Industrial Test Research on Stainless Steel Dust with Coal-based Hydrogen Metallurgy for Recycling Purpose
-
摘要:
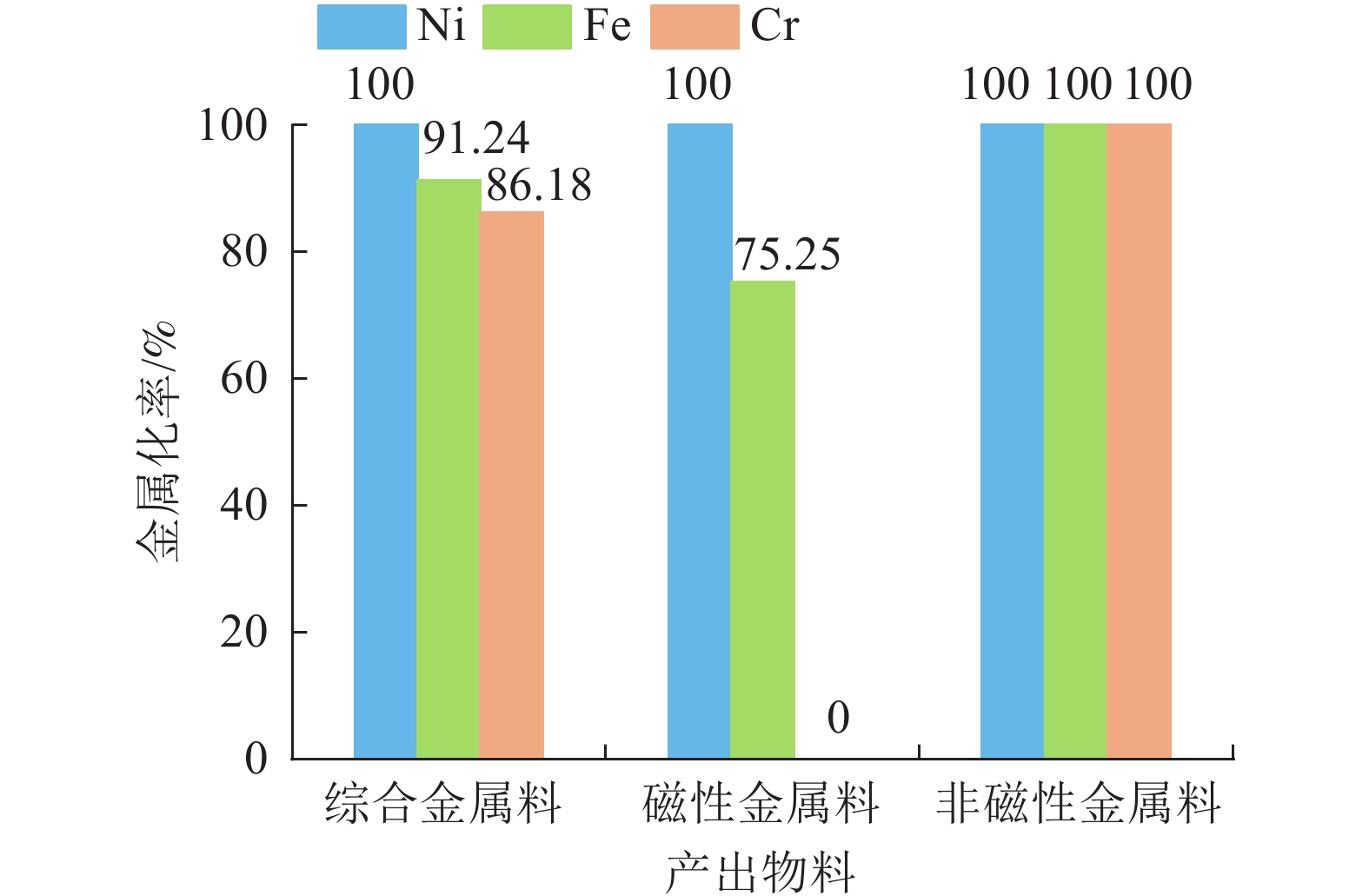
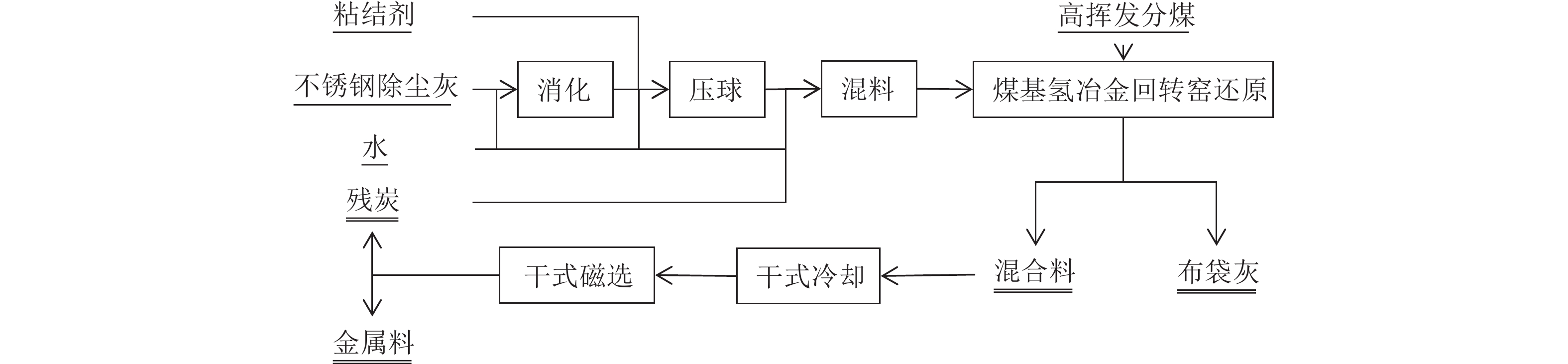
采用自主研发的煤基氢冶金技术和煤基氢冶金回转窑工业实验装置,系统开展了不锈钢除尘灰无害化、资源化工业实验,在氢冶金还原温度1 250 ℃、在窑时间3 h左右的条件下,取得镍、铁、铬金属化率分别为100%、91.24%和86.18%,产出所有物料均低于浸出毒性鉴别标准限值的优异结果。完成了不锈钢除尘灰煤基氢冶金过程的热力学分析。形成了以煤基氢冶金回转窑技术为核心,包含有干式冷却、干式磁选、重力跳汰分选等主要工序的不锈钢除尘灰煤基氢冶金回转窑无害化、资源化工艺包。
Abstract:The self-developed coal-based hydrogen metallurgical technology and coal-based hydrogen metallurgical rotary kiln industrial test device were used to carry out the industrial test on stainless steel dust with coal-based hydrogen metallurgy in the rotary kiln for harmless and recycling purpose. The metallization ratio of nickel, iron, and chromium are 100%, 91.24% and 86.18%, respectively, at the conditions of hydrogen metallurgical reduction temperature of 1 250 ℃ and the time in the kiln of about 3 h, and all the produced materials of which the indexes are lower than the standard limit of extraction toxicity identification. Thermodynamic analysis was carried out for coal-based hydrogen metallurgy process on stainless steel dust. It forms a harmless and recycling process package for stainless steel dust, including coal-based hydrogen metallurgical rotary kiln which is the core technology, dry cooling, dry magnetic separation, gravity jig separation and other main processes.
-
Key words:
- Coal-based hydrogen metallurgy /
- Stainless steel dust /
- Rotary kiln
-

-
表 1 不锈钢除尘灰主要化学成分/%
Table 1. Main chemical components of stainless steel dust
TFe Cr2O3 CaO SiO2 MgO Al2O3 Na2O K2O ZnO Ni S P C 其他 39.0 13.70 11.40 4.10 2.90 0.88 0.87 0.63 0.31 1.50 0.17 0.02 1.40 23.12 表 2 不锈钢除尘灰浸出毒性鉴别结果/(mg/L)
Table 2. Extraction toxicity identification results of stainless steel dust
样品危害成分浸出浓度 总铬 Cr6+ 危害成分浓度限值 <15 <5 不锈钢除尘灰 19.40 18.60 表 3 广汇煤元素分析结果/%
Table 3. Elemental analysis results of Guanghui coal
Car Har Oar Nar St, ad 60.86 4.59 14.61 0.84 0.18 表 4 煤基氢冶金回转窑工艺参数
Table 4. Process parameters of coal-based hydrogen metallurgy rotary kiln
项目 工艺参数 高温段温度/℃ 1 250 在窑时间/h 3 投料量/ (t/h) 5.9 残炭量/ (t/h) 1.8 抛煤量/ (t/h) 0.6 表 5 磁性金属料化学成分/%
Table 5. Chemical composition of magnetic metallized materials
TFe MFe SiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 S P Cr2O3 Ni C 49.10 36.95 16.99 10.72 2.85 9.06 1.25 0.10 4.30 0.66 1.72 表 6 非磁性金属料化学成分/%
Table 6. Chemical composition of non-magnetic metallized materials
TFe Si Al P Cr Ni 75.70 0.33 0.98 0.06 15.50 3.00 表 7 残炭化学成分/%
Table 7. Chemical composition of carbon residues
C TFe SiO2 CaO MgO Al2O3 S Cr2O3 Ni 87.31 4.29 2.67 2.01 0.89 1.34 0.38 1.06 0.05 表 8 布袋除尘灰化学成分/%
Table 8. Chemical composition of bag dust
TFe SiO2 CaO K2O Na2O ZnO Cr2O3 Ni C 8.50 2.23 4.00 16.32 14.45 11.02 3.75 0.18 1.48 表 9 各物料浸出毒性鉴别结果/(mg/L)
Table 9. Identification results of extraction toxicity of each material
样品危害成分浸出浓度 总铬 Cr6+ 危害成分浓度限值 <15 <5 非磁性金属料 0.16 0.03 磁性金属料 1.21 0.62 残炭 0.52 0.05 布袋灰 0.14 0.06 -
[1] 宋海琛, 彭兵. 不锈钢粉尘综合利用现状及研究进展[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2004(3): 18-22.SONG H C, PENG B. Status and research progress of comprehensive utilization of stainless steel dust[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2004(3): 18-22.
SONG H C, PENG B. Status and research progress of comprehensive utilization of stainless steel dust[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2004(3): 18-22.
[2] 李具仓. 不锈钢除尘灰的再生利用[J]. 钢铁研究学报, 2013(8): 19-23.LI J C. Recycling and utilization of stainless steel dust[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research. 2013(8): 19-23.
LI J C. Recycling and utilization of stainless steel dust[J]. Journal of Iron and Steel Research. 2013(8): 19-23.
[3] 刘卫东. 不锈钢除尘灰的再利用研究与实践[J]. 炼钢, 2011(6):66-69.LIU W D. Research and practice of reuse of stainless steel dust[J]. Steel Making, 2011(6):66-69.
LIU W D. Research and practice of reuse of stainless steel dust[J]. Steel Making, 2011(6):66-69.
[4] 李晨晓, 王书桓, 赵定国, 等. 石灰石微观形貌对其煅烧后物化性能影响[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(1):184-187.LI C X, WANG S H, ZHAO D G, et al. Effect of microscopic morphology of limestone on its physical and chemical properties after calcining[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):184-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.037
LI C X, WANG S H, ZHAO D G, et al. Effect of microscopic morphology of limestone on its physical and chemical properties after calcining[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):184-187. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.037
[5] 王烨敏, 匡亚莉. 柔性空气室跳汰机的性能及应用研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(2):97-101.WANG Y M, KUANG Y L. Research on performance and application of flexible air chamber jig[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(2):97-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.018
WANG Y M, KUANG Y L. Research on performance and application of flexible air chamber jig[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(2):97-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.02.018
[6] 张小兵, 王明华, 寇明月. 煤基氢冶金绿色短流程制钢新工艺探索性实验研究[J]. 矿冶工程, 2021, 41(6):174-177.ZHANG X B, WANG M H, KOU M Y. Exploratory test research on a new green short-process steelmaking process for coal-based hydrogen metallurgy[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2021, 41(6):174-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2021.06.042
ZHANG X B, WANG M H, KOU M Y. Exploratory test research on a new green short-process steelmaking process for coal-based hydrogen metallurgy[J]. Mining and Metallurgical Engineering, 2021, 41(6):174-177. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-6099.2021.06.042
[7] 汪金生, 吕炜, 赖平生, 等. 高铬型钒钛磁铁矿中铬氧化物还原热力学影响因素分析[J]. 中国科技论文, 2016(11):2509-2513.WANG J S, LYU Y, LAI P S, et al. Analysis of thermodynamic affecting factors on the reduction of chromium oxide in vanadium titanomagnetite with high chromium[J]. Chinese Scientific Papers, 2016(11):2509-2513. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2016.21.020
WANG J S, LYU Y, LAI P S, et al. Analysis of thermodynamic affecting factors on the reduction of chromium oxide in vanadium titanomagnetite with high chromium[J]. Chinese Scientific Papers, 2016(11):2509-2513. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-2783.2016.21.020
[8] 邱柏欣, 顾幸勇, 董伟霞, 等. 烧成温度对铬铁渣性能影响与表征[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(1):188-193.QIU B X, GU X Y, DONG W X, et al. Effect of firing temperatures on properties of ferrochromium slag and its characterization[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):188-193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.038
QIU B X, GU X Y, DONG W X, et al. Effect of firing temperatures on properties of ferrochromium slag and its characterization[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(1):188-193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.01.038
[9] Ihsan Barin, Ottmar Knacke. Thermochemical properties of inorganic substances[M]. 1973: 212-416.
[10] Ihsan Barin, Ottmar Knacke, Oswald Kubaschewski. Thermochemical properties of inorganic substances Supplement[M]. 1977: 135-166.
[11] 方觉非高炉炼铁工艺与理论[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社. 27-29.FANG J. Non-blast furnace ironmaking process and theory [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press. 27-29.
FANG J. Non-blast furnace ironmaking process and theory [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press. 27-29.
[12] 黄希祜. 钢铁冶金原理[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1990.78-80.HUANG X H. The principle of iron and steel metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1990: 78-80.
HUANG X H. The principle of iron and steel metallurgy [M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1990: 78-80.
-



 下载:
下载: