Absorption and Transport of Heavy Metals Copper and Cadmium in Alfalfa from Vanadium-titanium Magnetite Tailings
-
摘要:
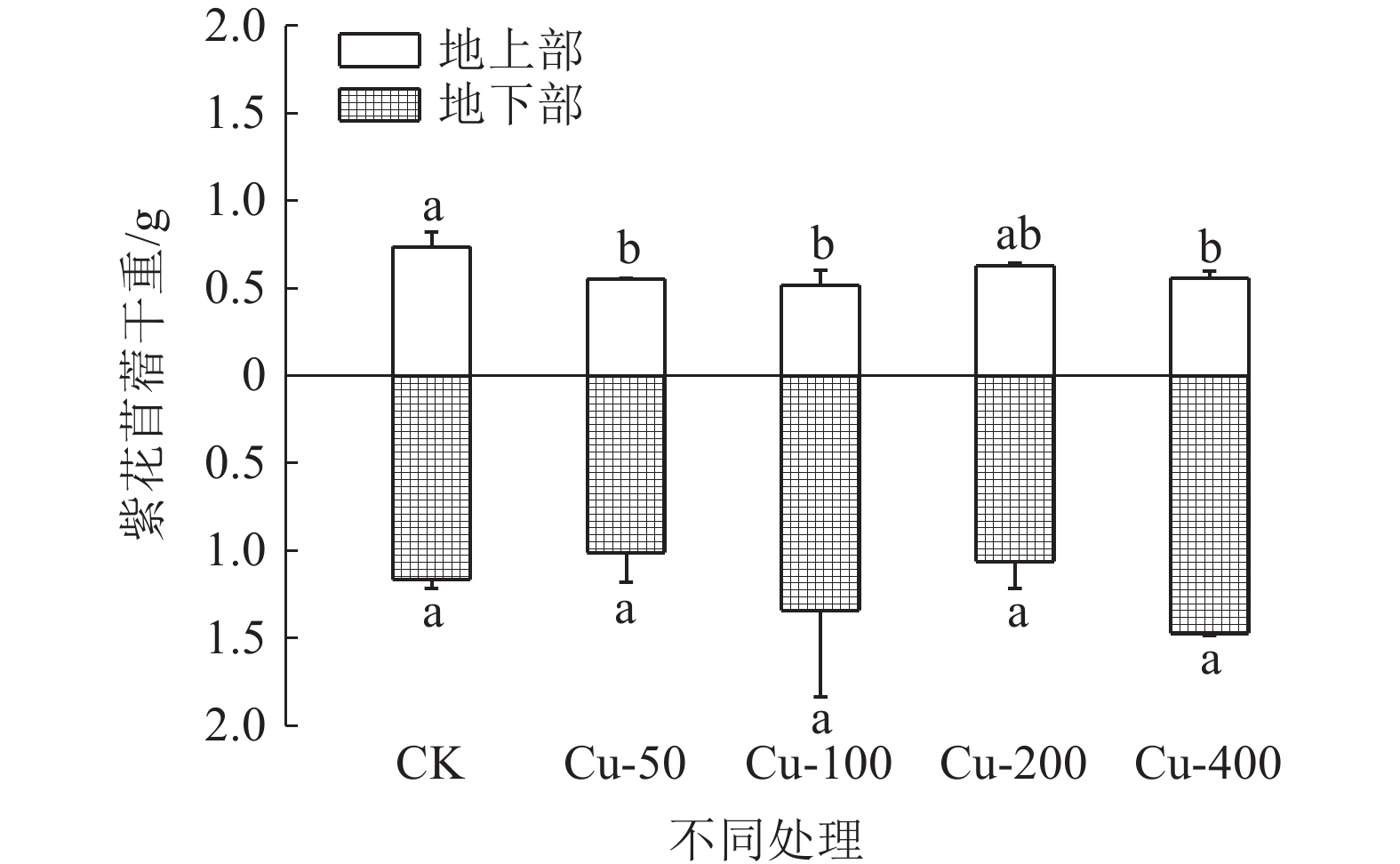
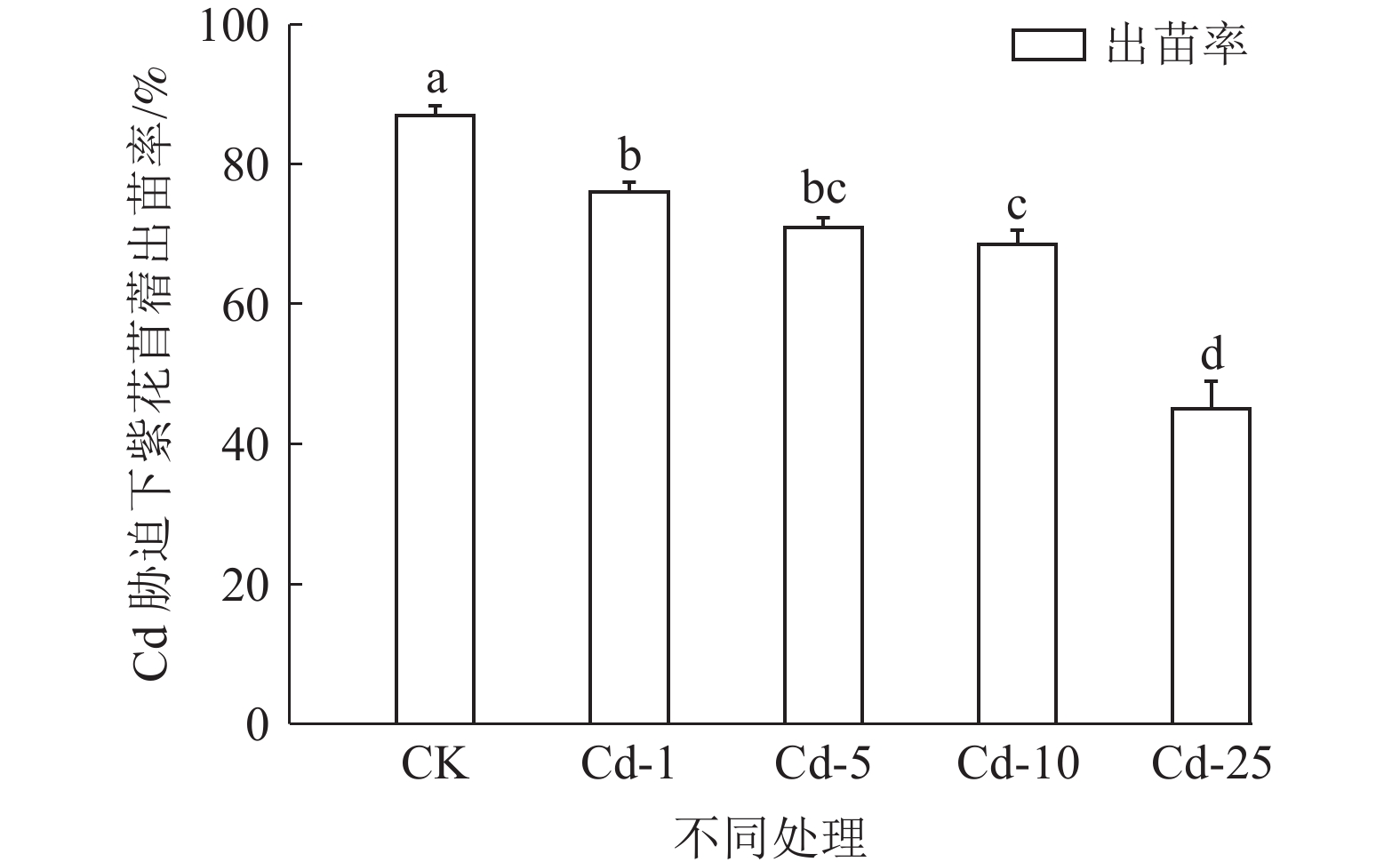
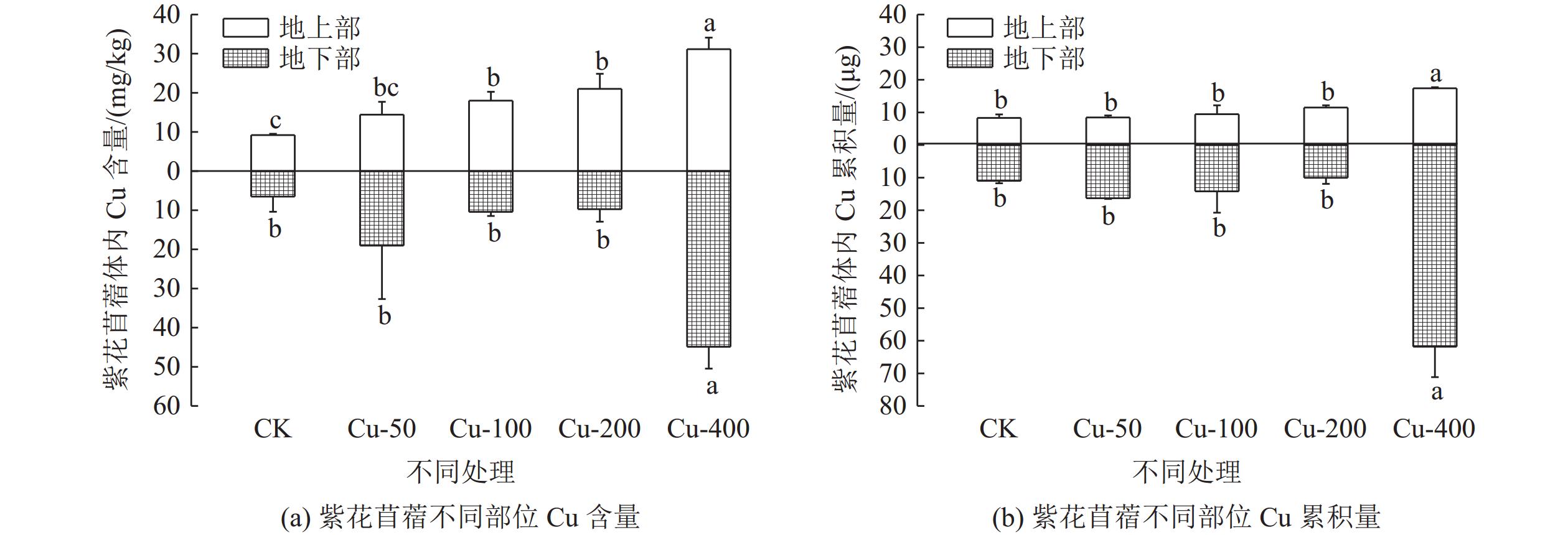
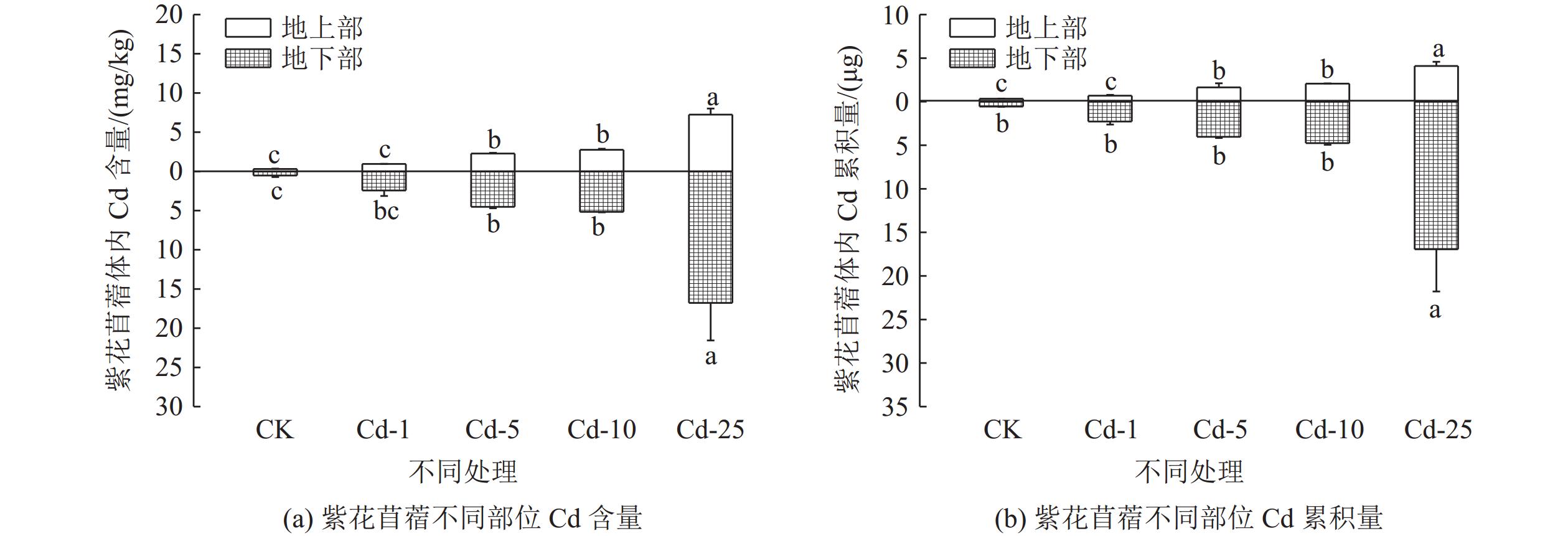
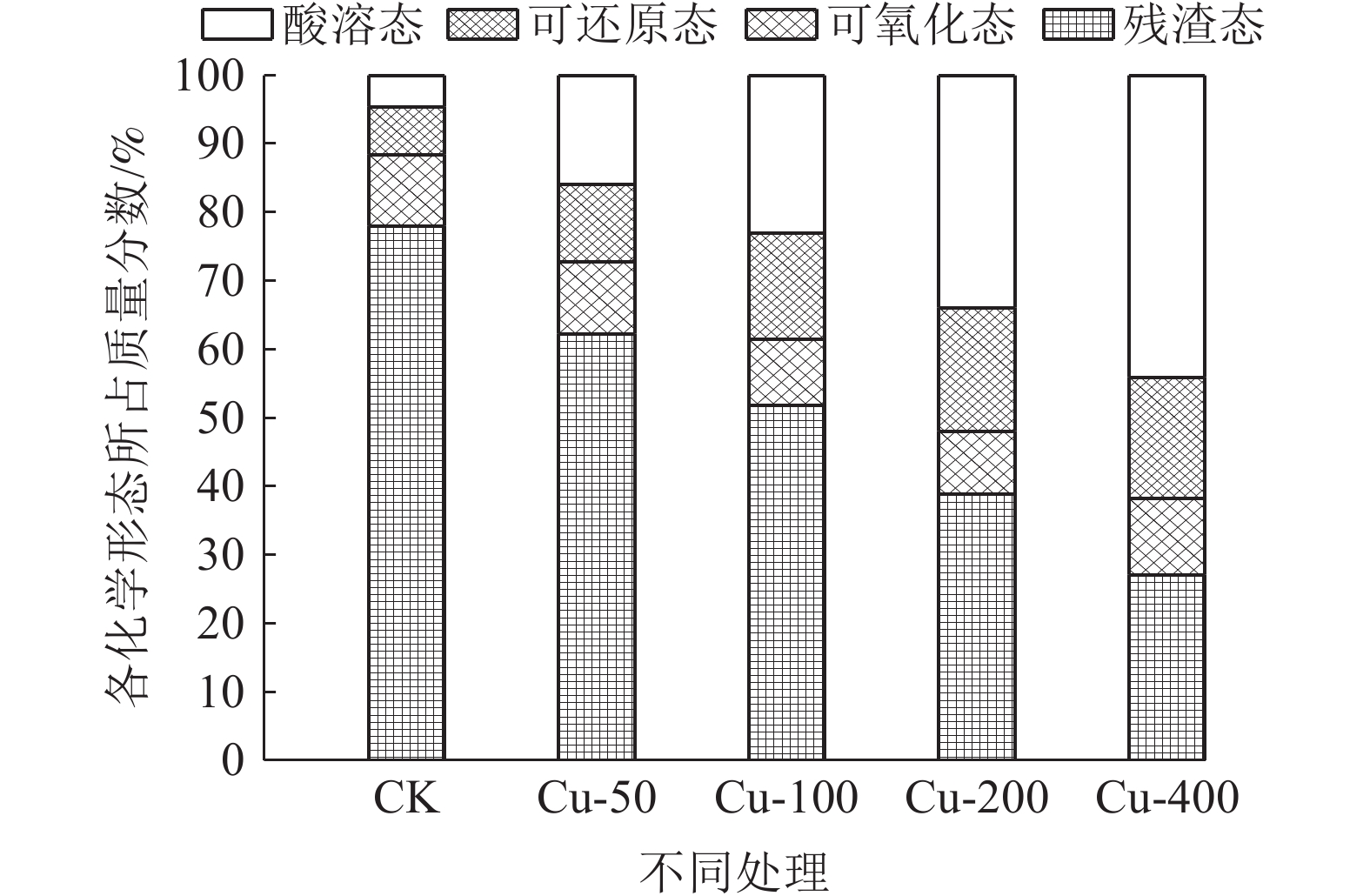
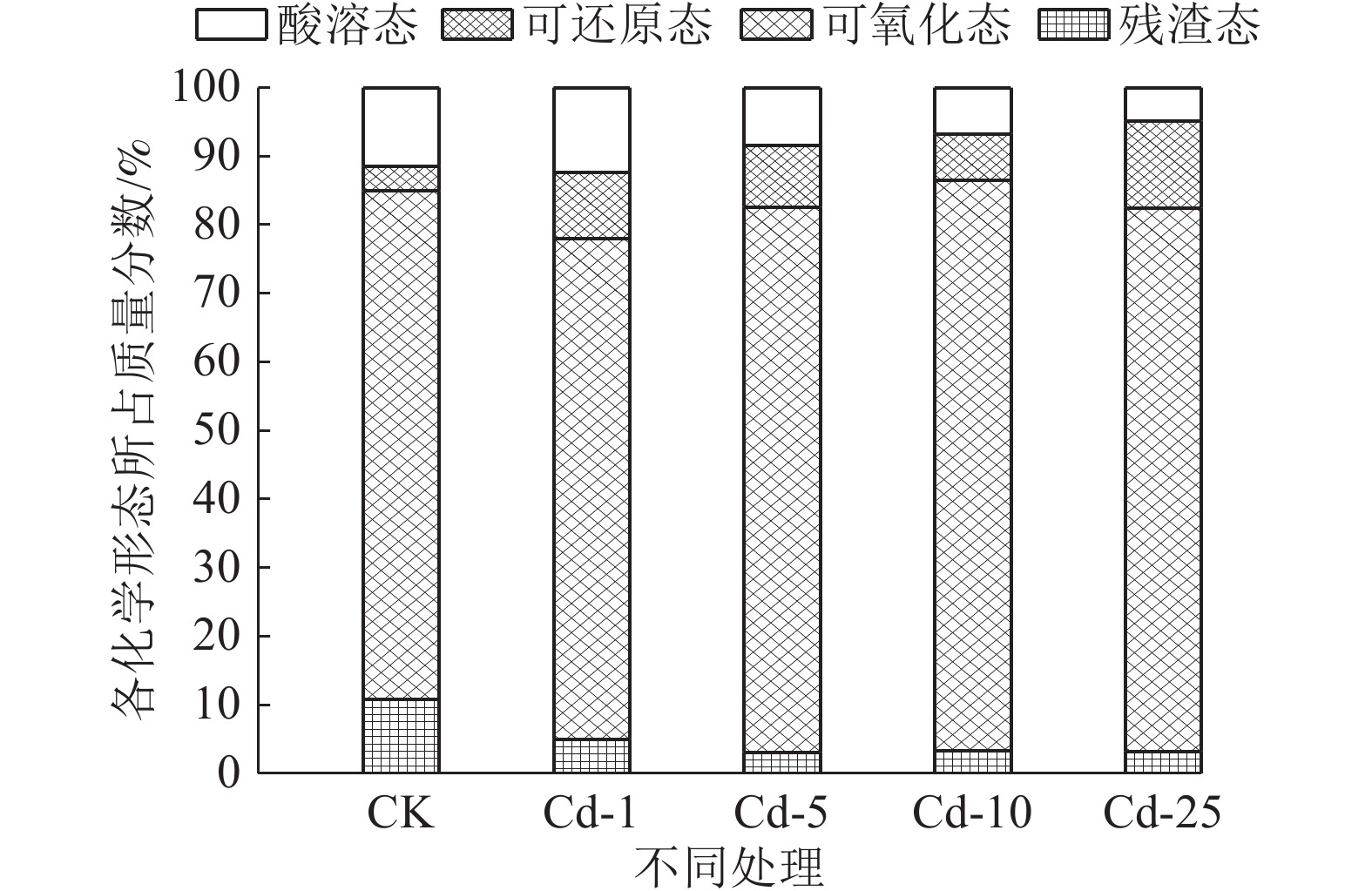
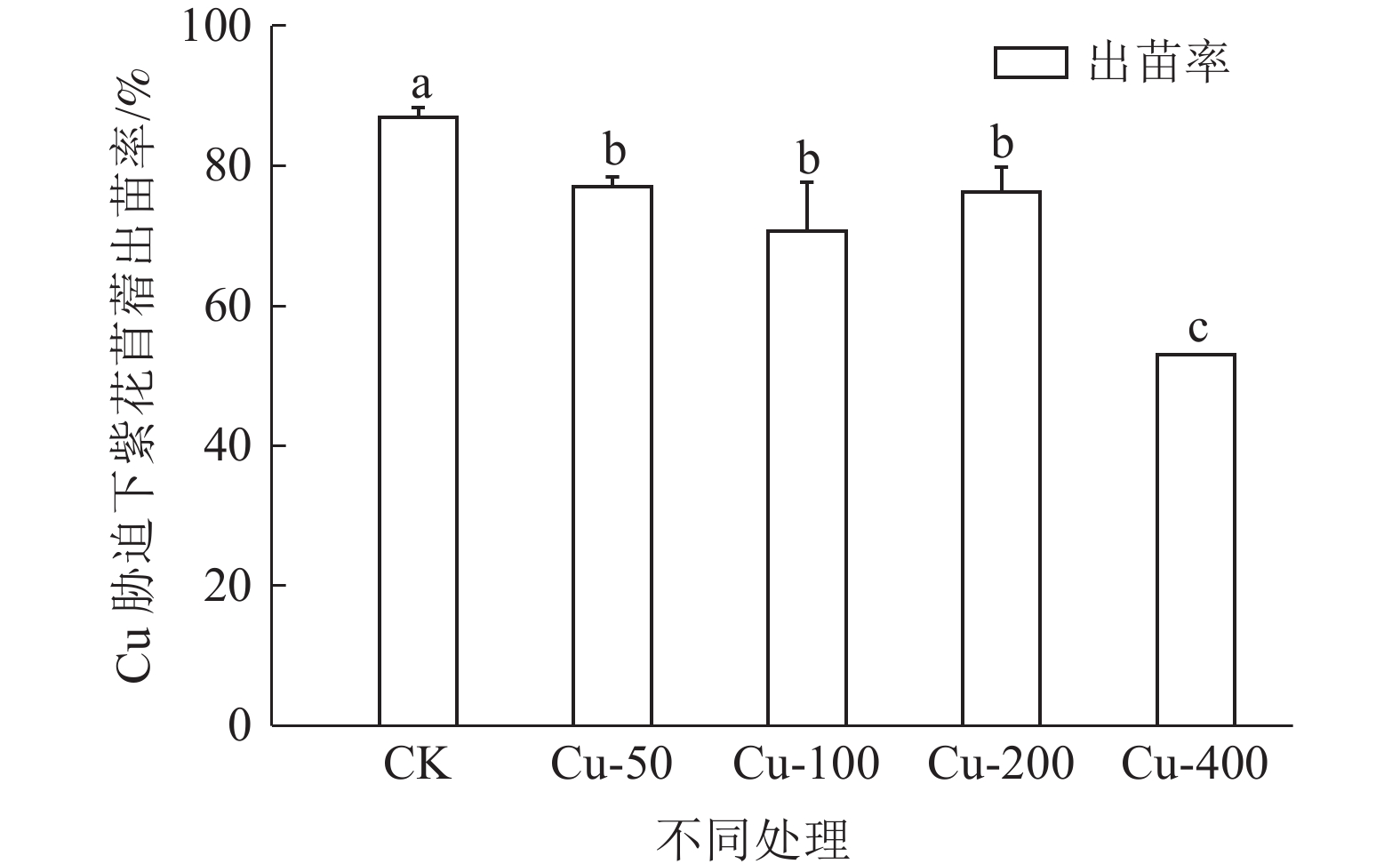
对矿山废弃地进行生态修复时会广泛应用植物修复,植物吸收尾矿重金属的能力不容小觑。为探究紫花苜蓿对钒钛磁铁尾矿重金属Cu和Cd的吸收特性,通过外源添加Cu和Cd到钒钛磁铁尾矿中模拟不同污染程度,并分析三个月后钒钛磁铁尾矿中Cu和Cd的赋存形态、紫花苜蓿长势及其体内对Cu和Cd吸收、转运情况,研究Cu和Cd胁迫下紫花苜蓿重金属的吸收、转运特性。结果表明,三个月后,Cu主要以酸溶态形式存在,Cd主要以可氧化态形式存在,生态风险都比较高。Cu的加入会抑制紫花苜蓿出苗及地上部生长,但紫花苜蓿对Cu的吸收量会显著增加,紫花苜蓿地上部地下部对Cu吸收量分别增加了1.78%~109.62%和48.46%~463.11%,地上部是Cu主要富集部位。Cd主要累积在紫花苜蓿根部,随着Cd胁迫浓度的增加紫花苜蓿从根部向地上部转移Cd能力会增强。研究结果可为矿区植物修复研究提供理论基础。
Abstract:Phytoremediation technology is widely used in ecological restoration process of abandoned mines, and the ability of plants to absorb heavy metals should be taken into account. In order to explore the absorption characteristics of Cu and Cd in the tailings of vanadium-titanium magnetite by the restoration plant alfalfa, Cu and Cd were added externally to the tailings to simulate different pollution levels. After three months, the occurrence forms of Cu and Cd in vanadium-titanium magnetite tailings, the growth of alfalfa and the absorption and transport of Cu and Cd in alfalfa were analyzed to study the absorption and transport characteristics of alfalfa under Cu and Cd stress. The results showed that after three months, Cu mainly existed in acid-soluble form and Cd mainly existed in oxidizable form, the ecological risk was relatively high. The addition of Cu could inhibit the emergence and shoot growth of alfalfa, but the uptake of Cu by alfalfa increased significantly. The uptake of Cu by the shoot and the ground increased by 1.78%~109.62% and 48.46%~463.11%, respectively. The shoot was the main enrichment site of Cu. Cd was mainly accumulated in the roots of alfalfa. With the increase of Cd stress concentration, the ability of alfalfa to transfer Cd from root to shoot increased. The results can provide a theoretical basis for the study of phytoremediation technology in mining areas.
-

-
表 1 实验材料部分理化性质/(mg/kg)
Table 1. Partical physical and chemical properties of materials
pH值 碱解氮 速效磷 全量重金属 Cu Zn Pb Cd Cr 尾矿 8.09 1.08 2.13 254.54 336.87 124.11 0.25 541.19 土壤环境质量标准 >7.5 - - 100 300 170 0.6 250 表 2 尾矿重金属元素的添加量
Table 2. Amounts of heavy metal elements added to tailings
种类 化合物 重金属元素添加/(mg/kg) CK 水平1 水平2 水平3 水平4 Cu CuSO4 0 50 100 200 400 Cd CdCl2 0 1 5 10 25 表 3 Cu胁迫下紫花苜蓿不同部位对Cu富集系数及转移系数
Table 3. BCF and TF of different parts of Alfalfa for Cu under Cu stress
地上部富集系数 地下部富集系数 转移系数 CK 0.046±0.007 9b 0.035±0.002 4b 1.69±0.096a Cu-50 0.063±0.000 95a 0.10±0.027a 0.66±0.16a Cu-100 0.051±0.002 6b 0.031±0.005 6b 1.75±0.040a Cu-200 0.044±0.001 4b 0.024±0.001 0b 1.20±0.33a Cu-400 0.067±0.000 79a 0.097±0.011a 0.70±0.089a 注:图中字母表示显著性差异,地上部、地下部单独比较。 表 4 Cd胁迫紫花苜蓿不同部位对Cd富集系数及转移系数
Table 4. BCF and TF of different parts of Alfalfa for Cd under Cd stress
地上部富集系数 地下部富集系数 转移系数 CK 0.47±0.062b 0.65±0.016b 0.60±0.06a Cd-1 0.57±0.027a 1.87±0.33a 0.47±0.10a Cd-5 0.51±0.028ab 0.96±0.056b 0.53±0.060a Cd-10 0.43±0.0055b 0.78±0.027b 0.47±0.10a Cd-25 0.48±0.030b 1.10±0.27b 0.44±0.08a 注:图中字母表示显著性差异,地上部、地下部单独比较 -
[1] 郝建璋, 曾冠武. 钒钛磁铁矿铁、钒、钛一步分离试验[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(6):73-78.HAO J Z, ZENG G W. New technique for the separation of iron, vanadium and titanium in vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6):73-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.06.013
HAO J Z, ZENG G W. New technique for the separation of iron, vanadium and titanium in vanadium titanium magnetite[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6):73-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.06.013
[2] 印万忠, 徐东, 杨耀辉, 等. 承德某钒钛磁铁矿尾矿资源化利用技术研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(6):37-42.YIN W Z, XU D, YANG Y H, et al. Research on the recycling technology for a vanadium- titanium magnetite tailings in Chengde[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6):37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.06.007
YIN W Z, XU D, YANG Y H, et al. Research on the recycling technology for a vanadium- titanium magnetite tailings in Chengde[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6):37-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.06.007
[3] 陈杜娟, 王志丰, 王婷霞. 某尾矿综合回收选矿实验研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(1):104-108.CHEN D J, WANG Z F, WANG T X. Experimental study on comprehensive recovery and beneficiation of tailings[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):104-108.
CHEN D J, WANG Z F, WANG T X. Experimental study on comprehensive recovery and beneficiation of tailings[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(1):104-108.
[4] 包扬, 苏德, 杨巍, 等. 铜尾矿库土壤修复效应及周边植被恢复模式研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2022(1):74-81.BAO Y, SU D, YANG W, et al. Study on soil remediation effect of copper tailings pond and surrounding vegetation restoration model[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(1):74-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2022.01.010
BAO Y, SU D, YANG W, et al. Study on soil remediation effect of copper tailings pond and surrounding vegetation restoration model[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2022(1):74-81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2022.01.010
[5] 刘应冬, 徐力, 王先达, 等. 攀枝花钒钛磁铁矿尾矿中主要金属元素淋滤浸出行为研究[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2020(6):84-90.LIU Y D, XU L, WANG X D, et al. Study on leaching behavior of main metal elements from Panzhihua vanadium-titanium magnetite tailings[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6):84-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.06.015
LIU Y D, XU L, WANG X D, et al. Study on leaching behavior of main metal elements from Panzhihua vanadium-titanium magnetite tailings[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2020(6):84-90. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2020.06.015
[6] 张英英, 施志国, 李彦荣, 等. 施用改良剂对重度镉胁迫下甜高粱重金属吸收和转运的调控效应[J]. 西南农业学报, 2021, 34(9):1959-1968.ZHANG Y Y, SHI Z G, LI Y R, et al. Effects of amendments on heavy metal uptake and transport in sorghum bicolor L. under severe cadmium stress[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(9):1959-1968.
ZHANG Y Y, SHI Z G, LI Y R, et al. Effects of amendments on heavy metal uptake and transport in sorghum bicolor L. under severe cadmium stress[J]. Southwest China Journal of Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 34(9):1959-1968.
[7] 艾艳君, 卢赛, 李富平, 等. 施加污泥堆肥对铅锌尾矿中黑麦草长势及重金属稳定性影响[J]. 矿产综合利用, 2021(4):29-35.AI Y J, LU S, LI F P, et al. Effect of sewage sludge compost addition on stabilization of heavy metal and growth of ryegrass in lead/zinc tailings[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(4):29-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.04.005
AI Y J, LU S, LI F P, et al. Effect of sewage sludge compost addition on stabilization of heavy metal and growth of ryegrass in lead/zinc tailings[J]. Multipurpose Utilization of Mineral Resources, 2021(4):29-35. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6532.2021.04.005
[8] YANQUN Z, YUAN L, SCHVARTZ C, et al. Accumulation of Pb, Cd, Cu and Zn in plants and hyperaccumulator choice in Lanping lead-zinc mine area, China[J]. Environment international, 2004, 30(4):567-576.
[9] 牛学奎, 吴学勇, 王薇, 等. 典型鼓风炉铅冶炼废渣堆场周边优势植物重金属富集特征研究[J]. 生态环境学报, 2021, 30(6):1293-1298.NIU X K, WU X Y, WANG W, et al. Study on enrichment characteristics of heavy metals from dominant plants around the waste slag yard of lead smelting in a typical blast furnace[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(6):1293-1298.
NIU X K, WU X Y, WANG W, et al. Study on enrichment characteristics of heavy metals from dominant plants around the waste slag yard of lead smelting in a typical blast furnace[J]. Ecology and Environmental Sciences, 2021, 30(6):1293-1298.
[10] 来思彤, 崔清亮, 刘金龙, 等. 紫花苜蓿茎叶功能特性指标的测定与分析[J]. 食品科学, 2020, 41(7):73-78.LAI S T, CUI Q L, LIU J L, et al. Determination and analysis of functional characteristics of alfalfa steams and leaves[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(7):73-78. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190416-205
LAI S T, CUI Q L, LIU J L, et al. Determination and analysis of functional characteristics of alfalfa steams and leaves[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(7):73-78. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190416-205
[11] NOUAIRI, MRABET, RABHI, et al. Cu tolerant Sinorhizobium meliloti strain is beneficial for growth, Cu accumulation, and mineral uptake of alfalfa plants grown in Cu excess[J]. Archives of Agronomy and Soil Science, 2015, 61(12):1707-1718. doi: 10.1080/03650340.2015.1036043
[12] 张杨杨, 李希铭, 高鹏, 等. 不同浓度镉胁迫下6种草本植物的耐性及富集特征的比较[J]. 草地学报, 2021, 29(6):1265-1276.ZHANG Y Y, LI X M, GAO P, et al. Comparison of tolerance and enrichment characteristic for six herbaceous plant under different levels Cd stress[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(6):1265-1276.
ZHANG Y Y, LI X M, GAO P, et al. Comparison of tolerance and enrichment characteristic for six herbaceous plant under different levels Cd stress[J]. Acta Agrestia Sinica, 2021, 29(6):1265-1276.
[13] 李大乐, 陈建文, 张红, 等. 铜污染对土壤细菌群落结构及重金属抗性基因的影响[J]. 环境科学学报, 2021, 41(3):1082-1090.LI D L, CHEN J W, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of copper pollution on soil bacterial community structure and heavy-metal resistance genes[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(3):1082-1090.
LI D L, CHEN J W, ZHANG H, et al. Effects of copper pollution on soil bacterial community structure and heavy-metal resistance genes[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae, 2021, 41(3):1082-1090.
[14] 迟晓杰. 基于高光谱遥感的紫花苜蓿修复金属尾矿效果研究[D]. 唐山: 华北理工大学, 2020.CHI X J. The remediation effect of alfalfa on mine tailings based on hyperspectral remote sensing[D]. Tangshan: North China University of Science and Technology, 2020.
CHI X J. The remediation effect of alfalfa on mine tailings based on hyperspectral remote sensing[D]. Tangshan: North China University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[15] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析[M]. 第3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000.BAO S D. Soil agrochemical analysis [M]. 3th Edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000.
BAO S D. Soil agrochemical analysis [M]. 3th Edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000.
[16] CAPPUYNS V, SWENNEN R, NICLAES M, Application of the BCR sequential extraction scheme to dredged pond sediments contaminated by Pb–Zn mining: A combined geochemical and mineralogical approach[J]. Geochem Explor, 2007, 93, 78–90.
[17] 孙厚云, 卫晓锋, 孙晓明, 等. 钒钛磁铁矿尾矿库复垦土地及周边土壤-玉米重金属迁移富集特征[J]. 环境科学, 2021, 42(3):1166-1176.SUN H Y, WEI X F, SUN X M, et al. Bioaccumulation and translocation characteristics of heavy metals in a Soil-Maize system in reclaimed land and surrounding areas of typical Vanadium-Titanium magnetite tailings[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3):1166-1176.
SUN H Y, WEI X F, SUN X M, et al. Bioaccumulation and translocation characteristics of heavy metals in a Soil-Maize system in reclaimed land and surrounding areas of typical Vanadium-Titanium magnetite tailings[J]. Environmental Science, 2021, 42(3):1166-1176.
[18] KOBRA M, SEYED MAJID G, TORKZADEH M M. Accumulation and phytoremediation of Pb, Zn and Ag by plants growing on Koshk lead–zinc mining area, Iran[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments, 2017, 17(5):1310-1320.
[19] 张志飞, 龚梨霞, 文昭竹, 等. 酸铜对紫花苜蓿种子萌发及根系生长的影响[J]. 中国草地学报, 2017, 39(3):72-76.ZHANG Z F, GONG L X, WEN Z Z, et al. Effect of acid-copper stress on seed germination and root growth of medicago sativa[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2017, 39(3):72-76.
ZHANG Z F, GONG L X, WEN Z Z, et al. Effect of acid-copper stress on seed germination and root growth of medicago sativa[J]. Chinese Journal of Grassland, 2017, 39(3):72-76.
[20] 朱剑飞, 李铭红, 谢佩君, 等. 紫花苜蓿、黑麦草和狼尾草对Cu、Pb复合污染土壤修复能力的研究[J]. 中国生态农业学报, 2018, 26(2):303-313.ZHU J F, LI M H, XIE P J, et al. Phytoremediation of single and combined pollution of Cu and Pb by Medicago sativa, Lolium perenne, and Pennisetum alopecuroides[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco- Agriculture, 2018, 26(2):303-313.
ZHU J F, LI M H, XIE P J, et al. Phytoremediation of single and combined pollution of Cu and Pb by Medicago sativa, Lolium perenne, and Pennisetum alopecuroides[J]. Chinese Journal of Eco- Agriculture, 2018, 26(2):303-313.
[21] 付川, 余顺慧, 黄怡民, 等. 紫花苜蓿对铜胁迫生理响应的傅里叶变换红外光谱法研究[J]. 生态学报, 2014, 34(5):1149-1155.FU C, YU S H, HUANG Y M, et al. Physiological response of Medicago sativa L. to copper stress by FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(5):1149-1155.
FU C, YU S H, HUANG Y M, et al. Physiological response of Medicago sativa L. to copper stress by FTIR spectroscopy[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica, 2014, 34(5):1149-1155.
[22] LU T, KE M, LAVOIE M, et al. Rhizosphere microorganisms can influence the timing of plant flowering[J]. Microbiome, 2018, 6(1):231.
[23] 许敏, 韩玉林, 原海燕, 等. 添加铜尾矿矿砂的栽培基质对黄花苜蓿幼苗生长及部分生理指标的影响[J]. 植物资源与环境学报, 2014, 23(2):74-79.XU M, HAN Y L, YUAN H Y, et al. Effects of culture substrate added with copper tailing sand on growth and some physiological indexes of Medicago falcata seedlings[J]. Journal of Plants Resources and Environment, 2014, 23(2):74-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2014.02.11
XU M, HAN Y L, YUAN H Y, et al. Effects of culture substrate added with copper tailing sand on growth and some physiological indexes of Medicago falcata seedlings[J]. Journal of Plants Resources and Environment, 2014, 23(2):74-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7895.2014.02.11
[24] 张丽萍, 沈亚婷. 紫花苜蓿对铜的吸收、积累和耐受机制研究[J]. 分析化学, 2017, 45(8):1129-1136.ZHANG L P, SHEN Y T. Study on copper absorption, accumulation and tolerance mechanism of alfalfa[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 45(8):1129-1136. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.170124
ZHANG L P, SHEN Y T. Study on copper absorption, accumulation and tolerance mechanism of alfalfa[J]. Chinese Journal of Analytical Chemistry, 2017, 45(8):1129-1136. doi: 10.11895/j.issn.0253-3820.170124
[25] LIU J J, WEI Z, LI J H. Effects of copper on leaf membrane structure and root activity of maize seedling[J]. Botanical Studies, 2014, 55:47. doi: 10.1186/s40529-014-0047-5
[26] 刘大林, 王秀萍, 胡楷崎, 等. 土壤镉含量对高粱属植物生理生化特性的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2011, 30(11):2478-2482.LIU D L, WANG X P, HU K Q, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on the physiological and biochemical indices of sorghum plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2011, 30(11):2478-2482.
LIU D L, WANG X P, HU K Q, et al. Effects of cadmium stress on the physiological and biochemical indices of sorghum plants[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2011, 30(11):2478-2482.
[27] 保琼莉, 唐一然, 保万魁, 等. 镉对不同品种苜蓿种子萌发及幼苗生长的影响[J]. 生态学杂志, 2020, 39(5):1695-1705.BAO Q L, TANG Y R, BAO W K, et al. Effects of cadmium on seed germination and seedling growth of different alfalfa varieties[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(5):1695-1705.
BAO Q L, TANG Y R, BAO W K, et al. Effects of cadmium on seed germination and seedling growth of different alfalfa varieties[J]. Chinese Journal of Ecology, 2020, 39(5):1695-1705.
[28] EJAZUL I, MUHAMMAD T K, SAMRA I S, et al. Biochemical mechanisms of signaling: Perspectives in plants under arsenic stress[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015, 114:126-133. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2015.01.017
[29] 周鹏飞, 张世文, 罗明, 等. 矿业废弃地不同生态修复模式下植物多样性及重金属富集迁移特征[J]. 环境科学, 2022, 43(2):985-994.ZHOU P F, ZHANG S W, LUO M, et al. Characteristics of plant diversity and heavy metal enrichment and migration under different ecological restoration modes in abandoned mining areas[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(2):985-994.
ZHOU P F, ZHANG S W, LUO M, et al. Characteristics of plant diversity and heavy metal enrichment and migration under different ecological restoration modes in abandoned mining areas[J]. Environmental Science, 2022, 43(2):985-994.
[30] 李希铭, 宋桂龙. 镉胁迫对紫花苜蓿镉吸收特征及根系形态影响[J]. 草业学报, 2016, 25(2):178-186.LI X M, SONG G L. Cadmium uptake and root morphological changes in Medicago sativa under cadmium stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2):178-186. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2015401
LI X M, SONG G L. Cadmium uptake and root morphological changes in Medicago sativa under cadmium stress[J]. Acta Prataculturae Sinica, 2016, 25(2):178-186. doi: 10.11686/cyxb2015401
[31] 尹国丽, 师尚礼, 寇江涛, 等. Cd胁迫对紫花苜蓿种子发芽及幼苗生理生化特性的影响[J]. 西北植物学报, 2013, 33(8):1638-1644.YIN G L, SHI S L, KOU J T, et al. Seed germination and physiological and biochemical characteristics of alfalfa under cadmium Stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2013, 33(8):1638-1644. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2013.08.1638
YIN G L, SHI S L, KOU J T, et al. Seed germination and physiological and biochemical characteristics of alfalfa under cadmium Stress[J]. Acta Botanica Boreali-Occidentalia Sinica, 2013, 33(8):1638-1644. doi: 10.7606/j.issn.1000-4025.2013.08.1638
-



 下载:
下载: