Optimization Study on the Microwave Drying of Red Mud Using Response Surface Methodology
-
摘要:
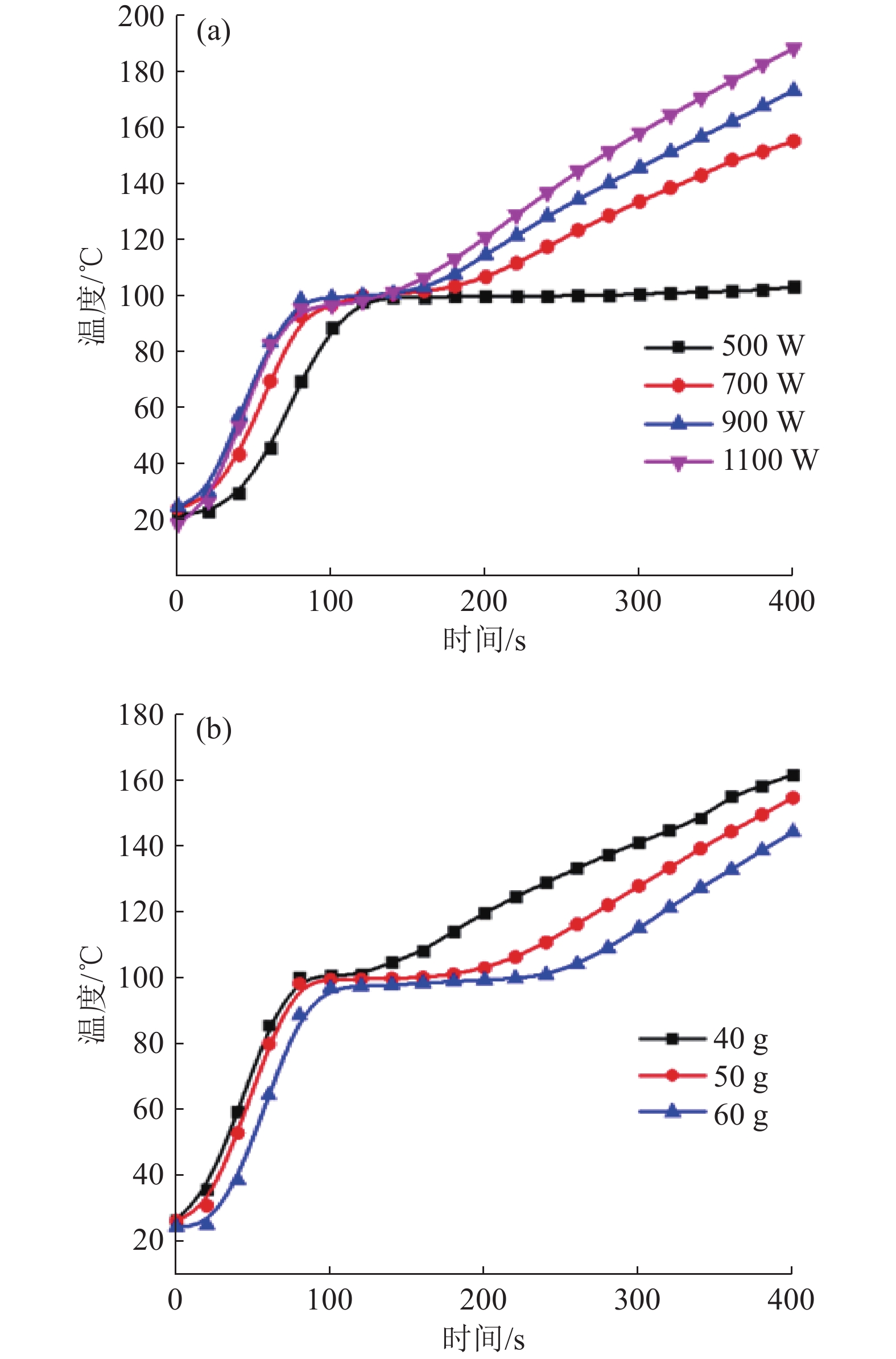
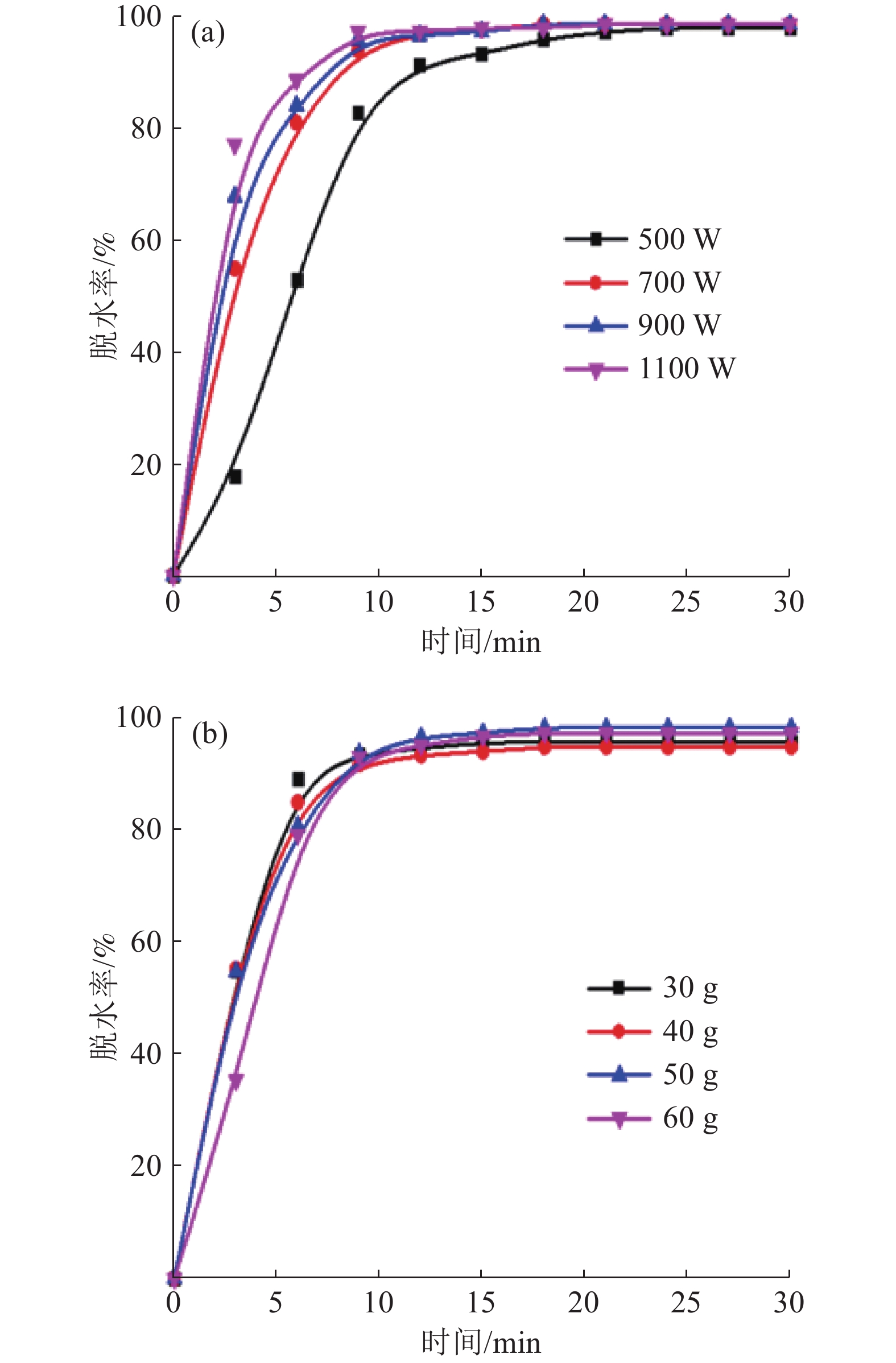
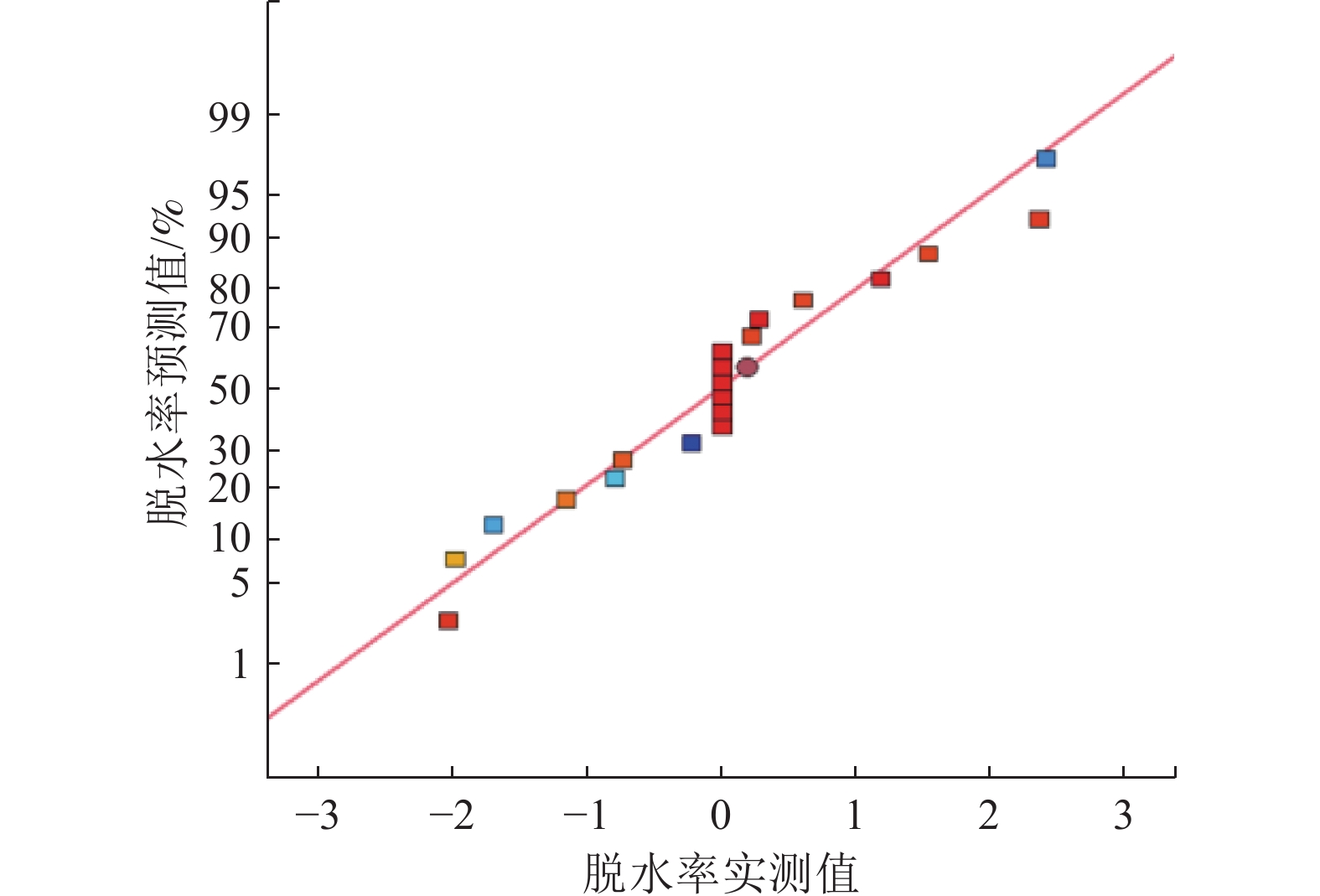
赤泥作为一种铝生产工业废弃物,有价金属元素种类丰富,具有较高的综合利用价值。论文开展了微波清洁干燥赤泥实验研究,考查了微波功率、物料量对赤泥温升行为的影响,表明赤泥升温速率与微波功率成正比,与物料量成反比;在单因素实验基础上,进行了响应曲面法优化实验研究,分别考查了微波功率、物料量和干燥时间对赤泥脱水率的影响,建立了各因素与脱水率之间的数学模型,获得了微波清洁干燥赤泥响应曲面优化工艺参数:控制微波干燥温度为100 ℃,微波功率为700 W,物料量为50 g,干燥时间为12 min时,赤泥的脱水率为97.95%,与模型预测值(98.58%)较为接近。研究结果为赤泥的资源化利用奠定了一定实验基础。
Abstract:As a kind of industrial waste from aluminum production, red mud is rich in valuable metal elements and has high comprehensive utilization value. The effects of microwave power and material amount on the temperature rise behavior of red mud were investigated. The results show that the heating rate of red mud is directly proportional to the microwave power and inversely proportional to material amount. Based on the single factor experiment, the optimization experiment of response surface method was carried out. The effects of microwave power, material amount and drying time on the dehydration rate of red mud were investigated respectively. The mathematical model between each factor and dehydration rate was established, and the optimization process parameters of response surface of microwave clean drying red mud were obtained: Control of microwave drying temperature was 100 ℃, microwave power was 700 W, material quantity was 50 g, drying time was 12 min, dehydration rate of red mud was 97.95%, and the model prediction was similar (98.58%). The results laid a certain experimental foundation for the resource utilization of red mud.
-
Key words:
- Red mud /
- Microwave drying /
- Dehydration rate /
- Response Surface
-

-
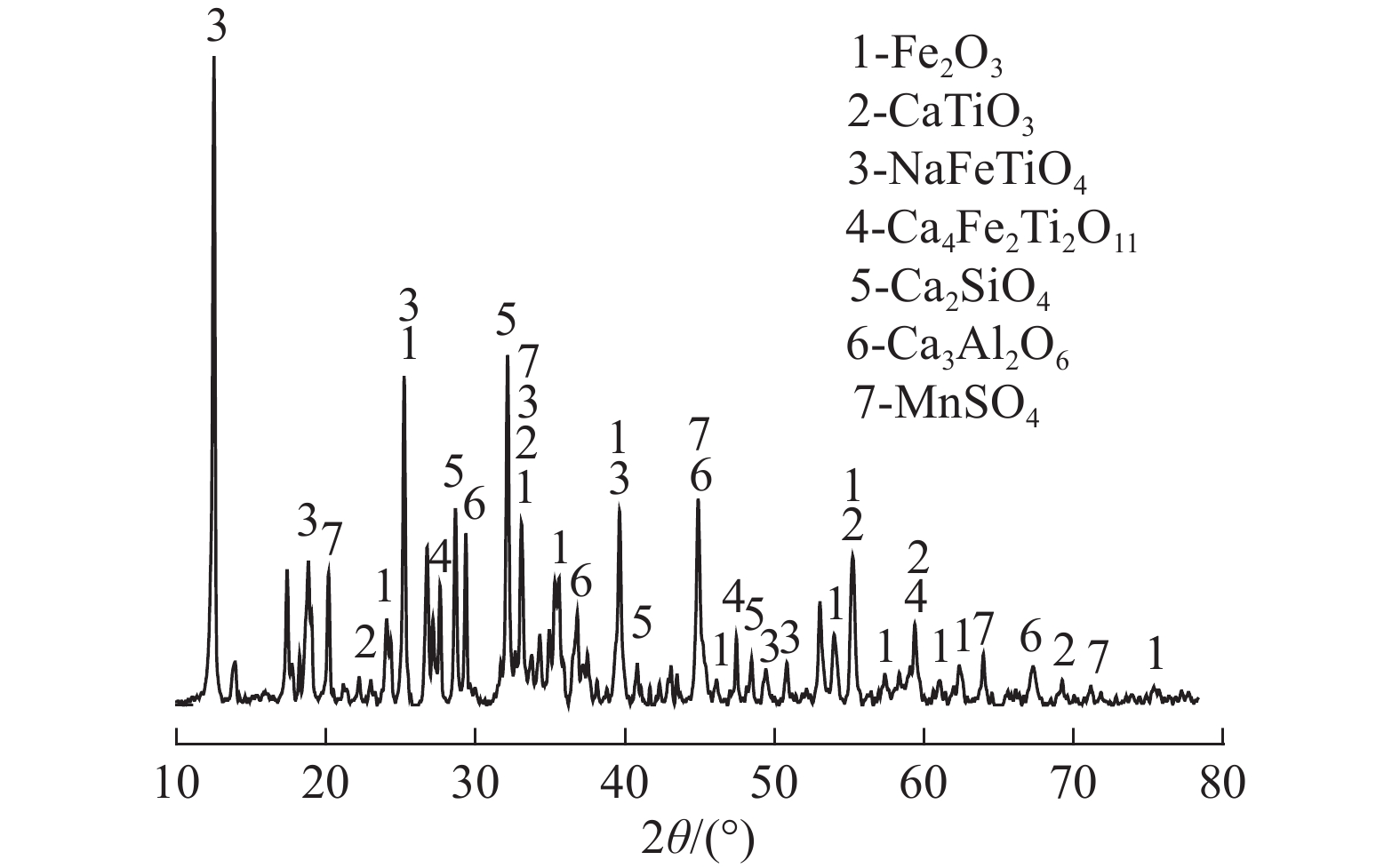
表 1 赤泥的多元素化学成分/%
Table 1. Chemical composition of the sample
Na2O MnO Al2O3 SiO2 P2O5 K2O CaO TiO2 S Fe2O3 0.304 0.069 7 10.1 11.3 0.295 2.62 26.2 6.02 0.906 41.1 表 2 响应曲面法因素水平编码
Table 2. Response surface method factor level coding
因素 水平 -1 0 1 微波功率X1 /W 300 700 1 100 物料量X2/ g 40 50 60 干燥时间X3/min 6 12 18 表 3 中心组合实验设计方案与实验结果
Table 3. Test design scheme and results
序号 影响因素 脱水率/% 微波功率X1/W 物料量X2/g 干燥时间X3/min 1 300.00 40.00 6.00 48.81 2 1 100.00 40.00 6.00 86.86 3 300.00 60.00 6.00 34.19 4 1 100.00 60.00 6.00 93.55 5 300.00 40.00 18.00 90.17 6 1 100.00 40.00 18.00 93.48 7 300.00 60.00 18.00 94.58 8 1 100.00 60.00 18.00 95.26 9 27.28 50.00 12.00 4.00 10 1 372.72 50.00 12.00 98.69 11 700.00 33.18 12.00 93.55 12 700.00 66.82 12.00 92.17 13 700.00 50.00 1.91 34.41 14 700.00 50.00 22.09 98.87 15 700.00 50.00 12.00 98.61 16 700.00 50.00 12.00 98.61 17 700.00 50.00 12.00 98.61 18 700.00 50.00 12.00 98.61 19 700.00 50.00 12.00 98.61 20 700.00 50.00 12.00 98.61 表 4 响应设计的模型拟合性分析
Table 4. Model fit analysis of response design
时序模型的平方和 来源 平方和 自由度 均方差 F Prob>F 评估 平均与总和 1.445×105 1 1.445×105 线性与平均 5 774.96 3 1 924.99 8.93 0.001 0 2FI与线性 1 244.60 3 414.87 2.45 0.110 1 二次方与2FI 2 131.09 3 710.36 99.37 <0.000 1 建议的 二次方与二次方 69.68 4 17.42 58.03 <0.000 1 残差 1.80 6 0.30 总和 1.537×105 20 7 685.85 模型概率统计 来源 标准 校正R2 预测R2 预测残差平方和 评估 偏差 R2 线性型 14.68 0.626 2 0.556 1 0.396 7 5 563.53 交互型 13.02 0.761 2 0.650 9 0.424 1 5 310.86 二次方型 2.67 0.992 2 0.985 3 0.933 5 613.51 建议的 表 5 响应面二次模型的方差分析
Table 5. Variance analysis of response surface quadratic model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 Prob > F Model 9 150.65 9 1 016.74 142.23 <0.000 1 X1 2 798.17 1 2 798.17 391.43 <0.000 1 X2 0.065 1 0.065 9.034×10-3 0.926 2 X3 2 976.72 1 2 976.72 416.40 <0.000 1 X1X2 23.39 1 23.39 3.27 0.100 6 X1X3 1 210.81 1 1 210.81 169.38 <0.000 1 X2X3 10.40 1 10.40 1.45 0.255 6 X12 1 213.71 1 1 213.71 169.78 <0.000 1 X22 50.63 1 50.63 7.08 0.023 8 X32 1 127.84 1 1 127.84 157.77 <0.000 1 残差 71.49 10 7.15 失拟项 71.49 5 14.30 纯差 0.000 5 0.000 总误差 9 222.14 19 表 6 回归模型优化工艺参数
Table 6. Optimization process parameters of regression model
微波功率/
W物料量/
g干燥温度/
℃干燥时间/
min脱水率 /% 预测值 实验值 700 50 100 12 98.58 97.95 -
[1] 吴世超, 朱立新, 孙体昌, 等. 赤泥综合利用现状及展望[J]. 金属矿山, 2019(6):38-44.WU S C, ZHU L X, SUN T C, et al. Comprehensive utilization status and prospect of red mud[J]. Metal Mine, 2019(6):38-44.
WU S C, ZHU L X, SUN T C, et al. Comprehensive utilization status and prospect of red mud[J]. Metal Mine, 2019(6):38-44.
[2] 李义伟, 付向辉, 李立, 等. 赤泥综合回收利用研究进展及展望[J]. 稀土, 2020, 41(6):97-107.LI Y W, FU X H, LI L, et al. Research progress on comprehensive recovery of bauxite residue: a comprehensive review[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2020, 41(6):97-107.
LI Y W, FU X H, LI L, et al. Research progress on comprehensive recovery of bauxite residue: a comprehensive review[J]. Chinese Rare Earths, 2020, 41(6):97-107.
[3] ZHANG J Z, YAO Z Y, WANG K, et al. Sustainable utilization of bauxite residue (Red Mud) as a road material in pavements: a critical review[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 270(8):121419.
[4] MICHELLE P B, LUCAS F A, LARISSA S R, et al. Evaluation and application of sintered red mud and its incorporated clay ceramics as materials for building construction[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology, 2020, 9(2):2186-2195. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.12.049
[5] 李先海, 苏振楠, 谢显胜, 等. 赤泥掺合对水泥混凝土性能及微结构影响研究[J]. 轻金属, 2022(2):5-9.LI X H, SU Z N, XIE X S, et al. Study on the effect of red mud admixture on the performance and microstructure of cement concrete[J]. Light Metals, 2022(2):5-9.
LI X H, SU Z N, XIE X S, et al. Study on the effect of red mud admixture on the performance and microstructure of cement concrete[J]. Light Metals, 2022(2):5-9.
[6] Liu W C, Yang J K, Xiao B. Application of Bayer red mud for iron recovery and building material production from alumosilicate residues[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009, 161(1):474-478. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.03.122
[7] 常军. 拜耳法赤泥综合回收铝和铁的研究[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2018.CHANG J. Research on comprehensive recovery of aluminum and iron from red mud by bayer process[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2018.
CHANG J. Research on comprehensive recovery of aluminum and iron from red mud by bayer process[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Science and Technology, 2018.
[8] 薛真, 薛彦辉, 王力. 拜耳法赤泥中铝铁的盐酸浸出过程研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2018(6):139-143.XUE Z, XUE Y H, WANG L. Study on the hydrochloric acid leaching process of aluminum and iron from Bayer process red mud[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(6):139-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2018.06.029
XUE Z, XUE Y H, WANG L. Study on the hydrochloric acid leaching process of aluminum and iron from Bayer process red mud[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2018(6):139-143. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2018.06.029
[9] 路梦雨, 王智勇, 戴惠新, 等. 从赤泥中回收钪研究进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(5):9-16.LU M Y, WANG Z Y, DAI H X, et al. Research progress of recovering scandium from red mud[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(5):9-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.05.002
LU M Y, WANG Z Y, DAI H X, et al. Research progress of recovering scandium from red mud[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(5):9-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.05.002
[10] 李博琦, 谢贤, 纪翠翠, 等. 赤泥提钛技术研究现状与展望[J]. 矿冶, 2020, 29(6):87-93.LI B Q, XIE X, JI C C, et al. Research status and prospect of titanium extraction technology from red mud[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2020, 29(6):87-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2020.06.017
LI B Q, XIE X, JI C C, et al. Research status and prospect of titanium extraction technology from red mud[J]. Mining and Metallurgy, 2020, 29(6):87-93. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-7854.2020.06.017
[11] 高建阳. 氧化铝工业废弃赤泥直接还原技术研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2011(2):37-40.GAO J Y. Technological research on direct reduction of obsolete red mud in alumina industry[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2011(2):37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2011.02.011
GAO J Y. Technological research on direct reduction of obsolete red mud in alumina industry[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2011(2):37-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2011.02.011
[12] 张继军, 赵敏刚, 徐彦国. 新型组合干燥器在镍精矿干燥中的应用[J]. 化学工程, 2009, 37(1):8-10.ZHANG J J, ZHAO M G, XU Y G. Application of novel combination dryer in nickel concentrate drying[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2009, 37(1):8-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2009.01.003
ZHANG J J, ZHAO M G, XU Y G. Application of novel combination dryer in nickel concentrate drying[J]. Chemical Engineering (China), 2009, 37(1):8-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9954.2009.01.003
[13] 茹赛红, 曾晖, 方岩雄, 等. 微波干燥和热风干燥对金萱茶叶品质影响[J]. 化工进展, 2012, 31(10):2183-2186.RU S H, ZENG H, FANG Y X, et al. Effect of microwave drying and hot air drying on quality of Jin Xuan tea[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2012, 31(10):2183-2186.
RU S H, ZENG H, FANG Y X, et al. Effect of microwave drying and hot air drying on quality of Jin Xuan tea[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2012, 31(10):2183-2186.
[14] 衡银雪, 郑旭煦, 殷钟意, 等. 黄精微波真空-热风联合干燥工艺研究[J]. 应用化工, 2018, 47(5):952-955.HENG Y X, ZHENG X X, YIN Z Y, et al. Study on the microwave vacuum-hot air combined drying process of polygonatum sibiricum[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(5):952-955. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.05.026
HENG Y X, ZHENG X X, YIN Z Y, et al. Study on the microwave vacuum-hot air combined drying process of polygonatum sibiricum[J]. Applied Chemical Industry, 2018, 47(5):952-955. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-3206.2018.05.026
[15] 马爱元, 郑雪梅, 孙成余, 等. 微波技术在材料制备与矿物冶金中的应用[J]. 稀有金属, 2019, 44(10):1094-1107.MA A Y, ZHENG X M, SUN C Y, et al. Application of microwave technology in mineral metallurgy and material preparation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2019, 44(10):1094-1107.
MA A Y, ZHENG X M, SUN C Y, et al. Application of microwave technology in mineral metallurgy and material preparation[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals, 2019, 44(10):1094-1107.
[16] 刘璐, 魏光涛, 辛宗武, 等. 微波加热强化赤泥浸铁的研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2019, 42(6):6-10.LIU L, WEI G T, XIN Z W, et al. Study on the enhancement of iron leaching from red mud by microwave heating[J]. Non-metallic Minerals, 2019, 42(6):6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2019.06.002
LIU L, WEI G T, XIN Z W, et al. Study on the enhancement of iron leaching from red mud by microwave heating[J]. Non-metallic Minerals, 2019, 42(6):6-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2019.06.002
[17] 刘成龙, 周莉莉, 夏举佩, 等. 基于响应曲面法高效浸出煤矸石中钛的工艺优化[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(6):59-65.LIU C L, ZHOU L L, XIA J P, et al. Optimization of high-efficiency leaching of titanium from coal gangue with response surface method[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(6):59-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.06.011
LIU C L, ZHOU L L, XIA J P, et al. Optimization of high-efficiency leaching of titanium from coal gangue with response surface method[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(6):59-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.06.011
-



 下载:
下载: