Comprehensive Evaluation of Groundwater Dependent Ecosystems in the Surrounding Area of Dongting Lake
-
摘要:
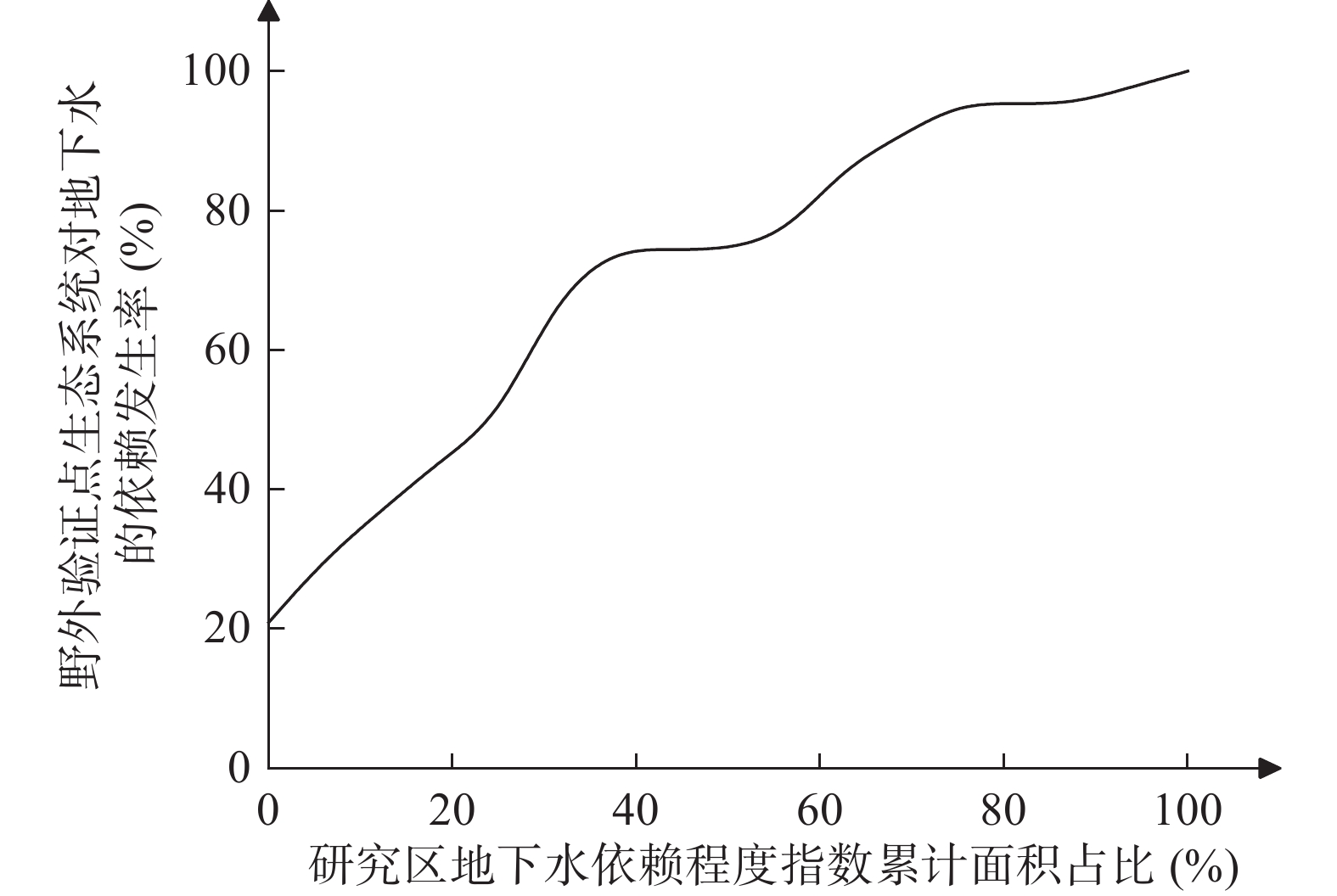
为了构建适用于洞庭湖环湖区地下水依赖型生态系统(Groundwater Dependent Ecosystems, GDEs)的综合评价指标体系,本文采用栅格叠加法,通过对多个生态指标的评分计算,建立了一套包括地下水位埋深、植被覆盖度、蒸散发、地形湿度指数及土壤有机碳含量等因子的评价体系。各因子的评分结果在GIS平台上进行空间叠加,得到洞庭湖区域GDEs的综合评价指数,并据此划分不同的依赖程度等级。研究结果表明,洞庭湖环湖区域GDEs的依赖程度差异显著,其中高度依赖地下水的区域主要分布在湖泊北部和西南部的湿地和沼泽地,覆盖率为67.78%。经成功率曲线法检验,评价结果合理,可为洞庭湖地下水资源的可持续管理及生态保护提供科学依据,同时也为其他湿地生态系统的评价和保护提供参考。
-
关键词:
- 地下水依赖型生态系统 /
- 综合评价 /
- GIS /
- 洞庭湖环湖区
Abstract:To construct a comprehensive evaluation index system suitable for Groundwater-Dependent Ecosystems (GDEs) in the Dongting Lake surrounding area, this study adopts a grid overlay method to establish a set of evaluation systems including factors such as groundwater depth, vegetation cover, evapotranspiration, topographic wetness index, and soil organic carbon content, etc., by scoring several ecological indicators. These indicators are spatially integrated on a GIS platform to generate an integrated evaluation index for GDEs in the Dongting Lake region. This enables the classification of varying degrees of groundwater dependency. The results show significant spatial heterogeneity in groundwater dependency levels across the study area. Notably, regions with high groundwater dependency, predominantly in the wetlands and marshes of the northern and southwestern parts of the lake, account for 67.78% of the total area. The evaluation results, validated using the success rate curve method, demonstrate high reliability, offering a robust scientific foundation for the sustainable management of groundwater resources and the ecological conservation of Dongting Lake. Furthermore, this study provides a valuable reference for the assessment and protection of other wetland ecosystems.
-

-
表 1 植被对地下水依赖程度综合指数评价等级划分
Table 1. Classification of comprehensive index for vegetation dependence on groundwater
评价指数 依赖程度分级 Ⅰ(非常低) Ⅱ(低) Ⅲ(中等) Ⅳ(高) Ⅴ(非常高) R R≤1.75 1.75<R≤2.5 2.5<R≤3.25 3.25<R≤4.0 R>4.0 表 2 洞庭湖环湖区GDEs评价指标及其量化分级
Table 2. GDEs evaluation indicators and the quantitative classification in the Dongting Lake surrounding area
评价指标 分级 备注 非常低 低 中等 高 非常高 Ⅰ(1分) Ⅱ(2分) Ⅲ(3分) Ⅳ(4分) Ⅴ(5分) 评分标准按5级分类 地下水位埋深(m) >10 [10,5.7) [5.7,3.7) [3.7,1) ≤1 依据常见地下水位埋深分区,结合植被
与地下水位关系确定植被覆盖度(%) <10 [10,30) [30,45) [45,60) ≥60 依据常用植被覆盖度划分标准 土壤类型 湖泊、
水库等潮土、
水稻土类红壤类 水稻土、
红壤类沼泽土类 根据土壤黏质含量的高低,
将土壤按持水能力由低到高划分蒸散发(mm/d) <5 [5,7.8) [7.8,10.3) [10.3,12.7) ≥12.7 根据数据统计特征,按照自然间断点法划分 地形湿度指数 <6 [6,6.5) [6.5,7) [7,7.5) ≥7.5 根据数据统计特征,按照自然间断点法划分 土壤有机碳(g/kg) <18 [18,21) [21,27) [27,48) ≥48 根据数据统计特征,按照自然间断点法划分 表 3 洞庭湖环湖区植被对地下水依赖程度评价结果图统计
Table 3. Statistical results of vegetation dependence on groundwater evaluation in the Dongting Lake surrounding area
类型 非常低 低 中等 高 非常高 面积(km2) 占比(%) 面积(km2) 占比(%) 面积(km2) 占比(%) 面积(km2) 占比(%) 面积(km2) 占比(%) 0 0 111 0.63 5616 31.59 10558 59.39 1490 8.39 -
[1] 曹思佳,李云良,陈 静,姚 静,赵贵章,李志萍.2023.2022年鄱阳湖极端干旱对洪泛区地下水文情势的影响[J]. 中国环境科学,43(12):6601-6610. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-6923.2023.12.036
[2] 陈立德.2019.江汉—洞庭地区与黄广—九江地区更新统划分与对比[J]. 中国地质调查,6(5):21-27.
[3] 董佳秋,张 俊,顾小凡,高海波,杨 波,杨晓东,赵春光,张铁钢,尹立河,王晓勇.2024.半干旱区流域尺度植被依赖地下水程度评价:以鄂尔多斯高原海流兔河流域为例[J]. 中国地质,51(6):1855-1867. doi: 10.12029/gc20220526002
[4] 高小雲,李 慧.2024.基于地下水依赖型生态系统分布图的全球旱地保护需求研究[J]. 水利水电快报,45(9):4.
[5] 国家质量监督检验检疫总局,中国国家标准化管理委员会.2009.中国土壤分类与代码(GB/T17296-2009)[S].
[6] 金晓媚,张 强,杨春杰.2013.海流兔河流域植被分布与地形地貌及地下水位关系研究[J]. 地学前缘,20(3):227-233.
[7] 李 月,彭 博,林韶恺,李 洋,周 盈,曾剑威.2024.基于景观类型及其生态风险评价的巢湖流域生态安全格局优化建议[J]. 华南地质,40(3):548-558. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0013.2024.03.010
[8] 刘广宁,吴 亚,王世昌,廖 金,余绍文,伏永朋,杜 尧,陈柳竹.2022.长江中游典型河湖湿地主要水环境问题及生态环境地质风险评价区划[J]. 华南地质,38(2):226-239. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2097-0013.2022.02.004
[9] 刘惠良,刘红峰.2021.洞庭湖湿地生物多样性保护的价值评估[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报,41(10):140-147.
[10] 刘 强,梁丽乔.2020.依赖地下水生态系统的生态水文研究评述[J]. 北京师范大学学报(自然科学版),56(5):693-699.
[11] 米湘成,张金屯,张 峰,上官铁梁,李爱华,郑凤英.1999.山西高原植被与土壤分布格局关系的研究[J]. 植物生态学报,23(4):336-344. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-264X.1999.04.006
[12] 吴 林,张鸿辉,王慎敏,周寅康.2005.基于栅格数据空间分析的土地整理生态评价—以江西省南康市凤岗镇为例[J]. 中国土地科学,19(3):24-28. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-8158.2005.03.005
[13] 肖 攀,喻 望,胡光明,赵幸悦子.2017.江汉-洞庭平原地下水功能评价与区划[J]. 人民长江,48(1):6-11+19.
[14] 袁玉洁. 2017. 变化环境下洞庭湖水文情势的演变及湿地保护研究[D]. 湖南大学博士学位论文.
[15] 张彩霞,杨勤科,李 锐.2005.基于DEM的地形湿度指数及其应用研究进展[J]. 地理科学进展,24(6):116-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-6301.2005.06.014
[16] 张绪财,金晓媚,朱晓倩,张 京.2019.格尔木河流域植被指数时空分布及其影响因素研究[J]. 现代地质,33(2):461-468.
[17] 张 燕,尹立河,王旭升,王 浪,王璐晨,张 俊,李福杰,张鹏伟.2024.新疆开孔河流域地下水依赖型植被生态系统的遥感识别[J]. 安全与环境工程,31(4):259-270.
[18] 赵卫东,龚俊豪,赵纪堂,杨文韬,高 飞.2019.顾及平原区微地貌的地形湿度指数及其地表水环境意义[J]. 合肥工业大学学报(自然科学版),42(1):113-118.
[19] 周国逸,熊 鑫.2019.土壤有机碳形成机制的探索历程[J]. 热带亚热带植物学报,27(5):481-490. doi: 10.11926/jtsb.4094
[20] 周 莉,李保国,周广胜.2005.土壤有机碳的主导影响因子及其研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展,20(1):99-105. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-8166.2005.01.016
[21] Liu F, Wu H Y, Zhao Y G, Li D C, Yang J L, Song X D, Shi Z, Zhu A X, Zhang G L. 2022. Mapping high resolution National Soil Information Grids of China[J]. Science Bulletin, 67(3): 328-340. doi: 10.1016/j.scib.2021.10.013
[22] Pandey H K, Singh V K, Singh S K, Sharma S K. 2023. Mapping and validation of groundwater dependent ecosystems (GDEs) in a drought-affected part of Bundelkhand region, India[J]. Groundwater for Sustainable Development, 23(Suppl): P100979.
[23] Rampheri M B, Dube T, Dondofema F, Dalu T. 2023. Identification and delineation of groundwater-dependent ecosystems (GDEs) in the Khakea–Bray transboundary aquifer region using geospatial techniques[J]. Geocarto International, 38(1): 1-24.
[24] Troch P A, Carrillo G, Sivapalan M, Wagener T, Sawicz K. 2013. Climate-vegetation-soil interactions and long-term hydrologic partitioning: signatures of catchment co-evolution[J]. Hydrology and Earth System Sciences, 17(6): 2209-2217. doi: 10.5194/hess-17-2209-2013
-




 下载:
下载: