Strength Characteristics and Mechanism of Tungsten Tailings Activated by the Different Biopolymers
-
摘要:
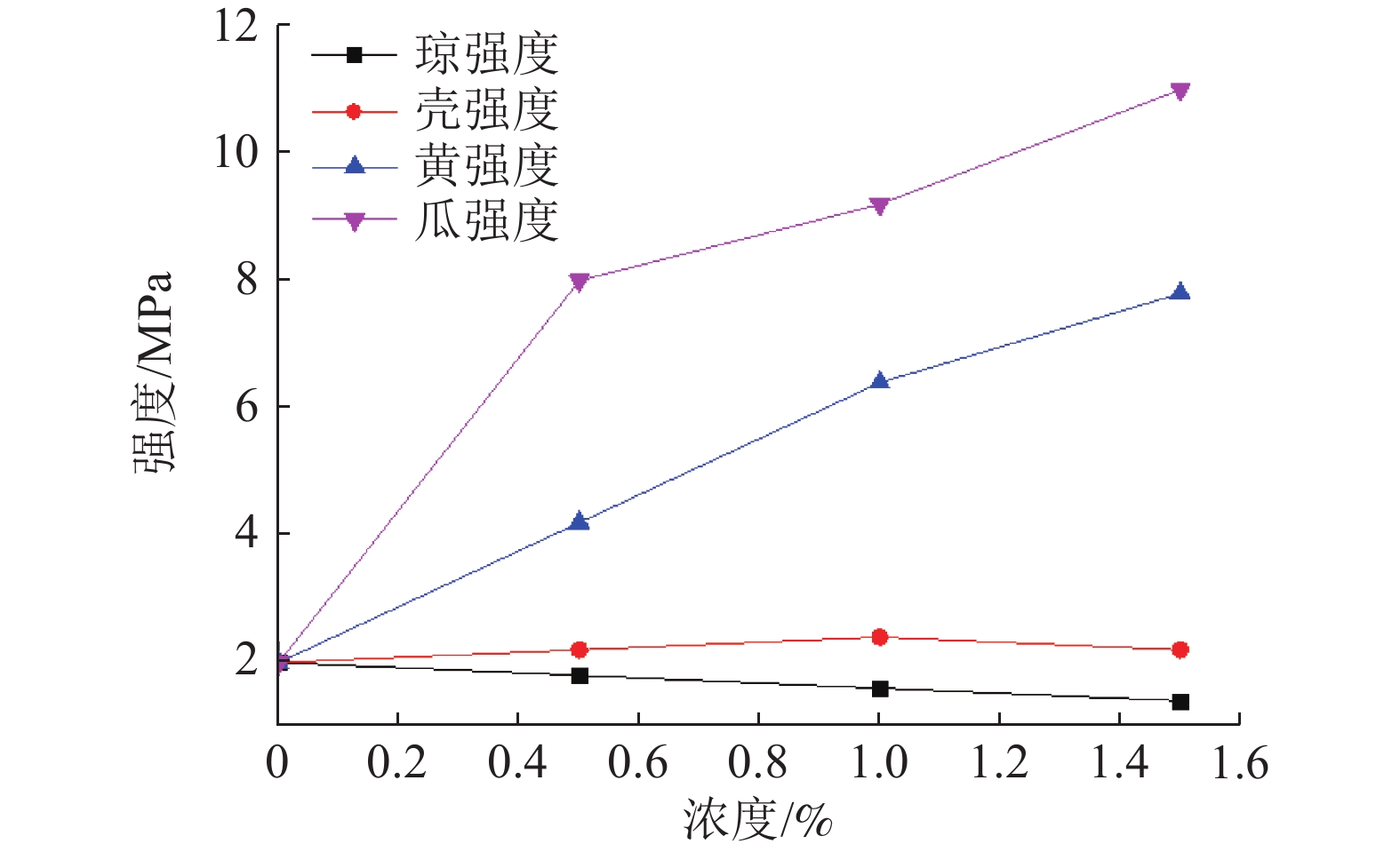
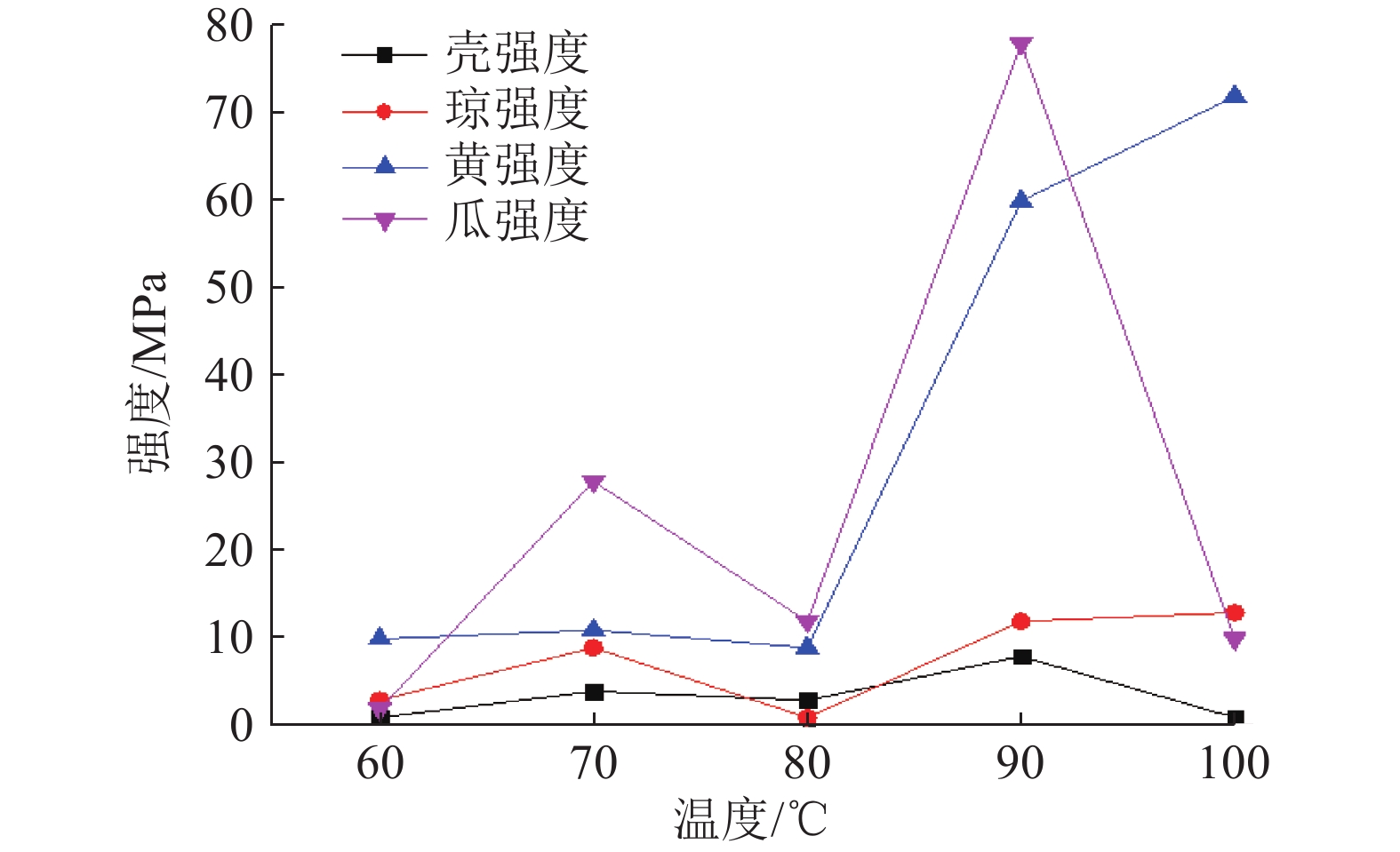
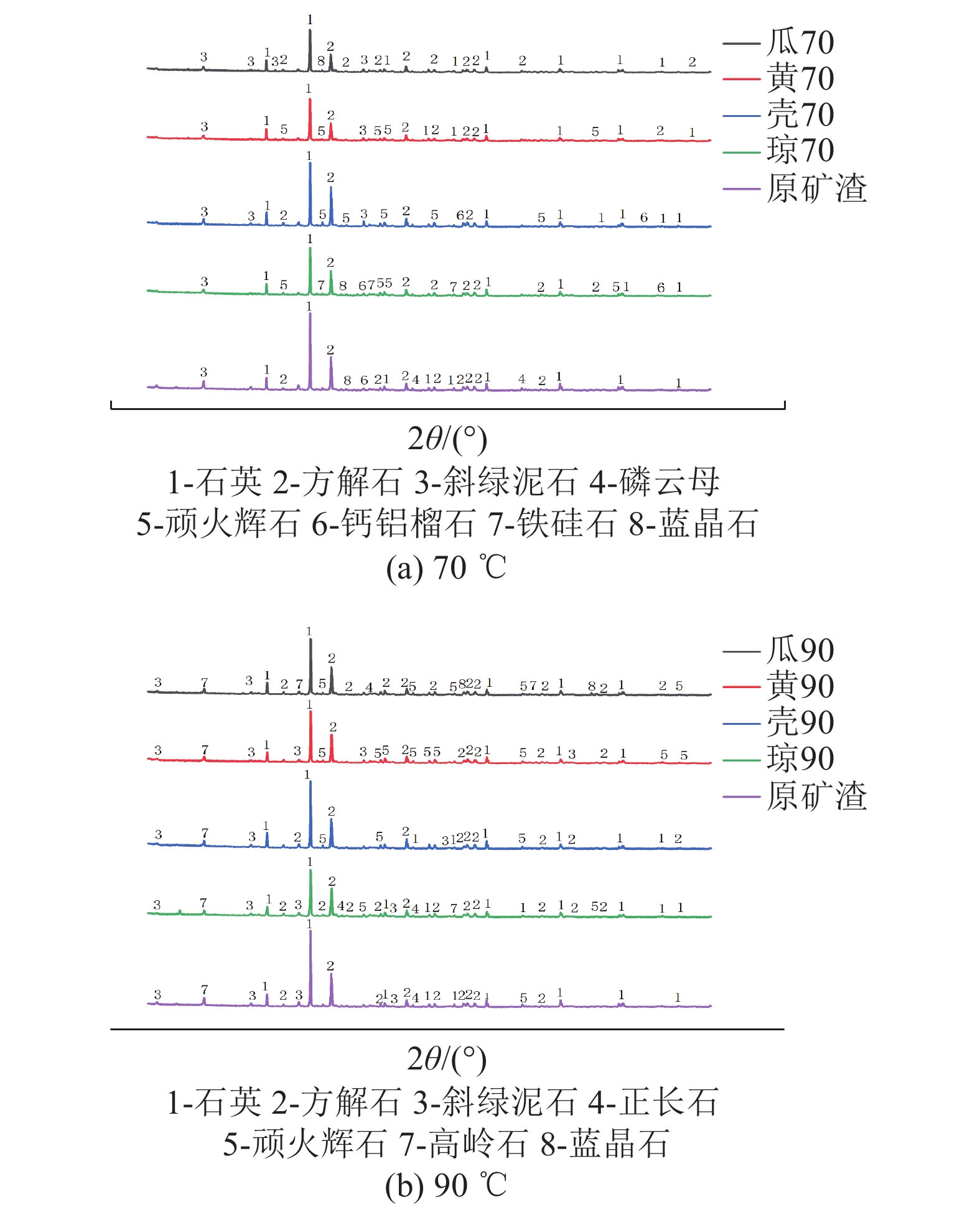
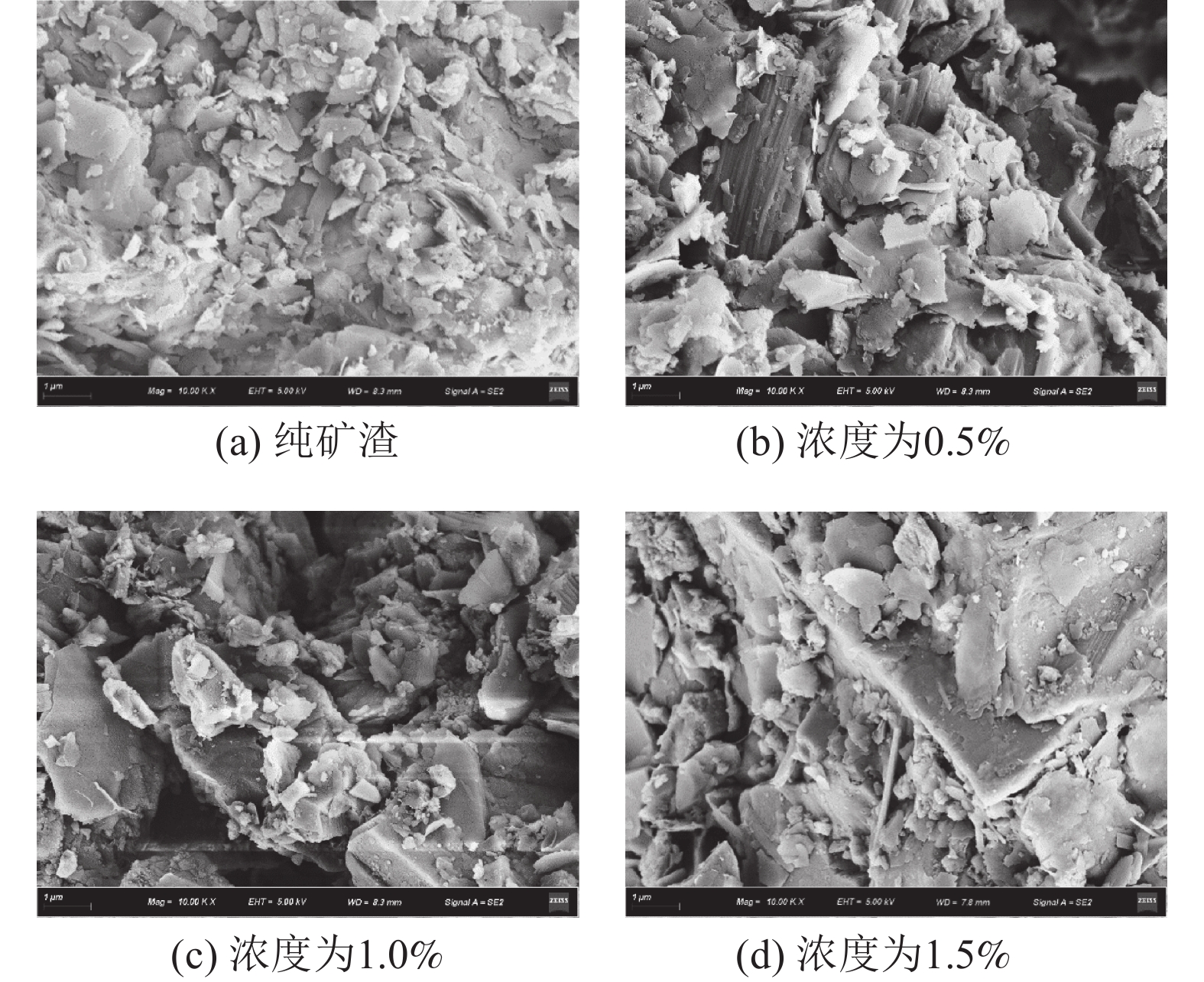
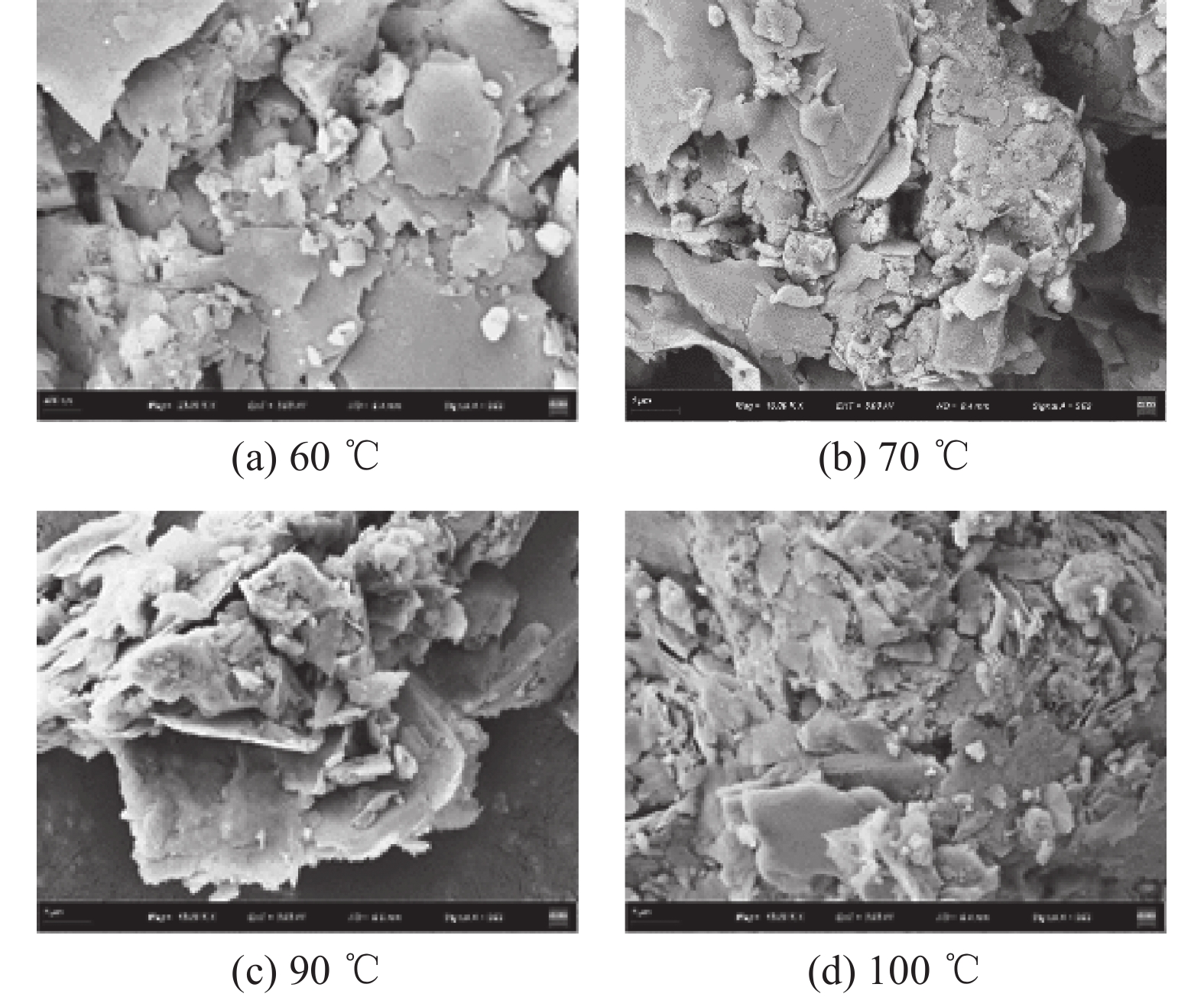
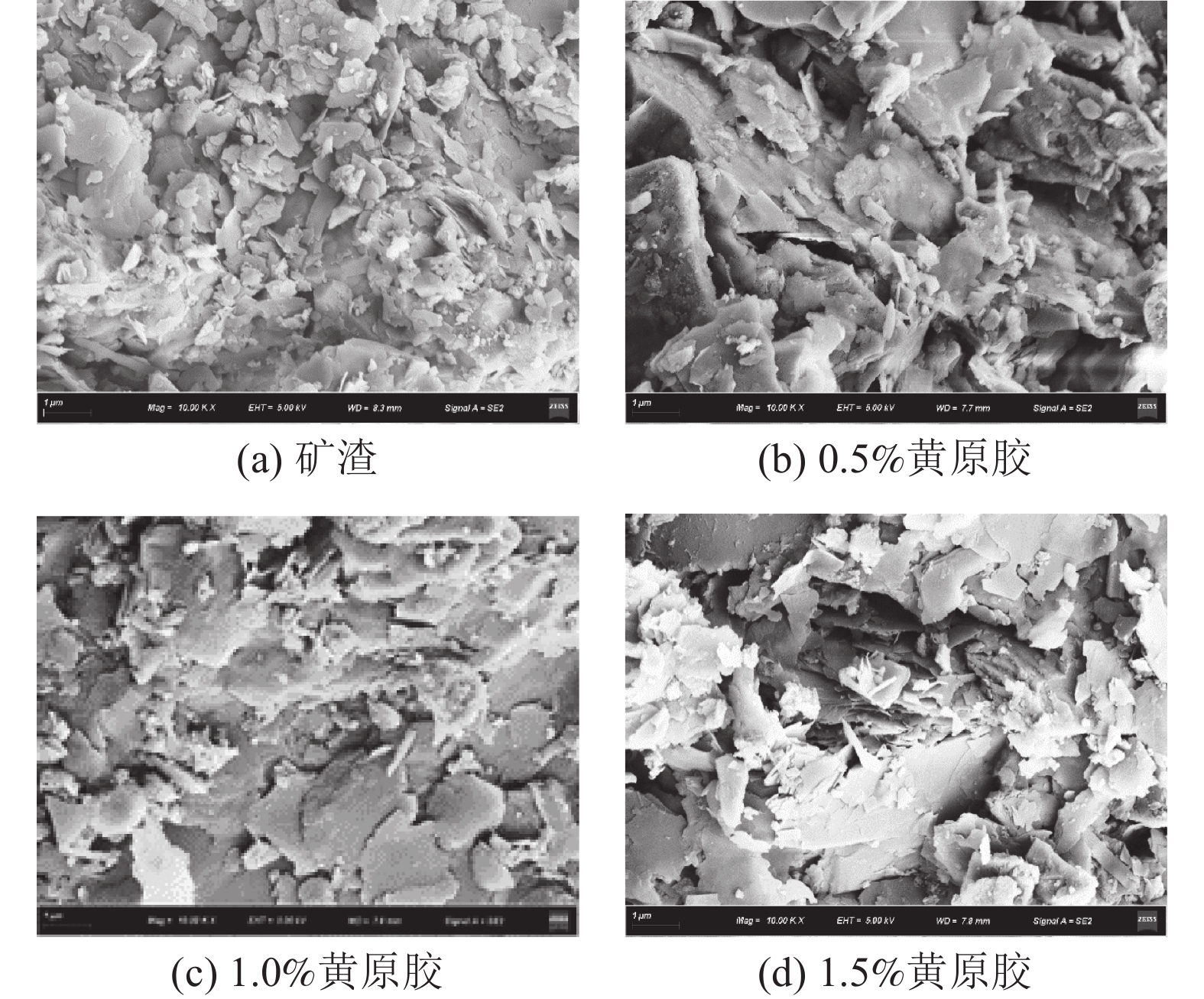
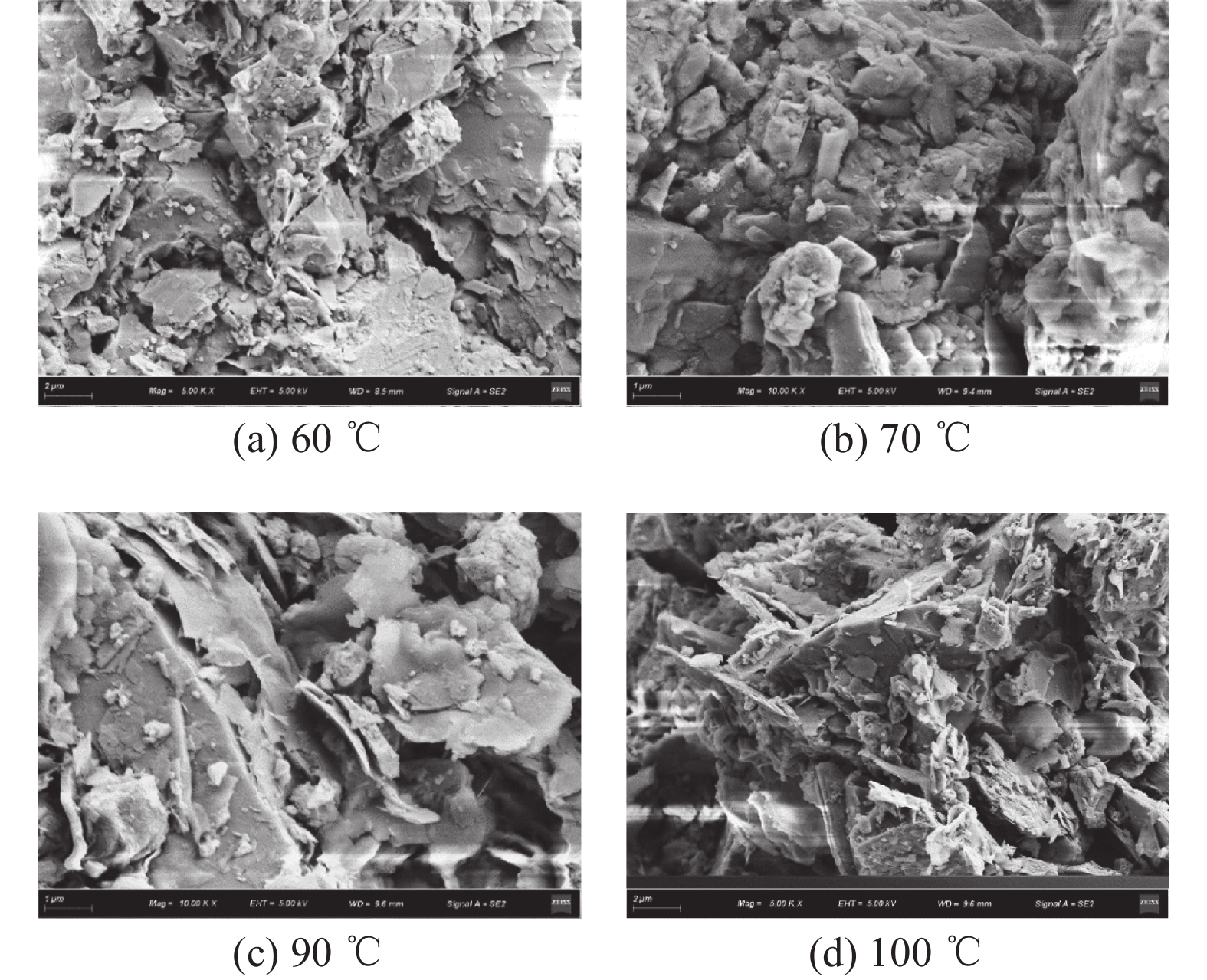
为研究不同生物聚合物对钨尾矿的无侧限抗压强度的影响,以桂林兴安某钨尾矿为研究对象,测试不同4种生物胶的不同浓度和养护温度作用下试件强度发展规律;同时,结合XRD和SEM分析不同实验条件下钨尾矿的微观特征,探明生物胶与钨尾矿作用的微观机理。实验结果表明,瓜尔胶和黄原胶对强度影响显著,而壳聚糖和琼脂作用较弱;不同生物胶改良钨尾矿的较佳养护温度:瓜尔胶和壳聚糖为90 ℃,黄原胶和琼脂为100 ℃;瓜尔胶(胶固比为1.5%)养护温度≥70 ℃以及黄原胶养护温度≥60 ℃时,试样强度均大于10 MPa。符合建砖MU10的要求。本研究为实现钨尾矿的再利用提供了理论依据。
Abstract:In order to study the effect of different biopolymers on the unconfined compressive strength of tungsten tailings which come from Xing’an of Guilin, the strength of specimens activated by four different biopolymers was tested, and the specimens were prepared by considering the curing temperatures and the biopolymer concentrations. At the same time, the microscopic characteristics of all specimens were analyzed by XRD and SEM for analyzing the microscopic mechanism. The results showed that guar gum and xanthan gum had significant effects on the strength, while chitosan and AGAR had weak effects. The optimal curing temperature of biopolymer activated tungsten tailings depends on the biopolymer type, as follows, 90 ℃ for Guar gum and chitosan, and 100 ℃ for xanthan gum and AGAR. In addition, the strength of samples activated by the guar which the mass ratio to solid is 1.5% curing at temperature ≥70 ℃ and by the xanthan gum curing at temperature ≥60 ℃ were more than 10 MPa. It meets the strength requirements of building brick MU10. This results provide a theoretical basis for reusing of tungsten tailings.
-
Key words:
- Tungsten tailings /
- Biopolymer /
- Unconfined compressive strength
-

-
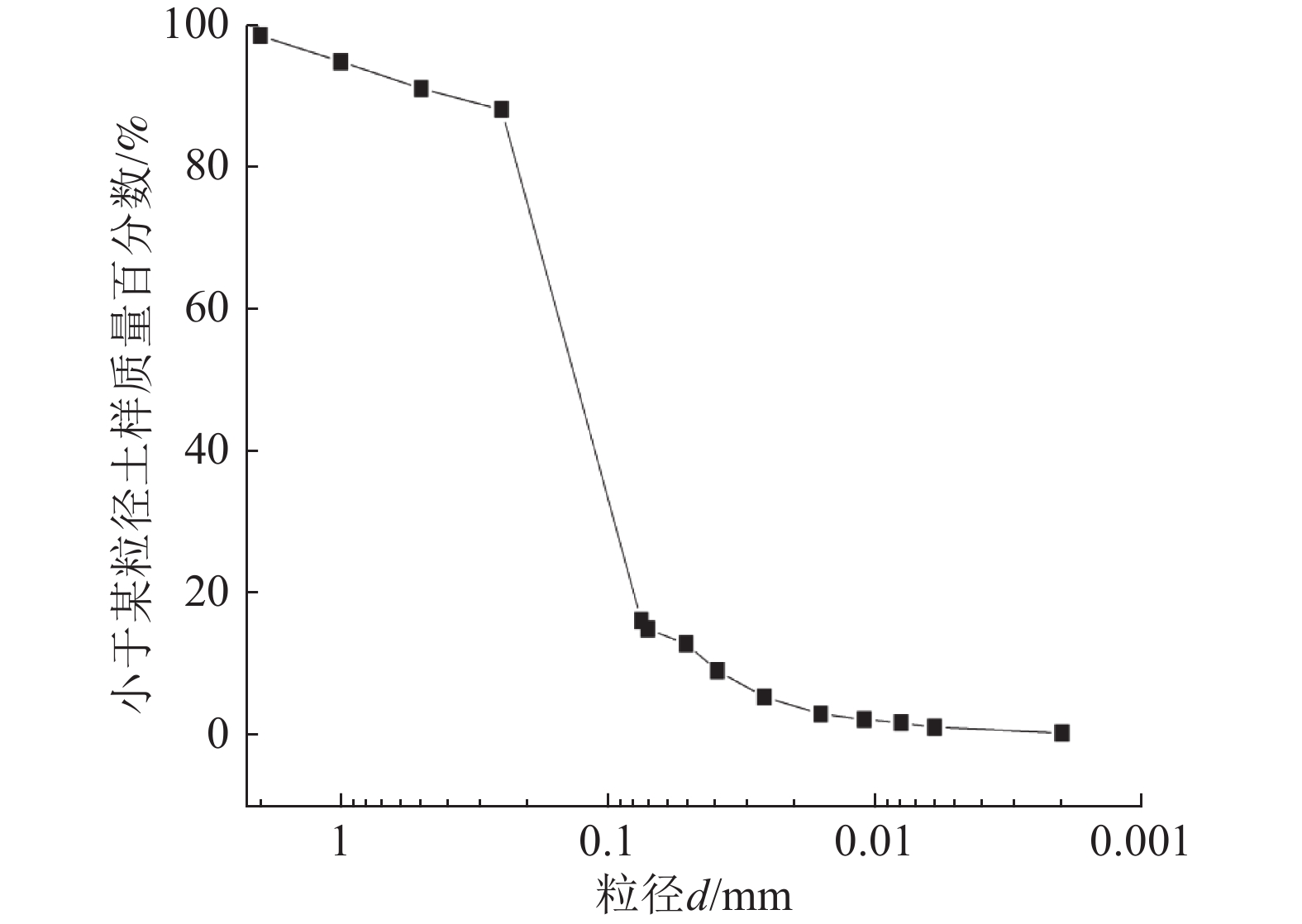
表 1 钨尾矿的主要矿物成分
Table 1. Main mineral composition of tungsten tailings
矿物 含量/% 矿物 含量/% 石英 43 钙铝榴石 7 斜长石 2 萤石 1 微斜长石 3 辉石 6 方解石 31 黏土 5 闪石 1 表 2 实验方案
Table 2. Test plan
序号 胶固比/% 养护
温度/℃序号 胶固比/% 养护
温度/℃1 0 80 5 1.5 60 2 0.5 6 70 3 1.0 7 90 4 1.5 8 100 -
[1] 邵光辉, 杨智, 唐彪, 等. 微生物诱导矿化加固粉土坡面的径流与侵蚀特性[J]. 高校地质学报, 2021, 27(6):707-715.SHAO G H, YANG Z, TANG B, et al. Properties of runoff and erosion on silt slope surface reinforced by microbial induced mineralization[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2021, 27(6):707-715. doi: 10.16108/j.issn1006-7493.2020111
SHAO G H, YANG Z, TANG B, et al. Properties of runoff and erosion on silt slope surface reinforced by microbial induced mineralization[J]. Geological Journal of China Universities, 2021, 27(6):707-715. doi: 10.16108/j.issn1006-7493.2020111
[2] HATAF N, GHADIR P, RANJBAR N. Investigation of soil stabilization using chitosan biopolymer[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2018, 170:1493-1500. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.256
[3] 倪静, 王子腾, 耿雪玉. 植物–生物聚合物联合法固土的实验研究[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2020, 42(11):2131-2137NI J, WANG Z T, GENG X Y. Experimental study on combined plant-biopolymer method for soil stabilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(11):2131-2137. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202011019
NI J, WANG Z T, GENG X Y. Experimental study on combined plant-biopolymer method for soil stabilization[J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2020, 42(11):2131-2137. doi: 10.11779/CJGE202011019
[4] 贾卓龙, 晏长根, 李博, 等. 瓜尔豆胶固化纤维黄土的抗侵蚀特性及生态护坡试验研究. 岩土工程学报, 2022, 44(10): 1881-1889.JIA Z L, YAN C G, LI B, et al. Experimental study on erosion resistance and ecological slope protection of guar gum-treated fiber-reinforcement loess [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(10): 1881-1889.
JIA Z L, YAN C G, LI B, et al. Experimental study on erosion resistance and ecological slope protection of guar gum-treated fiber-reinforcement loess [J]. Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering, 2022, 44(10): 1881-1889.
[5] 左晨希, 孙树林, 黄曼捷, 等. 黄原胶和玄武岩纤维改良黄土抗压强度实验研究[J]. 中国煤炭地质, 2022, 34(1):57-61.ZUO C X, SUN S L, HUANG M J, et al. Experimental study on loess compressive strength improvement through Xanthan gum and basalt fiber[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2022, 34(1):57-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2022.01.10
ZUO C X, SUN S L, HUANG M J, et al. Experimental study on loess compressive strength improvement through Xanthan gum and basalt fiber[J]. Coal Geology of China, 2022, 34(1):57-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1803.2022.01.10
[6] 贺勇 , 蒋文强, 陈科平, 等. 海因环氧树脂复合黏土-尾矿砂固化体强度特性及微观机制[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2022, 32(11): 3528-3540.HE Y, JIANG W Q, CHEN K P, et al. Strength characteristics and micro-mechanism of hydantoin epoxy resin composite clay tailings sand solidified body [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2022, 32(11): 3528-3540.
HE Y, JIANG W Q, CHEN K P, et al. Strength characteristics and micro-mechanism of hydantoin epoxy resin composite clay tailings sand solidified body [J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2022, 32(11): 3528-3540.
[7] 包扬, 苏德, 杨巍, 等. 铜尾矿库土壤修复效应及周边植被恢复模式研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(1):74-81.BAO Y, SU D, YANG W, et al. Study on soil remediation effect of copper tailings pond and surrounding vegetation restoration model[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(1):74-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2022.01.010
BAO Y, SU D, YANG W, et al. Study on soil remediation effect of copper tailings pond and surrounding vegetation restoration model[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(1):74-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2022.01.010
[8] 宁波, 闫艳, 左夏伟, 等. 铁尾矿砂混凝土力学特性实验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(4):159-164+175.NING B, YAN Y, ZUO X W, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of iron tailings concrete[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(4):159-164+175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.04.025
NING B, YAN Y, ZUO X W, et al. Experimental study on mechanical properties of iron tailings concrete[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(4):159-164+175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.04.025
[9] 吴孔逸, 曾小波, 何雪梅, 等. 湖南钨矿资源开发利用水平分析[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(3):127-131.WU K Y, ZENG X B, HE X M, et al. Analysis on the development and utilization level of mineral resources of tungsten in Hunan province[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(3):127-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.03.020
WU K Y, ZENG X B, HE X M, et al. Analysis on the development and utilization level of mineral resources of tungsten in Hunan province[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(3):127-131. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.03.020
[10] 崔棚, 黄威, 易清, 等. 钨矿全尾砂充填料的固化性能和机理研究[J]. 中国矿业, 2020, 29(4):108-115.CUI P, HUANG W, YI Q, et al. Study on the concreted properties and mechanism of filling materials of tungsten whole tailings[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2020, 29(4):108-115. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2020.04.022
CUI P, HUANG W, YI Q, et al. Study on the concreted properties and mechanism of filling materials of tungsten whole tailings[J]. China Mining Magazine, 2020, 29(4):108-115. doi: 10.12075/j.issn.1004-4051.2020.04.022
[11] 兰志强, 蓝卓越, 张镜翠. 钨尾矿资源综合利用研究进展[J]. 中国钨业, 2016, 31(2):37-42.LAN Z Q, LANG Z Y, ZHANG J C. Research progress on the comprehensive utilization of tungsten tailings[J]. China Tungsten Industry, 2016, 31(2):37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0622.2016.02.008
LAN Z Q, LANG Z Y, ZHANG J C. Research progress on the comprehensive utilization of tungsten tailings[J]. China Tungsten Industry, 2016, 31(2):37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0622.2016.02.008
-



 下载:
下载: