their sorption for aromatic compounds[J]. Environmental pollution, 2014, 195:84-90. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2014.08.018
[13] Yilangai R M, Manu A S, Pineau W, et al. The effect of biochar and crop veil on growth and yield of Tomato (Lycopersicum esculentus Mill) in Jos, North central Nigeria[J]. Current Agriculture Research Journal, 2014, 2(1):37. doi: 10.12944/CARJ.2.1.05
[14] 刘慧屿, 娄春荣, 韩英祚, 等. 秸秆生物炭与减量氮肥配施对玉米氮素利用率及土壤结构的影响[J]. 土壤通报, 2020, 51(5):1180-1188.LIU H Y, LOU C R, HAN Y Z, et al. Impact of biochar addition combined with reduced nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen use efficiency and soil structure in brown earth[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(5):1180-1188.
LIU H Y, LOU C R, HAN Y Z, et al. Impact of biochar addition combined with reduced nitrogen fertilizer on nitrogen use efficiency and soil structure in brown earth[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science, 2020, 51(5):1180-1188.
[15] 赵明柳, 唐守寅, 董海霞, 等. 硅酸钠对重金属污染土壤性质和水稻吸收Cd Pb Zn的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2016, 35(9):1653-1659.ZHAO M L, TANG S Y, DONG H X, et al. Effects of sodium silicate on soil properties and Cd, Pb and Zn absorption by rice plant[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(9):1653-1659. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016-0288
ZHAO M L, TANG S Y, DONG H X, et al. Effects of sodium silicate on soil properties and Cd, Pb and Zn absorption by rice plant[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2016, 35(9):1653-1659. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2016-0288
[16] 刘鸣达, 张婧婷, 马聪, 等. 施硅降低碱性土壤铅生物有效性的机制研究[J]. 农业环境科学学报, 2019, 38(3):555-562.LIU M D, ZHANG J T, MA C, et al. Preliminary study on the mechanism by which silicon application reduces lead bioavailability in alkaline soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(3):555-562. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-1414
LIU M D, ZHANG J T, MA C, et al. Preliminary study on the mechanism by which silicon application reduces lead bioavailability in alkaline soil[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science, 2019, 38(3):555-562. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-1414
[17] 王敬华, 张效年, 于天仁. 华南红壤对酸雨酸敏感性的研究[J]. 土壤学报, 1994, 31(4):348-355 .WANG J H, ZHANG X N, YU T R. Study on acid sensitivity of red soil in South China to acid rain[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1994, 31(4):348-355.
WANG J H, ZHANG X N, YU T R. Study on acid sensitivity of red soil in South China to acid rain[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica, 1994, 31(4):348-355.
[18] Ulrich B. Natural and anthropogenic components of soil acidification[J]. Zeitschrift für Pflanzenernä hrung und Bodenkunde, 1986, 149(6):702-717.
[19] 张祥, 王典, 姜存仓, 等. 生物炭对我国南方红壤和黄棕壤理化性质的影响[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2013, 21(8):979-984.ZHANG X, WANG D, JIANG C C, et al. Effect of biochar on physicochemical properties of red and yellow brown soils in the South China Region[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(8):979-984. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2013.00979
ZHANG X, WANG D, JIANG C C, et al. Effect of biochar on physicochemical properties of red and yellow brown soils in the South China Region[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco-Agriculture, 2013, 21(8):979-984. doi: 10.3724/SP.J.1011.2013.00979
[20] 廖柏寒, 李长生. 土壤对酸沉降缓冲机制探讨[J]. 环境科学, 1989, 10(1):30-34.LIAO B H, LI C S. Buffering mechanism of soil for acidic precipitation[J]. Environmental Science, 1989, 10(1):30-34. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.1989.01.001
LIAO B H, LI C S. Buffering mechanism of soil for acidic precipitation[J]. Environmental Science, 1989, 10(1):30-34. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0250-3301.1989.01.001
[21] 朱霞萍, 汪模辉, 李锡坤, 等. 珠江三角洲潮土和水稻土酸缓冲特性实验研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2010(1):47-50.ZHU X P, WANG M H, LI X K, et al. Study on acid buffer characters of fluvo-quic soil and paddy soil in the Pearl River Delta South China Region[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2010(1):47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2010.01.011
ZHU X P, WANG M H, LI X K, et al. Study on acid buffer characters of fluvo-quic soil and paddy soil in the Pearl River Delta South China Region[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control, 2010(1):47-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3865.2010.01.011
-



 下载:
下载: