Magnetic fabric study of the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous strata in Baoji area of Lhasa block
-
摘要:
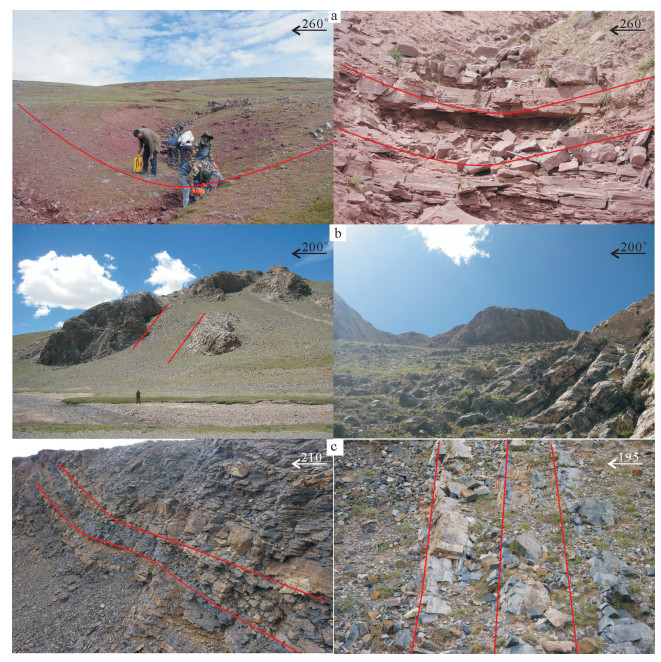
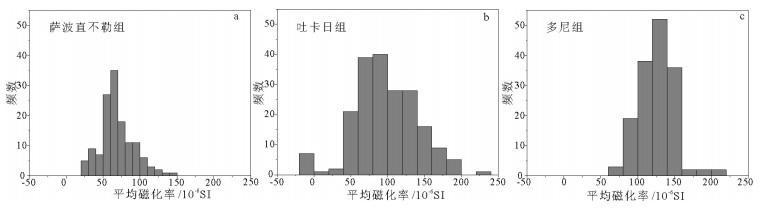
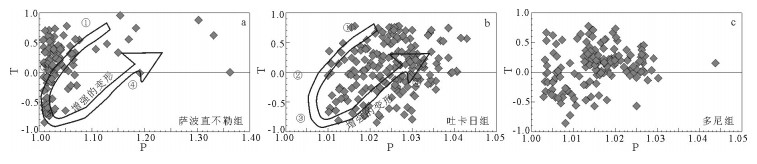
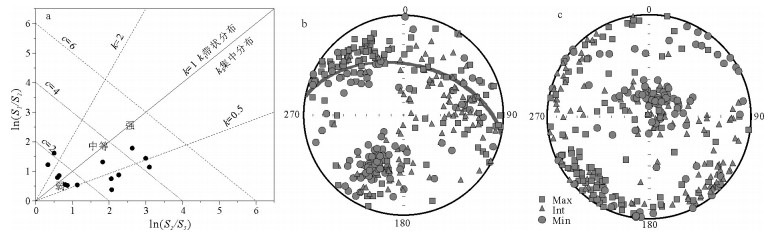
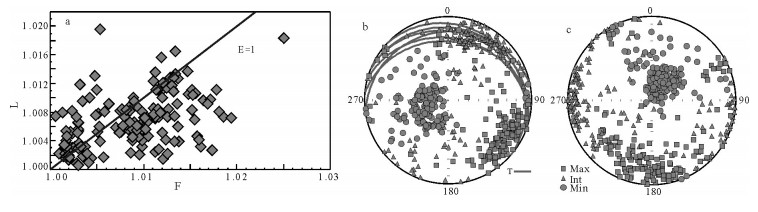
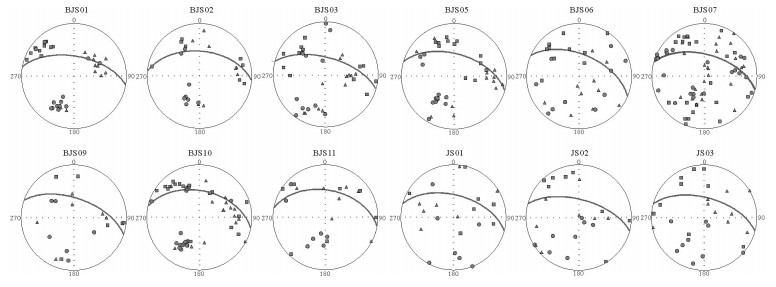
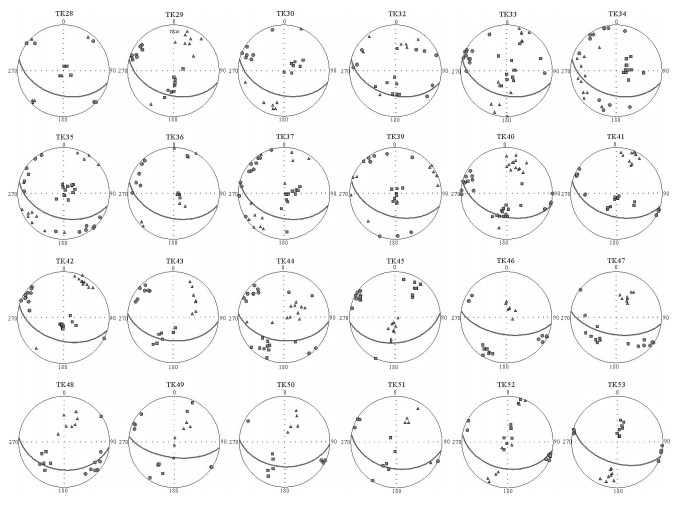
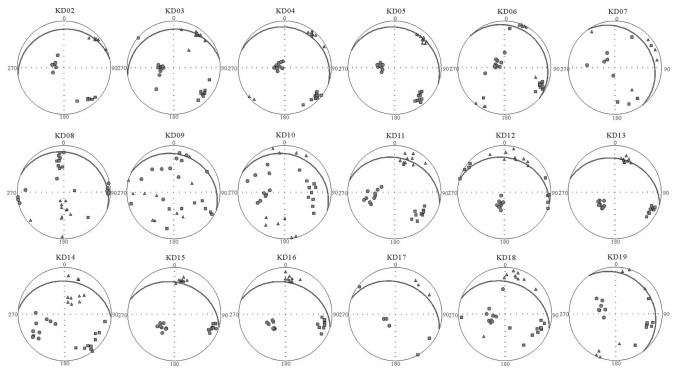
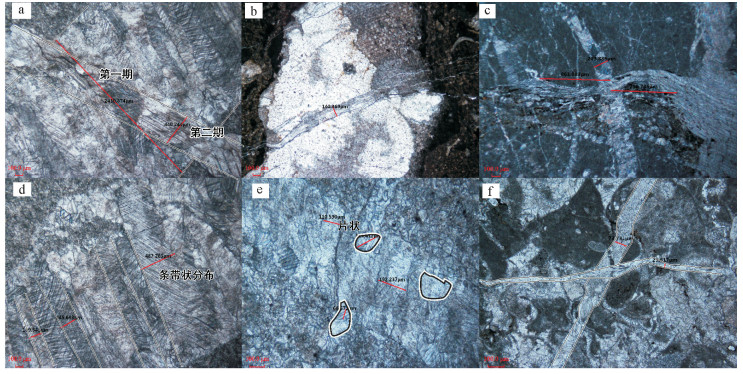
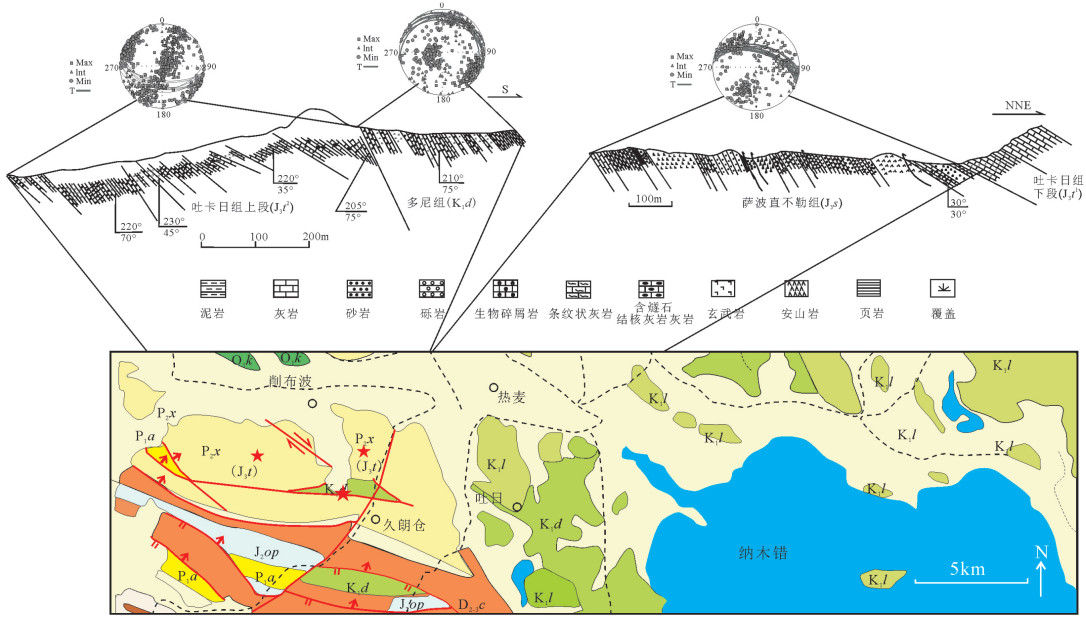
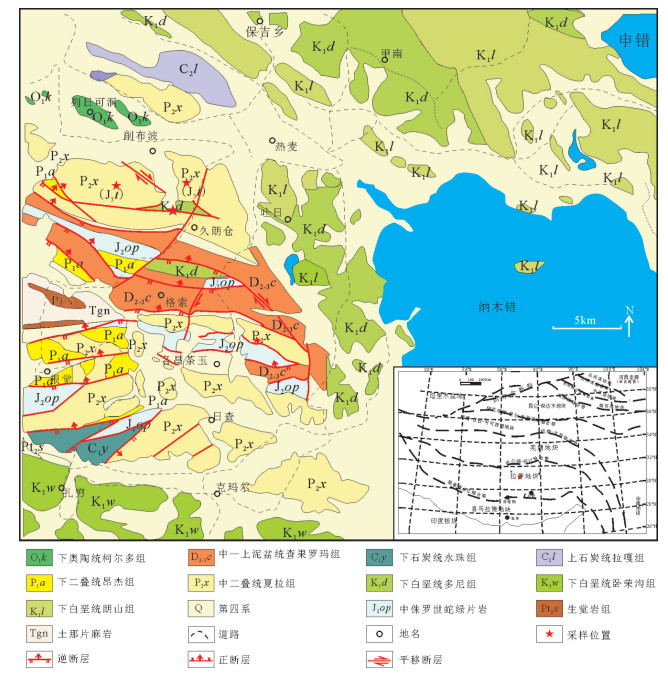
拉萨和羌塘地块拼合形成了青藏高原的核心,但迄今对两者的具体拼合时间仍存在激烈的争论。为进一步寻找约束两者碰撞时限的地质证据,对拉萨地块晚侏罗世-早白垩世地层的磁组构特征进行研究。结果显示:晚侏罗世地层磁组构特征显示其遭遇过较强的构造应力,吐卡日组地层磁化率主轴k1方位与地层面斜交,但经地层校正后,k1方位与区域褶皱方向一致,表明应力方位为北北东-南南西向;萨波直不勒组地层k1方位在地层校正前平行于层面,指示了垂直于主压应力的方向,推断晚侏罗世地层磁组构记录了同一期应力,应力方向均为北北东-南南西向。早白垩世多尼组地层磁组构显示其后期遭受的构造应力场强度弱,且与晚侏罗世应力并非同一期。因此,通过对比晚侏罗世与早白垩世地层的磁组构特征,认为保吉地区晚侏罗世地层磁组构记录了北北东-南南西向较强的构造应力,推断该期应力来源于拉萨-羌塘地块的碰撞拼合事件,而多尼组地层并未受该期应力场的影响,仅记录了区域褶皱隆起时的应力场。
Abstract:The Lhasa and Qiangtang blocks are at the heart of the Tibetan Plateau. However, the time for the specific combination of the two blocks is still in heated controversy. To further find geological evidence that can constrain the time limit between the two blocks, the authors studied the characteristics of the magnetic fabric of the Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous strata in Lhasa block. According to the results obtained, the magnetic structure of Late Jurassic strata encountered strong tectonic stress, and the principal axis k1 of the magnetic susceptibility of the Tukari Formation was oblique to the ground plane. After the stratigraphic correction, the k1 azimuth and regional fold direction consensus indicate that the stress azimuth was NNE-SSW; the k1 orientation of the Sabozhibule Formation was parallel to the plane (NNE-SSW) before the stratigraphic correction, indicating the direction perpendicular to the principal compressive stress and inferring the late tilting. The Late Jurassic formation magnetic structure recorded the same period of stress, and the stress direction was NNE-SSW. The Early Cretaceous Duoni Formation magnetic structure shows that the subsequent tectonic stress field intensity was weak, and was not in the same period as the Late Jurassic stress. Therefore, by comparing the magnetic fabric characteristics of the Late Jurassic and Early Cretaceous strata, the authors concluded that the magnetic fabric of the Late Jurassic in Baoji area recorded a strong tectonic stress in NNE-SSW, and that the stress in this period originated from the LhasaQiangtang block collision event, while the Duoni Formation was not affected by the stress field, only the stress field of the regional fold uplift was recorded.
-
Key words:
- Baoji area /
- Late Jurassic-Early Cretaceous /
- Tukari Formation /
- magnetic fabric
-

-
[1] 潘桂棠, 李兴振, 王立全, 等.青藏高原及邻区大地构造单元初步划分[J].地质通报, 2002, 21(11):701-708. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2002011160&flag=1
[2] 潘裕生.青藏高原的形成与隆升[J].地学前缘, 1999, 6(3):153-163. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1005-2321.1999.03.015
[3] 许志琴, 杨经绥, 侯增谦, 等.青藏高原大陆动力学研究若干进展[J].中国地质, 2016, 43(1):1-42. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgdizhi201601001
[4] 黄汲清, 陈国铭, 陈炳蔚, 等.特提斯-喜马拉雅构造域初步分析[J].地质学报, 1984, 1(1):1-17. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DZXE198401000.htm
[5] 文力, 魏鹏飞, 常华进, 等.青藏高原周边地区河流分形特征与地貌、构造活动耦合关系[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(6):965-974. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180601&flag=1
[6] Yin A, Harrison T M. Geologic Evolution of the HimalayanTibetan Orogen[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2000, (28):211-280.
[7] Metcalfe I. Gondwana dispersion and Asian accretion:Tectonic and palaeogeographic evolution of eastern Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2013, 66:1-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2012.12.020
[8] 蒲宗文, 杨振宇, 仝亚博, 等.青藏高原东南缘保山地体上新世地壳旋转变形运动的古地磁学研究及构造意义[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(5):759-775. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180502&flag=1
[9] Clark M K, Royden L H. Topographic ooze:Building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow[J]. Geology, 2000, 28(8):703. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(2000)28<703:TOBTEM>2.0.CO;2
[10] Chung S L, Lo C, Lee T, et al. Diachronous uplift of the Tibetan plateau starting 40 Myr ago[J]. Nature, 1998, 394:769-733. doi: 10.1038/29511
[11] Ding L, Xu Q, Yue Y H, et al. The Andean-type Gangdese Mountains:Paleoelevation record from the Paleocene-Eocene Linzhou Basin[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2014, 392:250-264. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2014.01.045
[12] Kapp P, DeCelles P G, Leier A L, et al. The Gangdese retroarc thrust belt revealed[J]. GSA Today, 2007, 17(7):4. doi: 10.1130/GSAT01707A.1
[13] Kapp P, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. Cretaceous-Tertiary shortening, basin development, and volcanism in central Tibet[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2005, 117(7):865. doi: 10.1130/B25595.1
[14] Murphy M A, Yin A, Harrison T M, et al. Did the Indo-Asian collision alone create the Tibetan plateau?[J]. Geology, 1997, 25(8):719-722. doi: 10.1130/0091-7613(1997)025<0719:DTIACA>2.3.CO;2
[15] 范建军, 李才, 王明, 等.班公湖-怒江缝合带洞错混杂岩物质组成、时代及其意义[J].地质通报, 2018, 37(8):1417-1427. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20180806&flag=1
[16] Li Y L, He J, Wang C S, et al. Cretaceous volcanic rocks in south Qiangtang Terrane:Products of northward subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean?[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2015, 104:69-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2014.09.033
[17] Song P P, Ding L, Li Z Y, et al. Late Triassic paleolatitude of the Qiangtang block:Implications for the closure of the Paleo-Tethys Ocean[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2015, 424:69-83. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2015.05.020
[18] Song P P, Ding L, Li Z Y, et al. An early bird from Gondwana:Paleomagnetism of Lower Permian lavas from northern Qiangtang (Tibet) and the geography of the Paleo-Tethys[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 2017, 475:119-133. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2017.07.023
[19] Huang Q T, Liu W L, Xia B, et al. Petrogenesis of the Majiari ophiolite (western Tibet, China):Implications for intra-oceanic subduction in the Bangong-Nujiang Tethys[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2017, 146:337-351. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2017.06.008
[20] Zhu D C, Wang Q, Zhao Z D, et al. Magmatic record of IndiaAsia collision[J]. Scientific Reports, 2015, 5(1):14289. doi: 10.1038/srep14289
[21] Kapp P, DeCelles P G, Gehrels G E, et al. Geological records of the Lhasa-Qiangtang and Indo-Asian collisions in the Nima area of central Tibet[J]. GSA Bulletin, 2007, 119(7/8):917-933. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=8d5fa47df1c2238edd961f9c8cbdf6ac
[22] Liu W L, Xia B, Zhong Y, et al. Age and composition of the Rebang Co and Julu ophiolites, central Tibet:implications for the evolution of the Bangong Meso-Tethys[J]. International Geology Review, 2014, 56(4):430-447. doi: 10.1080/00206814.2013.873356
[23] Huang T T, Xu J F, Chen J L, et al. Sedimentary record of Jurassic northward subduction of the Bangong-Nujiang Ocean:insights from detrital zircons[J]. International Geology Review, 2016, 59(2):166-184. http://cn.bing.com/academic/profile?id=af41d243151e46798826fd133337322a&encoded=0&v=paper_preview&mkt=zh-cn
[24] Li J X, Qin K Z, Li G M, et al. Geochronology, geochemistry, and zircon Hf isotopic compositions of Mesozoic intermediate-felsic intrusions in central Tibet:Petrogenetic and tectonic implications[J]. Lithos, 2014, 198/199:77-91. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.03.025
[25] Chen W W, Zhang S H, Ding J, et al. Combined paleomagnetic and geochronological study on Cretaceous strata of the Qiangtang terrane, central Tibet[J]. Gondwana Research, 2017, 41:373-389. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2015.07.004
[26] Zhang K J, Xia B, Zhang Y X, et al. Central Tibetan MesoTethyan oceanic plateau[J]. Lithos, 2014, 210/211:278-288. doi: 10.1016/j.lithos.2014.09.004
[27] Liu D L, Huang Q S, Fan S Q, et al. Subduction of the BangongNujiang Ocean:constraints from granites in the Bangong Co area, Tibet[J]. Geological Journal, 2014, 49(2):188-206. doi: 10.1002/gj.v49.2
[28] Zhang K J, Zhang Y X, Tang X C, et al. Late Mesozoic tectonic evolution and growth of the Tibetan plateau prior to the IndoAsian collision[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 2012, 114(3/4):236-249.
[29] Pan G T, Wang L Q, Li R S, et al. Tectonic evolution of the Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2012, 53:3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2011.12.018
[30] Yan M D, Zhang D W, Fang X M, et al. Paleomagnetic data bearing on the Mesozoic deformation of the Qiangtang Block:Implications for the evolution of the Paleo- and Meso-Tethys[J]. Gondwana Research, 2016, 39:292-316. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2016.01.012
[31] Yang Y T, Guo Z X, Luo Y J. Middle-Late Jurassic tectonostratigraphic evolution of Central Asia, implications for the collision of the Karakoram-Lhasa Block with Asia[J]. EarthScience Reviews, 2017, 166:83-110. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=c7389f5baf00f239d925ff8249aaf1f0
[32] 李超, 肖传桃, 龚文平, 等.班公湖-怒江缝合带中段构造演化再探讨[J].长江大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 8(3):41-43. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/cjdxxb-rkxb201103014
[33] 仲昭, 纪占胜, 武桂春, 等.西藏班戈县保吉乡纳木错西下石炭统珊瑚动物群的发现及其意义[J].地质论评, 2017, 63(增刊):349-350. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9146506
[34] 刘振宇, 贾海明, 黄维平, 等.西藏1:5万班戈县西南地区四幅区调成果与展望[J].中国地质调查, 2015, 2(7):8-12. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/xzyj201503017
[35] 孙倩, 纪占胜, 廖卫华, 等.西藏班戈县保吉地区萨波直不勒组珊瑚化石的发现及其意义[J].地质论评, 2017, 63(S1):323-324. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=9146510
[36] 孟亚洲, 纪占胜, 廖卫华, 等.西藏保吉地区晚侏罗世珊瑚动物群的发现及其意义[J].地质学报, 2016, 90(5):833-847. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2016.05.001
[37] 孟亚洲, 纪占胜, 姚建新, 等.西藏班戈县扎穷地区古生界混杂岩块中发现中生代化石[J].地质学报, 2017, 91(4):812-821. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5717.2017.04.008
[38] 梁寿生, 夏金宝.藏北班戈地区海相白垩系[J].青藏高原地质文集, 1983, 3(6):181-193. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=HY000001808476
[39] 武桂春, 纪占胜, 姚建新, 等.纳木错西岸白云岩的时代修订及油浸现象发现的意义[J].地质学报, 2017, 8(12):2865-2879. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dizhixb201712020
[40] 陈国荣, 陈玉禄, 张宽忠, 等.班戈县幅地质调查新成果及主要进展[J].地质通报, 2004, 23(5):520-524. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=20040593&flag=1
[41] Hrouda F E. Magnetic anisotropy of rocks and its application in geology and geophysics[J]. Geophysical Surveys, 1982, 5(1):37-82. doi: 10.1007/BF01450244
[42] Somma R. The south-western side of the Calabrian Arc (Peloritani Mountains):Geological, structural and AMS evidence for passive clockwise rotations[J]. Journal of Geodynamics, 2006, 41(4):422-439. doi: 10.1016/j.jog.2005.11.001
[43] Jackson M, Taux L. Anisotropy of Magnetic Susceptibility and Remanence:Developments in the Characterization of Tectonic, Sedimentary and Igneous Fabric[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 1991, 29(S1):371-376. doi: 10.1002/rog.1991.29.issue-s1
[44] 潘永信, 朱日祥.磁组构研究现状[J].地球物理学进展, 1998, 13(1):53-60. http://cdmd.cnki.com.cn/Article/CDMD-11415-1013265919.htm
[45] 王中蛟, 李学森.岩石磁各向异性分析及在构造地质学中的应用[J].云南地质, 2013, 32(1):106-109. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1885.2013.01.028
[46] 王开, 贾东, 罗良, 等.磁组构与构造变形[J].地球物理学报, 2017, 60(3):1007-1026. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dqwlxb201302019
[47] 罗良, 贾东, 陈竹新, 等.川西北磁组构演化及其揭示的应变特征[J].地质通报, 2006, 25(11):1342-1348. http://dzhtb.cgs.cn/gbc/ch/reader/view_abstract.aspx?file_no=2006011232&flag=1
[48] Pueyo Anchuela Ó, Pueyo E L, Pocoví Juan A, et al. Vertical axis rotations in fold and thrust belts:Comparison of AMS and paleomagnetic data in the Western External Sierras (Southern Pyrenees)[J]. Tectonophysics, 2012, 532/535:119-133. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2012.01.023
[49] Royden L H, B Clark B, Hilst R D. The Geological Evolution of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. Science, 2008, 321(5892):1054-1058. doi: 10.1126/science.1155371
[50] Bakhtari H R, Frizon De Lamotte D, Aubourg C, et al. Magnetic fabrics of Tertiary sandstones from the Arc of Fars (Eastern Zagros, Iran)[J]. Tectonophysics, 1998, 284(3/4):299-316. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=6186492ae466351b69358b25d7177b6c
[51] Borradaile G J, Henry B. Tectonic applications of magnetic susceptibility and its anisotropy[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 1997, 42(1):49-93. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-S0012-8252(96)00044-X/
[52] Parés J M, Pluijm B A V D, Dinarèsturell J. Evolution of magnetic fabrics during incipient deformation of mudrocks (Pyrenees, northern Spain)[J]. Tectonophysics, 1999, 307(1):1-14. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=b13c318ca7871ead49856d73ab625dc2
[53] Flinn D. The deformation matrix and the deformation ellipsoid[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 1979, 1(4):299-307. doi: 10.1016/0191-8141(79)90004-X
[54] Jelinek V. Characterization of the magnetic fabric of rocks[J]. Tectonophysics, 1981, 79(3):63-67. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/10.1016-0040-1951(81)90110-4/
[55] Woodcock N H. Specification of fabric shapes using aneigenvalue method[J]. GSA Bulletin, 1977, 88(9):1231. doi: 10.1130/0016-7606(1977)88<1231:SOFSUA>2.0.CO;2
[56] Ran B, Wang C S, Zhao X X, et al. New paleomagnetic results of the early Permian in the Xainza area, Tibetan Plateau and their paleogeographical implications[J]. Gondwana Research, 2012, 22(2):447-460. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2011.11.014
[57] Zhou Y N, Cheng X, Yu L, et al. Paleomagnetic study on the Triassic rocks from the Lhasa Terrane, Tibet, and its paleogeographic implications[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 2016, 121:108-119. doi: 10.1016/j.jseaes.2016.02.006
① 中国地质科学院地质力学研究所.中华人民共和国1: 25万区域地质调查报告(当雄县幅). 2003.
-



 下载:
下载: